AI And Wildlife Conservation: Benefits, Challenges, And The Future

Table of Contents
Benefits of AI in Wildlife Conservation
Artificial intelligence is rapidly revolutionizing various fields, and wildlife conservation is no exception. AI offers powerful tools to enhance monitoring, improve predictive capabilities, and bolster anti-poaching efforts.
Enhanced Monitoring and Surveillance
AI-powered surveillance is transforming how we monitor wildlife populations. Drones equipped with advanced cameras and AI-powered image recognition software can cover vast areas, identifying and tracking endangered species with unprecedented accuracy. This technology allows for:
- Real-time data analysis: Immediate alerts are triggered when threats like poaching or habitat encroachment are detected, enabling rapid response.
- Accurate population counts: AI algorithms can automatically identify and count individual animals from camera trap images, providing crucial data for conservation planning.
- Species identification: AI can distinguish between different species, even in challenging conditions, providing valuable insights into biodiversity.
For example, researchers are using AI-powered camera trap analysis to monitor tiger populations in India, enabling efficient tracking of individuals and assessment of population health. Similarly, drone technology with AI-powered image recognition is being used to monitor nesting sites of endangered seabirds, allowing for timely intervention to protect vulnerable chicks. These advancements in AI-powered surveillance and wildlife monitoring are crucial for effective conservation strategies.
Predictive Modeling and Habitat Analysis
AI algorithms excel at analyzing complex datasets to predict future trends. In wildlife conservation, this translates to:
- Predicting animal behavior: AI models can predict animal migration patterns, habitat preferences, and responses to environmental changes.
- Optimizing protected area design: AI can help identify optimal locations for protected areas based on factors like species distribution, habitat suitability, and threats.
- Forecasting disease outbreaks: AI can analyze environmental data and animal health records to predict potential outbreaks, enabling proactive disease management.
This predictive modeling allows for proactive and efficient conservation planning. For example, by predicting poaching hotspots, rangers can strategically allocate resources to prevent illegal activities more effectively. Similarly, predicting habitat suitability under climate change scenarios can help prioritize conservation efforts in areas likely to remain habitable for target species.
Anti-Poaching Efforts
Combating poaching is a critical challenge in wildlife conservation. AI offers innovative solutions:
- Acoustic monitoring: AI algorithms can analyze audio recordings to identify gunshots or distress calls from animals, alerting authorities to potential poaching incidents.
- Anomaly detection: AI can detect unusual patterns in animal movements or habitat use, potentially indicating poaching activity or other threats.
- Movement tracking: AI can analyze tracking data to predict the movements of poachers, aiding in law enforcement efforts.
These anti-poaching technologies are significantly enhancing the effectiveness of conservation efforts. By improving early warning systems and enabling more strategic allocation of resources, AI is playing a pivotal role in preventing wildlife crime.
Challenges of Implementing AI in Wildlife Conservation
While the potential benefits are immense, the implementation of AI in wildlife conservation faces several challenges.
Data Availability and Quality
Training effective AI models requires large, high-quality datasets. This poses a significant challenge in many conservation contexts:
- Data scarcity: Data collection in remote areas can be expensive and logistically difficult.
- Data bias: Existing datasets may reflect biases in data collection methods, potentially leading to inaccurate or unfair outcomes.
- Data quality: Ensuring data accuracy and consistency is crucial for training reliable AI models.
Addressing these issues requires strategic data collection efforts, focusing on quality and representation. Improved data management techniques and machine learning datasets are essential for the successful application of AI.
Computational Resources and Costs
Implementing AI in wildlife conservation requires substantial computational resources:
- High computational power: AI algorithms can be computationally expensive, requiring powerful hardware and substantial energy consumption.
- Storage requirements: Large datasets require substantial storage capacity.
- Financial constraints: The cost of developing and deploying AI technologies can be prohibitive for many conservation organizations, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Securing funding for conservation technology and developing cost-effective AI solutions are crucial for widespread adoption.
Ethical Considerations
The use of AI in wildlife conservation raises several ethical considerations:
- Animal privacy: The constant monitoring of animals raises concerns about potential impacts on their behavior and well-being.
- Potential for misuse: AI technologies could be misused for purposes other than conservation, such as illegal wildlife trade.
