2% Decline In U.S. Economy: Analysis Of Spending And Tariff Effects
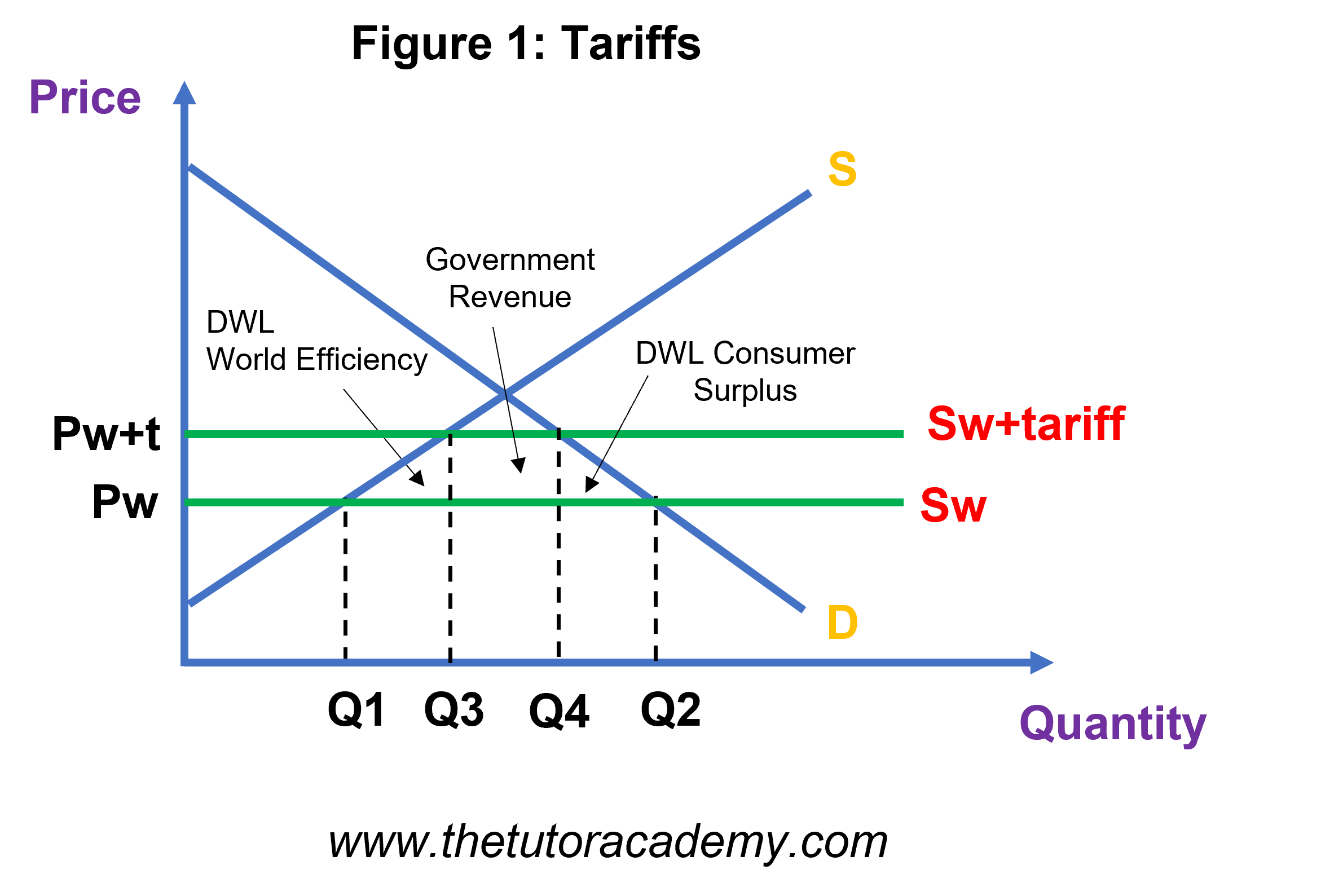
Table of Contents
The Role of Reduced Consumer Spending in the Economic Decline
The decline in consumer spending plays a significant role in the overall 2% drop in the U.S. economy. Consumer spending accounts for a substantial portion of the GDP, making its fluctuations a key indicator of economic health. Several factors contribute to this reduced spending:
-
Falling Retail Sales: Recent retail sales figures show a concerning downward trend, directly correlating with the GDP decline. Data reveals a significant decrease in spending across various sectors, indicating a broader weakening in consumer demand. This is further supported by visualizations showing a clear negative correlation between retail sales and GDP growth over the past quarter.
