10-Year Mortgages In Canada: Exploring The Reasons For Low Adoption
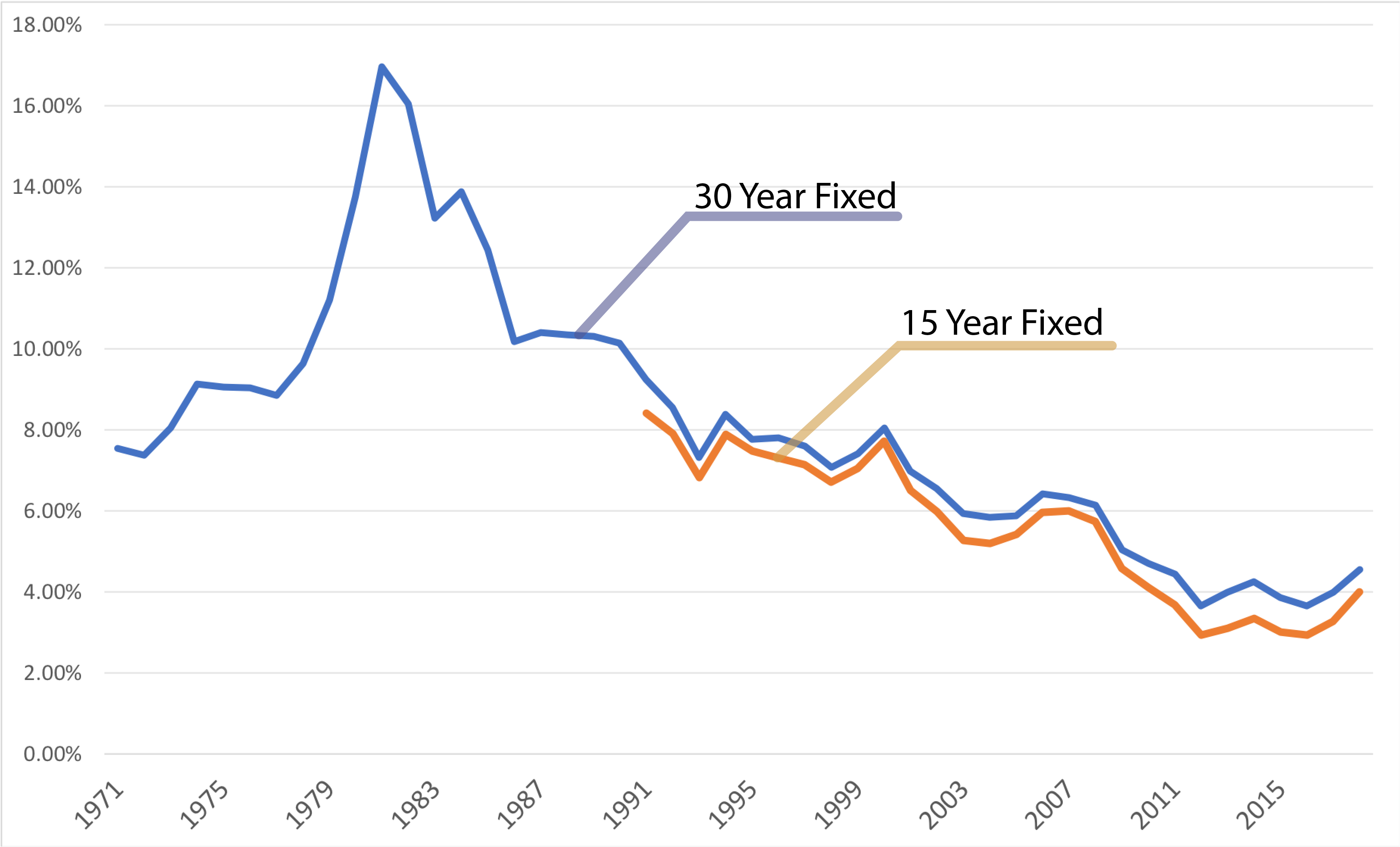
Table of Contents
The Canadian mortgage landscape is predominantly shaped by the ubiquitous 5-year fixed-rate mortgage. However, a longer-term alternative exists: the 10-year mortgage. Offering the potential for significant long-term savings and financial stability, these mortgages surprisingly remain underutilized. This article delves into the key reasons why 10-year mortgages in Canada haven't gained widespread adoption, exploring the factors that deter Canadian homeowners from embracing this longer-term financing solution.
Higher Initial Interest Rates and Potential Rate Increases
A primary reason for the low adoption of 10-year mortgages is the often higher initial interest rate compared to shorter-term options. This difference, even if seemingly small, significantly impacts affordability and can act as a major barrier for many borrowers.
The upfront cost concern
The upfront cost is a critical factor. Borrowers are acutely sensitive to initial payments, often prioritizing lower monthly payments in the short term, even if it means paying more in the long run. This short-term focus makes the higher initial rate of a 10-year mortgage a significant deterrent.
- Higher initial payments: The higher interest rate translates directly into larger monthly payments at the outset, making a 10-year mortgage seem less accessible than a shorter-term option.
- Uncertainty about future rates: The uncertainty around future interest rate fluctuations magnifies the perceived risk. While a fixed rate provides certainty for the 10-year term, a rate hike during the term is a worry.
- Potential for higher overall interest: If interest rates rise substantially during the 10-year term, the overall interest paid over the life of the mortgage could exceed that of a shorter-term mortgage, even with a lower initial rate.
Predicting long-term interest rates
Predicting interest rate movements over a decade is inherently difficult. Economic forecasting is an inexact science, and unexpected shifts can significantly impact long-term mortgage costs.