- Responsible AI: Developing and deploying AI in a responsible and ethical manner is crucial to ensure that these technologies benefit both wildlife and humans.
Addressing these AI ethics concerns requires careful consideration and transparent development processes, prioritizing the well-being of animals and ensuring accountability.
The Future of AI and Wildlife Conservation
The future of AI and wildlife conservation is bright, with ongoing advancements poised to further revolutionize the field.
Advancements in AI Technology
Rapid advancements in areas such as:
- Deep learning: More sophisticated algorithms are continually being developed, improving the accuracy and efficiency of AI-powered conservation tools.
- Computer vision: Improved image recognition capabilities will enable more accurate and efficient wildlife identification and monitoring.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP can be used to analyze large volumes of text data, such as scientific publications and news reports, to gain insights into conservation issues.
These AI advancements will undoubtedly lead to more powerful and effective conservation technologies.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Successful implementation of AI in wildlife conservation requires strong collaboration:
- Collaboration between organizations: Conservation organizations, researchers, and technology developers need to work together to develop and deploy effective AI solutions.
- Open-source initiatives: Sharing data and software tools will accelerate the development and adoption of AI in conservation.
- Data sharing: Facilitating the sharing of high-quality data across organizations and researchers is crucial for training robust AI models.
These collaborations and partnerships are fundamental to maximizing the impact of AI on conservation efforts.
Citizen Science and Public Engagement
Involving the public in data collection and analysis is essential:
- Citizen science initiatives: Engaging citizens in tasks such as image annotation and data validation can significantly enhance data quality and availability.
