Activision Blizzard Acquisition: FTC's Appeal Against Microsoft

Table of Contents
Main Points:
2.1 The FTC's Case Against the Merger:
H3: Anti-Competitive Concerns:
The FTC's primary argument hinges on the assertion that the merger would create an anti-competitive environment within the gaming market. They argue that Microsoft, already a significant player with its Xbox console and Game Pass subscription service, acquiring Activision Blizzard – the publisher of iconic franchises like Call of Duty, World of Warcraft, and Candy Crush – would grant them undue market dominance. This dominance, the FTC claims, could lead to several anti-competitive practices.
- Call of Duty Exclusivity: The FTC fears Microsoft could make Call of Duty exclusive to Xbox, significantly harming competitors like PlayStation and potentially harming PC gaming competition through exclusivity deals as well.
- Cloud Gaming Domination: Microsoft’s cloud gaming ambitions, combined with Activision Blizzard's vast catalog, could stifle competition in the burgeoning cloud gaming market, potentially leading to higher prices and less innovation for consumers.
- Market Share Consolidation: The combined market share of Microsoft and Activision Blizzard would be substantial, potentially creating a near-monopoly in certain segments of the gaming market.
Keywords: Anti-competitive practices, market dominance, Call of Duty exclusivity, cloud gaming competition, market power
H3: The Role of Market Power:
The FTC emphasizes that the combined entity would wield excessive market power, allowing Microsoft to dictate prices, limit choices, and stifle innovation.
- Pre-Merger Market Share: The FTC likely presented data showing the individual market shares of Microsoft and Activision Blizzard before the merger.
- Post-Merger Projections: Their analysis probably projected a significantly increased market share for the combined entity, highlighting the potential for market concentration and monopoly power. This likely included specific market share figures for consoles, PC gaming and cloud gaming.
- Dominant Position: The argument centers on the assertion that this increased market share would place Microsoft in a dominant position, allowing them to suppress competition and harm consumers.
Keywords: Market share, market concentration, monopoly power, dominant position, market analysis
H3: Evidence and Arguments Presented by the FTC:
The FTC's case relies on a significant body of evidence, aiming to demonstrate the anti-competitive nature of the merger.
- Expert Testimony: Economists and industry experts likely testified on the potential anti-competitive effects of the merger.
- Market Research: Data on consumer behavior, game sales, and market trends would be crucial to their arguments.
- Internal Documents: The FTC likely accessed and presented internal documents from both Microsoft and Activision Blizzard, supporting their claims.
Keywords: Evidence, witness testimony, expert analysis, market research, regulatory filings, documents
2.2 Microsoft's Defense of the Acquisition:
H3: Microsoft's Arguments for the Merger:
Microsoft countered the FTC’s claims, arguing that the acquisition would benefit consumers and increase competition.
- Consumer Benefits: Microsoft highlighted potential benefits such as increased game availability through Game Pass, enhanced game development resources, and potential price reductions.
- Innovation: They argued that the combined resources would lead to greater innovation in game development and technology.
- Expanded Market Reach: Microsoft claimed the merger would allow them to bring Activision Blizzard games to a wider audience, including those who don't currently own an Xbox.
Keywords: Consumer benefits, innovation, game development investment, market expansion, platform competition
H3: Proposed Remedies and Concessions:
To address the FTC's concerns, Microsoft proposed several remedies.
- Call of Duty Availability: They offered to keep Call of Duty available on PlayStation and other platforms for an extended period.
- Cloud Gaming Agreements: Agreements to ensure fair access to cloud gaming services were likely part of their concessions.
- Regulatory Commitments: Microsoft likely made other regulatory commitments to demonstrate their intention to avoid anti-competitive behavior.
Keywords: Remedies, concessions, consent decree, regulatory compliance, antitrust compliance
H3: Legal Strategies Employed by Microsoft:
Microsoft employed several legal strategies to defend the acquisition.
- Market Definition: They likely argued for a narrower market definition to minimize the apparent impact of the merger on competition.
- Competitive Effects: They challenged the FTC's assessment of the competitive effects of the merger.
- Legal Precedent: They cited relevant legal precedents and case law to support their arguments.
Keywords: Legal precedent, antitrust law, regulatory framework, legal strategy, court proceedings, market definition
2.3 The Appeal Process and Potential Outcomes:
H3: The Appeal Process:
The FTC's appeal followed a specific legal process, involving various stages and potential legal challenges.
- Administrative Law Judge: The initial phase involved an Administrative Law Judge reviewing the evidence and making a recommendation.