- Imperfect economic forecasting: The inherent uncertainty in predicting economic trends and interest rate behaviour over such a long period makes a 10-year commitment feel risky.
- Economic shocks: Unforeseen economic downturns or inflation spikes can negatively affect borrowers locked into a long-term, fixed-rate mortgage.
- Missed refinancing opportunities: The possibility of missing out on potentially lower interest rates if rates decline during the 10-year term weighs heavily on many borrowers' minds. This fear of missed opportunities is a significant psychological barrier.
Limited Availability and Lender Restrictions
The limited availability of 10-year mortgages from Canadian lenders further contributes to their low adoption. This scarcity restricts borrower choices and introduces additional challenges.
Fewer Lenders Offering 10-Year Mortgages
Not all Canadian mortgage lenders offer 10-year mortgage options. This limited selection reduces competition and potentially impacts the terms and conditions offered.
- Increased competition among borrowers: A smaller pool of lenders offering 10-year mortgages creates a more competitive environment for borrowers, potentially leading to less favorable terms.
- Reduced flexibility: Borrowers might find it harder to secure specific mortgage features or terms with fewer lenders offering this type of mortgage.
- Challenges for non-standard financial situations: Borrowers with non-standard financial situations might find it even more difficult to secure a 10-year mortgage due to the limited lender options.
Stricter Lending Criteria
Lenders often apply stricter lending criteria to 10-year mortgages, reflecting the longer-term commitment and associated risk.
- Higher credit scores: Applicants are often required to have higher credit scores to qualify for a 10-year mortgage.
- Larger down payments: A larger down payment might be needed to mitigate the lender’s risk.
- Stringent income verification: Lenders will conduct more thorough income verification processes to ensure long-term repayment capacity.
The Psychological Barrier of Long-Term Commitment
Beyond the financial considerations, a significant psychological barrier prevents many Canadians from opting for a 10-year mortgage.
Uncertainty and Life Changes
Life is inherently unpredictable. A 10-year commitment can feel daunting to borrowers anticipating potential life changes—job relocation, family expansion, or unexpected financial challenges.
- Penalties for early repayment: The penalties for breaking a 10-year mortgage can be substantial, making early repayment a costly option.
- Unforeseen circumstances: Unforeseen circumstances could create significant financial hardship if locked into a long-term agreement with inflexible terms.
- Preference for shorter-term planning: Many Canadians prefer the flexibility of shorter-term mortgages, aligning better with their shorter-term planning horizons.
Fear of Missed Opportunities
The fear of missing out on lower interest rates is another psychological deterrent.
- Limited refinancing opportunities: A 10-year mortgage significantly limits the opportunity to refinance at more favorable rates should interest rates decline.
- Fluctuating interest rates: This concern is particularly acute in an environment of fluctuating interest rates, where the potential for better terms in the future is a strong consideration.
- Desire for flexibility: Borrowers often prefer the flexibility to adjust their mortgage terms in response to market changes, a flexibility a 10-year mortgage does not offer.
Conclusion
The relatively low adoption of 10-year mortgages in Canada results from a combination of factors: higher initial interest rates, limited availability, stricter lending criteria, and the psychological barriers associated with a long-term financial commitment. While offering potential long-term cost savings and stability, the perceived risks and lack of widespread availability deter many. If you're considering your home financing options, carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of a 10-year mortgage against shorter-term alternatives. Consult with a mortgage professional to determine if a 10-year mortgage in Canada aligns with your individual financial circumstances, risk tolerance, and long-term goals. Explore the possibilities—a 10-year mortgage might be the right choice for you.

Featured Posts
-
 Sabrina Carpenter To Headline Fortnite Virtual Festival Fans React
May 06, 2025
Sabrina Carpenter To Headline Fortnite Virtual Festival Fans React
May 06, 2025 -
 The Case Against 10 Year Mortgages A Canadian Perspective
May 06, 2025
The Case Against 10 Year Mortgages A Canadian Perspective
May 06, 2025 -
 The Economic Fallout Of Trumps Trade Deal Strategy
May 06, 2025
The Economic Fallout Of Trumps Trade Deal Strategy
May 06, 2025 -
 Rihannas Parisian Fenty Beauty Glam A Sweet Fan Moment
May 06, 2025
Rihannas Parisian Fenty Beauty Glam A Sweet Fan Moment
May 06, 2025 -
 Russias Putin Avoiding Nuclear Weapons In Ukraine Conflict
May 06, 2025
Russias Putin Avoiding Nuclear Weapons In Ukraine Conflict
May 06, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Savage X Fenty Rihannas Wedding Night Lingerie Campaign
May 06, 2025
Savage X Fenty Rihannas Wedding Night Lingerie Campaign
May 06, 2025 -
 Shop Rihannas Wedding Night Lingerie Collection From Savage X Fenty
May 06, 2025
Shop Rihannas Wedding Night Lingerie Collection From Savage X Fenty
May 06, 2025 -
 Wedding Night Lingerie Rihannas Savage X Fenty Collection Revealed
May 06, 2025
Wedding Night Lingerie Rihannas Savage X Fenty Collection Revealed
May 06, 2025 -
 Rihannas Savage X Fenty Lingerie For The Ultimate Wedding Night
May 06, 2025
Rihannas Savage X Fenty Lingerie For The Ultimate Wedding Night
May 06, 2025 -
 Rihanna And A Ap Rocky Relationship Rumors Heat Up
May 06, 2025
Rihanna And A Ap Rocky Relationship Rumors Heat Up
May 06, 2025
