8 Economic Indicators Showing Trump's Trade War's Effect On Canada
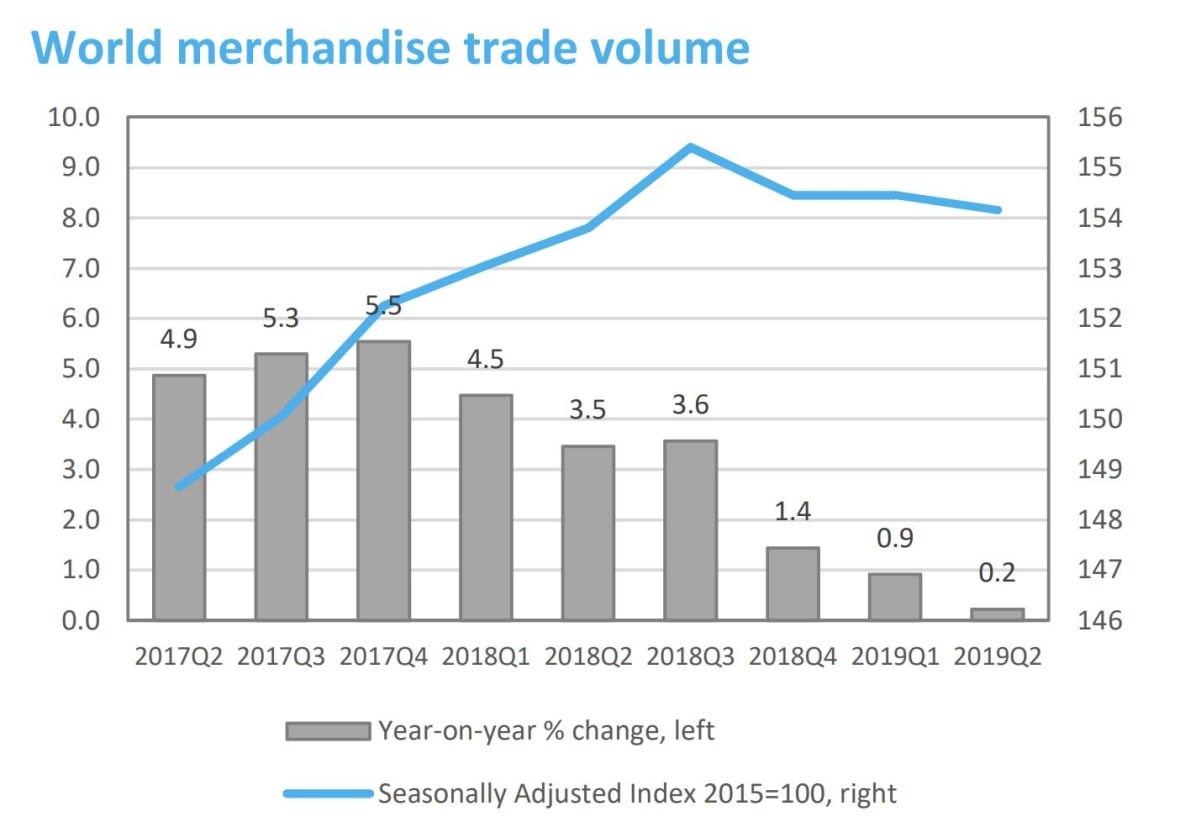
Table of Contents
Impact on Bilateral Trade between the US and Canada
The imposition of tariffs during Trump's trade war immediately impacted bilateral trade between the US and Canada. This section analyzes the decline in trade volume and shifts in specific sectors.
-
Decline in Bilateral Trade Volume: The imposition of tariffs led to a noticeable decline in the overall volume of goods and services exchanged between the two countries. Statistics from Statistics Canada and the US Census Bureau show a clear decrease in both imports and exports during this period. The reduction wasn't uniform across all sectors, with some experiencing more significant impacts than others.
