Analysis: Why Most Dutch Don't Want EU Retaliation Against Trump Tariffs
Table of Contents
H2: Economic Concerns and Reliance on US Trade
The Dutch economy, renowned for its export-oriented nature, exhibits a high degree of vulnerability to international trade disputes. This vulnerability is amplified by the Netherlands' strong trade relationship with the United States. Significant portions of Dutch exports, particularly within the agricultural sector, are destined for the American market.
- Export Dependence: The Netherlands' reliance on exports makes it especially susceptible to the negative consequences of trade wars. A significant portion of GDP is tied to international trade.
- Agricultural Exports: Dutch agricultural exports, encompassing products like dairy, flowers, and horticultural goods, represent a substantial portion of total exports to the US. These sectors are highly sensitive to tariff increases.
- Economic Vulnerability: Retaliatory tariffs imposed by the EU against the US could significantly harm Dutch exporters, potentially leading to job losses, decreased profits, and broader economic slowdown. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are especially vulnerable.
- Escalation Fears: The fear of an escalating trade war, leading to further retaliatory measures and broader economic damage, played a significant role in shaping Dutch public opinion. The potential knock-on effects on global supply chains added to these concerns.
Specific examples highlight this vulnerability. The Dutch dairy industry, a major exporter to the US, faced the prospect of significant revenue losses due to increased tariffs. Similarly, the horticulture sector, a cornerstone of the Dutch economy, was also directly threatened. These economic anxieties fueled public opposition to measures that risked exacerbating the situation.
H2: Political Considerations and Transatlantic Relations
Beyond economic concerns, the Dutch perspective was shaped by deeply ingrained political considerations and a long-standing commitment to strong transatlantic relations.
- Prioritizing US Ties: Many Dutch citizens prioritize maintaining strong ties with the United States, viewing the relationship as crucial for security and economic prosperity.
- Damage to Relations: Retaliatory tariffs were seen by some as potentially damaging to already strained transatlantic relations. The perception was that such actions could further undermine diplomatic efforts.
- Weakening Alliances: Concerns arose that retaliatory measures could weaken crucial alliances and complicate efforts to de-escalate trade tensions, potentially harming international cooperation more broadly.
- Geopolitical Implications: Public understanding of the broader geopolitical implications of the trade dispute—particularly concerning the EU's relationship with a major global partner—influenced their opinions against aggressive retaliation.
The historical context of Dutch-US relations, characterized by strong diplomatic ties and shared strategic interests, underscores the importance of maintaining a positive and productive partnership for the Netherlands. This historical context further informed public reservations towards measures that could jeopardize these important connections.
H3: The Role of the Agricultural Sector
The Dutch agricultural sector played a pivotal role in shaping public opinion. Its significant export-orientation and direct exposure to US tariffs made it a particularly vocal opponent of EU retaliation.
- Tariff Impacts: The Dutch agricultural sector, comprising dairy, horticulture, and other farming activities, is heavily reliant on US exports. Tariffs directly impacted profitability and competitiveness.
- Farmer Concerns: Farmers and agricultural organizations actively voiced their concerns against retaliation, emphasizing the potential for job losses and economic hardship in rural areas.
- Rural Economy: The potential economic distress in rural communities, heavily reliant on agriculture, was a key driver of public opposition to further escalation.
Examples of specific agricultural products significantly affected by the tariffs, along with data on job losses and economic decline in affected regions, illustrate the tangible impact on the Dutch population. The powerful lobbying efforts of agricultural groups further amplified these concerns in the public sphere.
H2: Public Perception and Media Influence
Media coverage significantly influenced how the Dutch public perceived the trade dispute and the potential consequences of EU retaliation.
- Media Framing: The manner in which the issue was framed in the media (e.g., focusing on economic risks versus geopolitical strategy) profoundly shaped public sentiment.
- Public Opinion Polls: Consistent public opinion polls revealed a widespread opposition to EU retaliation among the Dutch population, reinforcing the notion that economic anxieties were prevalent.
- Information Dissemination: The flow of information, including analyses of the potential economic impacts, played a crucial role in shaping public discourse and influencing individual viewpoints.
Analysis of media coverage and public opinion surveys reveals a clear pattern. News outlets emphasizing potential economic damage to Dutch industries contributed significantly to the negative public perception of EU retaliation. In contrast, media focusing primarily on the geopolitical aspects of the dispute had a less pronounced influence on public opinion.
3. Conclusion:
This analysis illuminates the complex interplay of economic vulnerabilities, geopolitical considerations, and public perception that led to widespread opposition within the Netherlands to the EU's retaliatory measures against Trump-era tariffs. The Dutch case study underscores the critical need to incorporate domestic economic and political realities when crafting trade policy responses. The strong dependence of the Dutch economy on exports, particularly agricultural exports to the US, coupled with the prioritization of maintaining strong transatlantic relationships, resulted in a strong public pushback against measures that risked further damaging these already strained relationships.
Call to Action: Further research is essential to understand the long-term implications of this public sentiment and to inform future strategies for navigating trade disputes and managing public opinion on EU trade policy. This research should address the ongoing impact of tariffs, the need for balanced approaches to trade negotiations, and, crucially, the sensitivities of the Dutch economy and its close relationship with the US market. Only through a careful consideration of these factors can the EU effectively manage future trade disputes and maintain the support of its member states.