- Federal Court of Appeals: The FTC’s appeal likely went to a Federal Court of Appeals for review.
- Supreme Court: In the event of further appeal, the Supreme Court is the ultimate arbiter.
Keywords: Appeal, court proceedings, legal challenges, judicial review, regulatory process, administrative law
H3: Potential Impacts of the Outcome:
The outcome of the FTC's appeal has profound implications for the gaming industry and beyond.
- Game Development: A blocked merger could impact future game development, potentially slowing down innovation.
- Pricing: The decision could influence game pricing and subscription models.
- Future Mergers and Acquisitions: The case sets a precedent for future mergers and acquisitions in the tech industry.
Keywords: Industry impact, competition policy, regulatory implications, mergers and acquisitions, future of gaming, antitrust
Conclusion: The Future of the Activision Blizzard Acquisition: What Happens Next?
The FTC's appeal against the Activision Blizzard Acquisition represents a significant clash between the pursuit of competition and the ambition of corporate expansion. Both sides presented compelling arguments, with the FTC highlighting potential anti-competitive concerns and Microsoft emphasizing consumer benefits and innovation. The outcome of this appeal will have far-reaching consequences for the gaming industry, impacting competition, pricing, and future mergers. It is crucial to stay informed about the developments in this landmark case, which will undoubtedly shape the future landscape of gaming and tech regulation. Follow reputable news sources, check official court filings, and stay tuned for updates on this pivotal Activision Blizzard Acquisition and the FTC's appeal. The implications are far-reaching and will likely influence the regulatory landscape for years to come.

Featured Posts
-
 Lets Rewatch The Gta Vi Trailer A Frame By Frame Breakdown
May 05, 2025
Lets Rewatch The Gta Vi Trailer A Frame By Frame Breakdown
May 05, 2025 -
 Shopifys New Lifetime Program Impact On Developer Revenue
May 05, 2025
Shopifys New Lifetime Program Impact On Developer Revenue
May 05, 2025 -
 Sesame Street And Laugh In Veteran Ruth Buzzi Dies At 88
May 05, 2025
Sesame Street And Laugh In Veteran Ruth Buzzi Dies At 88
May 05, 2025 -
 Inside The Wildest Crypto Party A Two Day Account
May 05, 2025
Inside The Wildest Crypto Party A Two Day Account
May 05, 2025 -
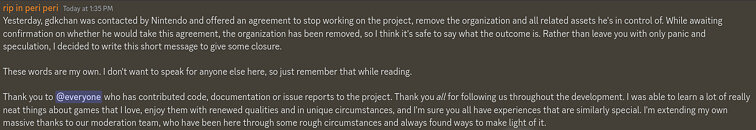 Ryujinx Emulator Project Ends After Reported Nintendo Intervention
May 05, 2025
Ryujinx Emulator Project Ends After Reported Nintendo Intervention
May 05, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Calgary Flames Wolf Playoff Outlook And Calder Trophy Possibilities In Nhl Com Interview
May 05, 2025
Calgary Flames Wolf Playoff Outlook And Calder Trophy Possibilities In Nhl Com Interview
May 05, 2025 -
 All Caps 2025 Capitals Playoff Strategy And Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc Collaboration
May 05, 2025
All Caps 2025 Capitals Playoff Strategy And Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc Collaboration
May 05, 2025 -
 Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc Partners With Capitals For 2025 Playoffs Initiatives
May 05, 2025
Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc Partners With Capitals For 2025 Playoffs Initiatives
May 05, 2025 -
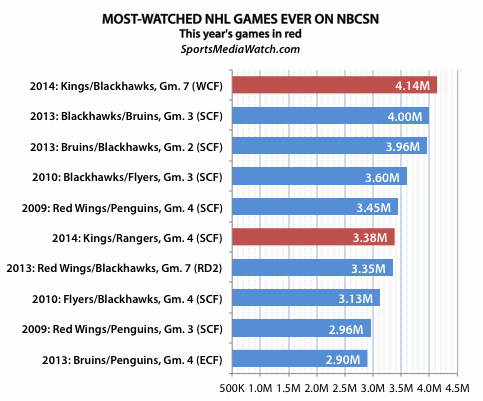 Us Tv Ratings For Stanley Cup Playoffs Fall Short Of Expectations
May 05, 2025
Us Tv Ratings For Stanley Cup Playoffs Fall Short Of Expectations
May 05, 2025 -
 Stanley Cup Playoffs A Decline In Us Viewership Explained
May 05, 2025
Stanley Cup Playoffs A Decline In Us Viewership Explained
May 05, 2025