-
Eroding Consumer Confidence: Consumer confidence indices, which measure consumer optimism about the future economy, have plummeted. This decreased confidence translates directly into reduced purchasing decisions, as consumers postpone non-essential spending and prioritize saving. The uncertainty surrounding the economy contributes to this pessimism, leading to a vicious cycle of decreased spending and further economic contraction.
-
Squeezed Disposable Income: Inflation continues to erode disposable income, leaving consumers with less money to spend after essential expenses. While wage growth has occurred in certain sectors, it hasn't kept pace with inflation in many cases, resulting in a net decrease in purchasing power. This squeeze on disposable income forces consumers to cut back on discretionary spending, further impacting economic growth.
-
Shifting Spending Patterns: Consumer spending patterns are changing, with a noticeable shift towards prioritizing essential goods and services over non-essential items. This shift indicates a heightened awareness of economic uncertainty, pushing consumers towards a more cautious approach to their spending habits. Further analysis is needed to determine the long-term implications of these altered habits.
The Lingering Impact of Tariffs on the U.S. Economy
The ongoing impact of tariffs imposed during the trade war continues to negatively affect the U.S. economy. These tariffs, while intended to protect domestic industries, have had unintended consequences:
-
Increased Import Costs: Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers and businesses. This increase in import costs contributes significantly to inflation, reducing consumer purchasing power and hindering business investment.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Tariffs have disrupted global supply chains, leading to delays, shortages, and increased costs for businesses reliant on imported components or materials. This disruption impacts manufacturing output and hinders economic growth across various sectors.
-
Manufacturing Sector Impact: The manufacturing sector, heavily reliant on international trade, has been particularly hard hit by tariffs. Case studies illustrate significant job losses and production cuts in industries directly affected by increased import costs and supply chain disruptions. This sector's struggles further contribute to the overall economic decline.
-
Retaliatory Tariffs and Global Impact: The imposition of tariffs often triggers retaliatory measures from other countries, leading to a broader decline in international trade and exacerbating global economic instability. This interconnectedness highlights the significant global implications of trade disputes and the importance of international cooperation.
Interconnectedness of Spending and Tariff Effects
The effects of reduced consumer spending and tariffs are not isolated but intricately interconnected, creating a complex economic challenge.
-
Exacerbated Negative Effects: Reduced consumer spending exacerbates the negative effects of tariffs by further decreasing demand for goods and services, both domestically produced and imported. This creates a downward spiral, with decreased demand leading to further job losses and economic contraction.
-
Multiplier Effect: The initial decline in spending and production can trigger a multiplier effect, where the initial decrease leads to further reductions in economic activity throughout the economy. This cascading effect amplifies the impact of both reduced consumer spending and tariffs.
-
Increased Recession Risk: The combined impact of these factors significantly increases the risk of a recession. The decreased consumer confidence, combined with the increased costs and disruptions from tariffs, creates a precarious economic climate.
-
Policy Response: Government policy responses, such as fiscal stimulus (increased government spending) or monetary policy adjustments (interest rate changes), are crucial to mitigating the negative impacts and stimulating economic recovery. The effectiveness of these policies will be critical in determining the speed and strength of the recovery.
Conclusion
This analysis highlights the significant contribution of both reduced consumer spending and persistent tariff impacts to the 2% decline in the U.S. economy. The interconnectedness of these factors suggests a complex economic challenge requiring a multifaceted approach to address. The reduced consumer confidence, coupled with the increased costs and disruptions from tariffs, has created a challenging economic climate.
Understanding the intricacies of the 2% U.S. economy decline, and the influence of consumer spending and tariffs, is crucial for navigating this period of economic uncertainty. Further research and analysis focusing on specific sectors and policy implications are necessary to develop effective strategies for recovery. Stay informed about the ongoing developments in the U.S. economy and their impact on your finances by regularly consulting reputable economic news sources. Monitor updates on the U.S. economy decline and the ongoing effects of spending and tariffs to make informed decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Dragon Dens Duncan Bannatyne Supports Moroccan Childrens Charity
May 31, 2025
Dragon Dens Duncan Bannatyne Supports Moroccan Childrens Charity
May 31, 2025 -
 India Covid 19 Risk Assessing The Threat From Hong Kong And Singapore Outbreaks
May 31, 2025
India Covid 19 Risk Assessing The Threat From Hong Kong And Singapore Outbreaks
May 31, 2025 -
 Achieving The Good Life Steps To A More Meaningful Existence
May 31, 2025
Achieving The Good Life Steps To A More Meaningful Existence
May 31, 2025 -
 Alcaraz Begins Barcelona Open With Straight Sets Victory
May 31, 2025
Alcaraz Begins Barcelona Open With Straight Sets Victory
May 31, 2025 -
 Banksy Print Market A 22 777 000 Year
May 31, 2025
Banksy Print Market A 22 777 000 Year
May 31, 2025