Featured Posts
-
 Hong Kong Dining Roucous Cheese Omakase A Comprehensive Review
May 18, 2025
Hong Kong Dining Roucous Cheese Omakase A Comprehensive Review
May 18, 2025 -
 Trumps Swift Statement Ignites Maga Enthusiasm
May 18, 2025
Trumps Swift Statement Ignites Maga Enthusiasm
May 18, 2025 -
 Unlocking Potential The Value Of Middle Managers In Todays Workplace
May 18, 2025
Unlocking Potential The Value Of Middle Managers In Todays Workplace
May 18, 2025 -
 The Kanye West Taylor Swift Feud And The Super Bowl
May 18, 2025
The Kanye West Taylor Swift Feud And The Super Bowl
May 18, 2025 -
 Rekord Teylor Svift Samye Prodavaemye Vinilovye Plastinki Za Desyatiletie
May 18, 2025
Rekord Teylor Svift Samye Prodavaemye Vinilovye Plastinki Za Desyatiletie
May 18, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Republican Divisions Deepen Over Medicaid Cuts
May 18, 2025
Republican Divisions Deepen Over Medicaid Cuts
May 18, 2025 -
 Medicaid Cuts A Republican Rift
May 18, 2025
Medicaid Cuts A Republican Rift
May 18, 2025 -
 Should Investors Worry About Elevated Stock Market Valuations Bof As View
May 18, 2025
Should Investors Worry About Elevated Stock Market Valuations Bof As View
May 18, 2025 -
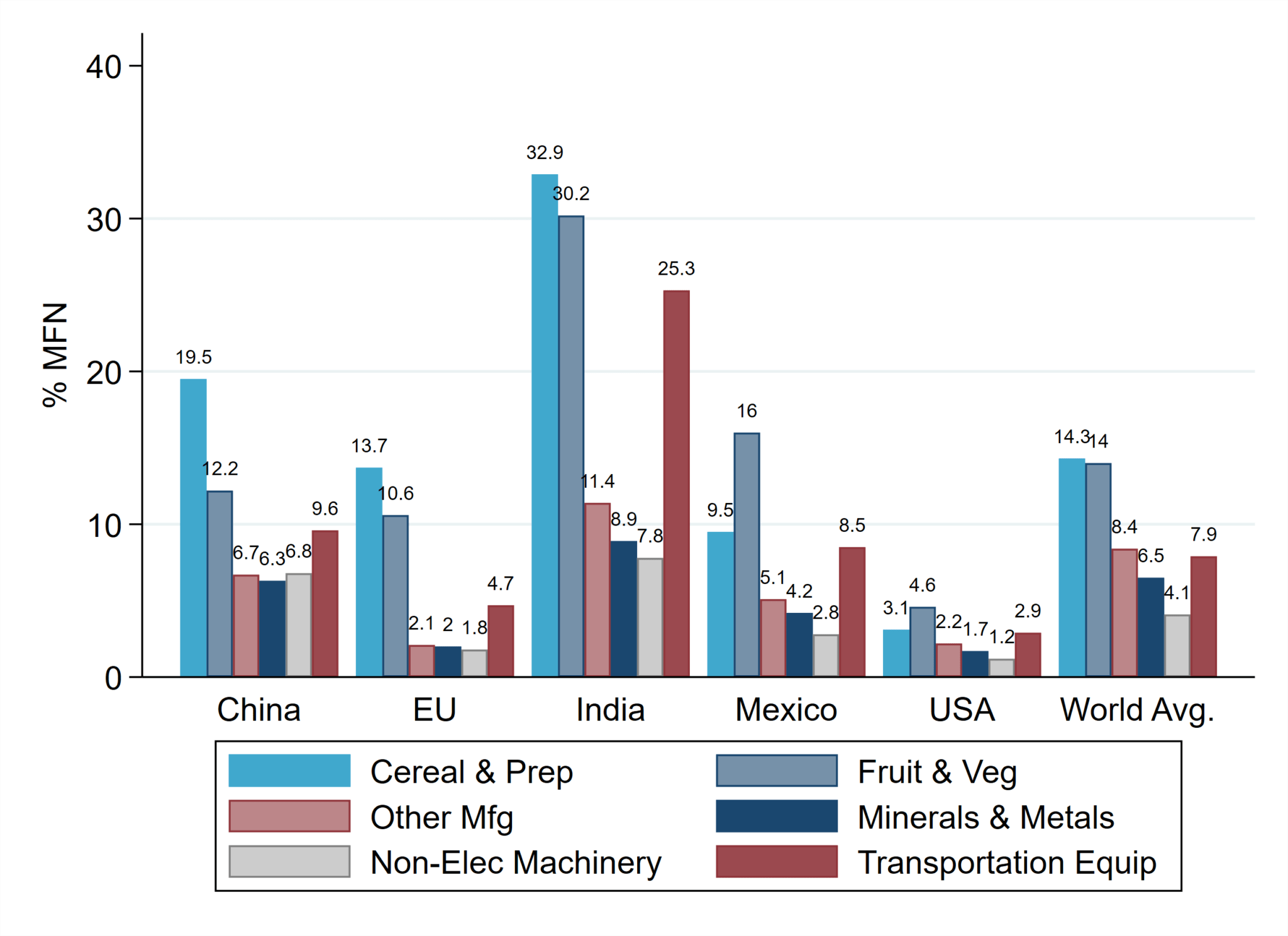 No Immediate Decision Trump On Indias Proposed Tariff Cuts
May 18, 2025
No Immediate Decision Trump On Indias Proposed Tariff Cuts
May 18, 2025 -
 Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof A Offers A Perspective For Investors
May 18, 2025
Stock Market Valuation Concerns Bof A Offers A Perspective For Investors
May 18, 2025