-
Heavily Impacted Sectors: Sectors like lumber, dairy, and the automotive industry faced particularly harsh consequences. Canadian lumber producers, for example, faced significant tariff increases, impacting their competitiveness in the US market. Similarly, Canadian dairy farmers experienced reduced access to the US market, affecting their profitability and overall production. The automotive sector, deeply integrated across the border, experienced supply chain disruptions and reduced production due to tariffs.
-
Shift in Trading Partners: Faced with trade disruptions from the US, Canada actively sought to diversify its trade relationships. This involved exploring new markets and strengthening existing ties with other countries, mitigating some of the negative impacts of the trade war, but not entirely offsetting the losses.
-
Statistical Evidence: Charts illustrating the decrease in bilateral trade volume between the US and Canada during the trade war period, broken down by sector, would provide compelling visual evidence of these impacts. (Note: Actual charts would need to be included here using relevant data sources).
Changes in Canadian GDP Growth
The Trump trade war undeniably influenced Canada's economic growth trajectory. This section examines the effect on GDP growth and related economic activity.
-
Quantifying the Impact: While attributing a precise percentage of GDP decline solely to the trade war is complex due to other global economic factors, studies suggest it contributed to a slowdown in Canada's GDP growth rate during the period. Economic models can be used to isolate the impact of trade disruptions on overall GDP.
-
Recessionary Pressures: Although Canada avoided a full-blown recession, the trade war undeniably contributed to increased economic uncertainty and dampened investor confidence, creating headwinds for economic growth and potentially delaying any recovery.
-
Ripple Effects: The reduced trade impacted not only directly involved sectors but also related industries. For example, decreased automotive production had knock-on effects on parts suppliers and transportation services, illustrating the interconnected nature of the Canadian economy.
-
Credible Sources: Referencing reports from the Bank of Canada, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and other reputable economic forecasting institutions is crucial for supporting the analysis and ensuring credibility.
Fluctuations in the Canadian Dollar (CAD)
The trade war's impact extended to the Canadian dollar's exchange rate against the US dollar.
-
Correlation with Trade War: Increased uncertainty and negative sentiment surrounding the trade conflict led to volatility in the CAD/USD exchange rate. A weakening CAD could be partially attributed to reduced trade and investor apprehension.
-
Impact of Weaker CAD: A weaker CAD, while boosting export competitiveness in some sectors, also increased the cost of imports, potentially contributing to inflation and impacting consumer purchasing power.
-
Investor Sentiment and Uncertainty: The fluctuating exchange rate reflected the broader economic uncertainty created by the trade war, as investors reacted to changing market conditions and forecasts.
-
Illustrative Charts: Visual representation of CAD movements throughout the period would strengthen the analysis, demonstrating the correlation between the trade war and exchange rate volatility. (Again, actual charts with data would be needed here).
Effect on Canadian Employment and Unemployment Rates
The trade war's influence on employment and unemployment in Canada requires careful analysis.
-
Overall Employment Impact: While overall job losses weren't catastrophic, specific sectors experienced significant job reductions or slower hiring. The overall employment rate may have been minimally impacted, but specific job losses within sectors affected by tariffs were noticeable.
-
Sector-Specific Job Losses: Sectors directly impacted by tariffs, such as manufacturing and agriculture, likely faced higher unemployment rates. This would need to be supported by sector-specific employment data.
-
Regional Variations: The impact wasn't uniform across all regions of Canada. Provinces and regions more reliant on trade with the US likely felt the effects more acutely.
-
Unemployment Data: Statistics on unemployment rates and job creation/loss figures from Statistics Canada would provide concrete evidence to support the analysis.
Inflationary Pressures and Consumer Prices
The trade war's tariffs directly influenced the cost of goods and consumer prices.
-
Tariffs and Import Prices: Tariffs on imported goods directly increased their prices, leading to inflationary pressures. This particularly affected consumers relying on imported goods.
-
Consumer Spending and Purchasing Power: Increased prices reduced consumer purchasing power, potentially impacting overall consumer spending and economic growth.