- Raising awareness: Educating the public about the benefits of AI in wildlife conservation can foster support and engagement.
Citizen science and public engagement can significantly amplify conservation efforts and foster broader support for these vital initiatives.
Conclusion
AI is rapidly transforming the landscape of wildlife conservation. While challenges exist regarding data availability, computational resources, and ethical considerations, the benefits of enhanced monitoring, predictive modeling, and anti-poaching efforts are undeniable. The future of wildlife conservation hinges on embracing innovative technologies like AI. Learn more about how you can contribute to this vital field and help protect our planet's biodiversity through AI-powered wildlife conservation, supporting organizations involved in these efforts, or participating in citizen science initiatives. The power of AI in wildlife conservation lies not only in its technological advancements but also in the collaborative spirit needed to harness its potential for the benefit of all species.

Featured Posts
-
 Nine Home Runs Power Yankees To Victory Judges Historic Performance
Apr 23, 2025
Nine Home Runs Power Yankees To Victory Judges Historic Performance
Apr 23, 2025 -
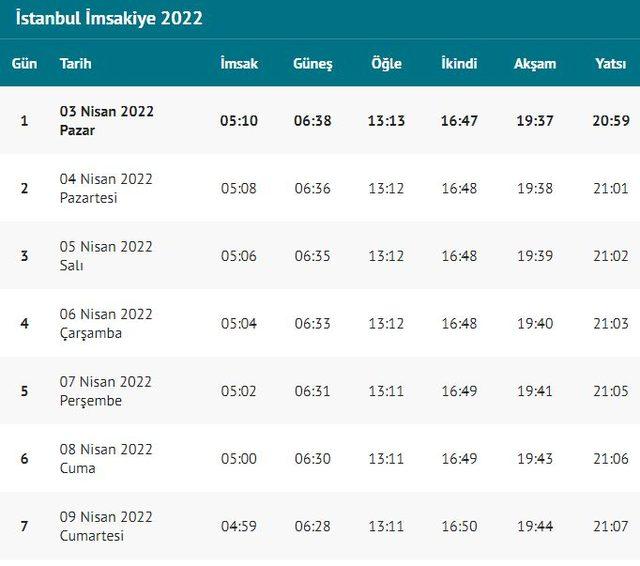 Ramazan Imsakiyesi 2024 Istanbul Ankara Izmir Iftar Ve Sahur Saatleri
Apr 23, 2025
Ramazan Imsakiyesi 2024 Istanbul Ankara Izmir Iftar Ve Sahur Saatleri
Apr 23, 2025 -
 2025s Unsung Hero A Brewers Unexpected Clutch Hitting
Apr 23, 2025
2025s Unsung Hero A Brewers Unexpected Clutch Hitting
Apr 23, 2025 -
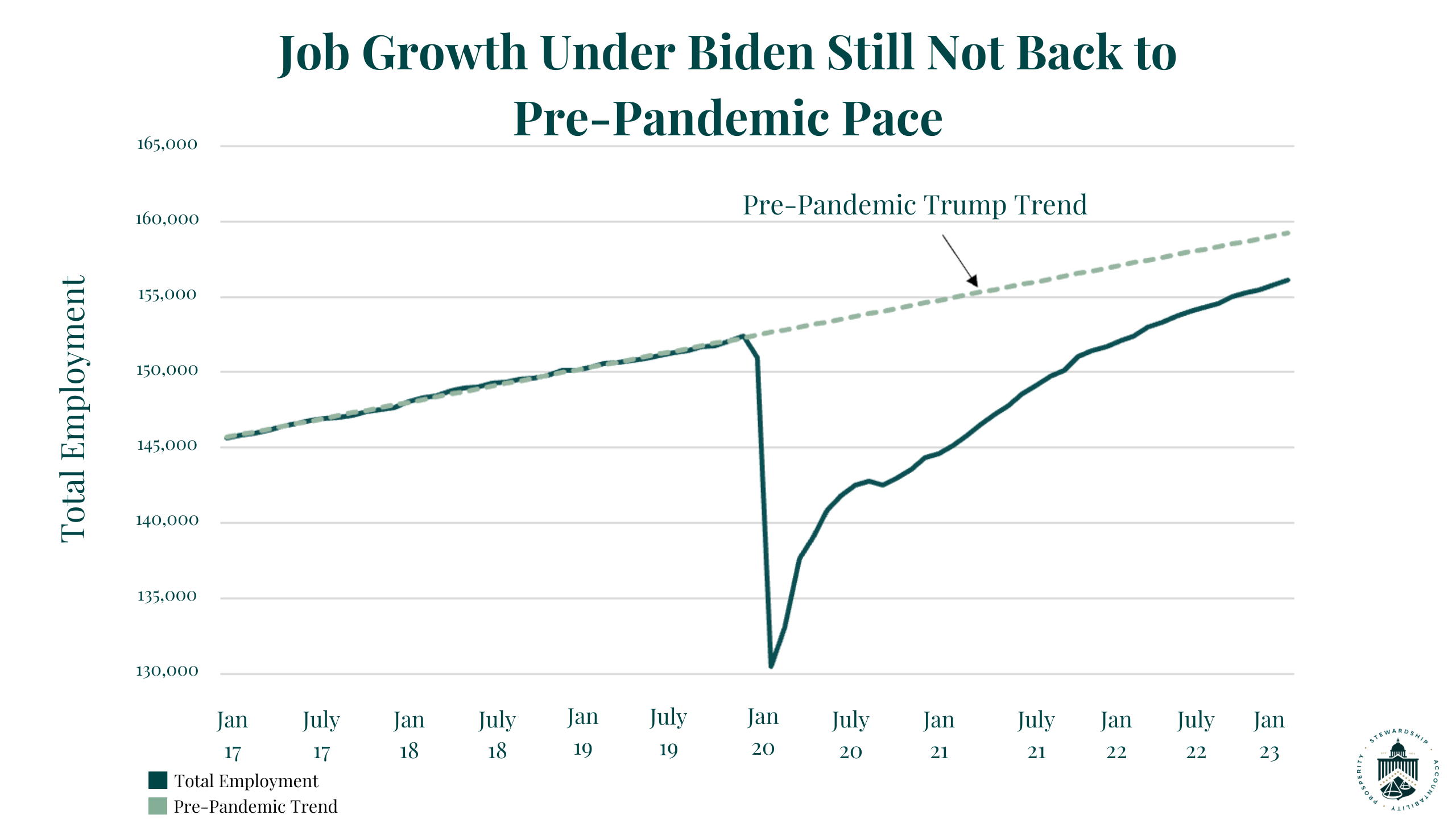 Economic Growth Under Trump A Critical Review Of The Evidence
Apr 23, 2025
Economic Growth Under Trump A Critical Review Of The Evidence
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Portefeuille Bfm Revue D Arbitrage Semaine Du 17 Fevrier 2024
Apr 23, 2025
Portefeuille Bfm Revue D Arbitrage Semaine Du 17 Fevrier 2024
Apr 23, 2025