-
Government Response: This section could explore if the Canadian government implemented any policies to mitigate the inflationary effects of the trade war, such as subsidies or targeted support for affected industries.
-
CPI Data: CPI (Consumer Price Index) data and other relevant price index changes are crucial to quantify the inflationary pressures and their extent.
Changes in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
The trade war's impact on FDI flows into Canada is an important indicator of long-term economic consequences.
-
Decreased FDI Inflows: The increased uncertainty created by the trade war likely discouraged some foreign investors, leading to a potential decrease in FDI inflows compared to pre-trade-war levels.
-
Economic Uncertainty: The unpredictable nature of the trade disputes and the potential for further escalation created an environment of risk aversion, leading some investors to postpone or cancel investment plans.
-
Long-Term Effects: The long-term effects on Canada's attractiveness as an investment destination could be significant, influencing future economic growth and development.
-
Statistical Evidence: Data on FDI flows before, during, and after the trade war period are essential to demonstrate any meaningful changes and support the analysis.
Impact on Specific Canadian Industries (e.g., Agriculture, Automotive)
A deeper dive into specific sectors reveals the granular impacts of the trade war.
-
Agriculture: The agricultural sector, particularly dairy and grains, faced direct challenges due to tariffs imposed by the US. This section would detail the impact on farmers, producers, and related industries.
-
Automotive: The automotive sector, deeply intertwined with US supply chains, experienced disruptions, production slowdowns, and potential job losses due to trade tensions.
-
Lumber: Canadian lumber producers faced significant challenges due to US tariffs. This would discuss the impact on production, employment, and market share.
-
Industry Reports and Case Studies: Support the analysis with reports from industry associations, case studies of specific companies impacted, and analysis of government support measures.
The Long-Term Implications of USMCA (formerly NAFTA)
The renegotiation of NAFTA into USMCA had significant implications for mitigating or exacerbating the trade war's effects.
-
USMCA and Mitigation: The USMCA aimed to create a more stable and predictable trade environment between the three countries, potentially mitigating some of the negative consequences of the trade war's uncertainty.
-
Long-Term Economic Implications: This section would discuss the long-term effects of USMCA on the Canadian economy, considering both positive and negative aspects.
-
Ongoing Challenges and Opportunities: The agreement presents both challenges and opportunities for Canadian businesses. This section would discuss the ongoing adaptations and strategies required by Canadian businesses to navigate the new trade landscape.
Conclusion
This analysis of eight key economic indicators reveals the significant impact of Trump's trade war on the Canadian economy. From decreased bilateral trade and fluctuations in the Canadian dollar to impacts on employment and inflation, the effects were widespread and multifaceted. Understanding these consequences is crucial for both policymakers and businesses operating within the US-Canada trade corridor. For further insights into the ongoing effects of trade policy changes on the Canadian economy, continue researching the impact of Trump's trade war on Canada and the implications of USMCA. Stay informed about the evolving dynamics of bilateral trade relations and their influence on Canadian economic indicators.

Featured Posts
-
 Guillermo Del Toro Game Name S World Is Unparalleled
May 30, 2025
Guillermo Del Toro Game Name S World Is Unparalleled
May 30, 2025 -
 Anderlecht Kan Et Godt Tilbud Ignoreres
May 30, 2025
Anderlecht Kan Et Godt Tilbud Ignoreres
May 30, 2025 -
 Freedom Of The Press Under Threat Sierra Leonean Journalists Targeted For Bolle Jos Investigations
May 30, 2025
Freedom Of The Press Under Threat Sierra Leonean Journalists Targeted For Bolle Jos Investigations
May 30, 2025 -
 Unauthorized Access Deutsche Bank Data Center Security Compromised
May 30, 2025
Unauthorized Access Deutsche Bank Data Center Security Compromised
May 30, 2025 -
 Gorillazs 25th Anniversary House Of Kong Exhibition And London Concert Dates
May 30, 2025
Gorillazs 25th Anniversary House Of Kong Exhibition And London Concert Dates
May 30, 2025
