Bank Of Canada Interest Rate Decision: Impact Of Tariffs And Job Market Weakness
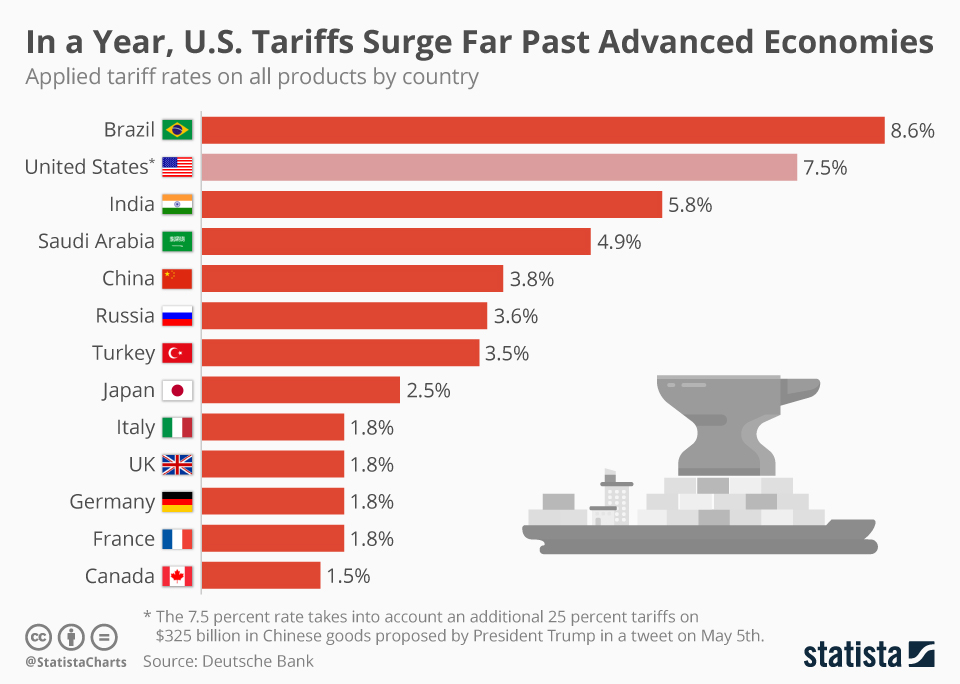
Table of Contents
The Looming Shadow of Tariffs on the Canadian Economy
Tariffs represent a significant challenge to the Canadian economy, impacting both inflation and business investment, thereby influencing the Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions.
Impact on Inflation
Tariffs contribute to inflationary pressures by increasing the cost of imported goods. This, in turn, can force the Bank of Canada to raise interest rates to control inflation.
- Examples of tariff-affected goods: Steel, aluminum, lumber, and various consumer goods are experiencing price increases due to tariffs.
- Resulting price increases: These increased costs are passed on to consumers, leading to higher prices at the grocery store, increased construction costs, and higher prices for manufactured goods.
- Impact on consumer spending: Higher prices reduce consumer purchasing power, potentially slowing economic growth.
Statistics Canada reported a year-over-year inflation rate of X% in [Month, Year], with imported goods contributing Y% to this increase. Further analysis of import/export data reveals a Z% decrease in trade volume since the implementation of certain tariffs.
Impact on Business Investment
The uncertainty surrounding tariffs discourages business investment and slows economic growth. Businesses hesitate to expand or invest in new projects when facing unpredictable trade costs.
- Industries significantly impacted by tariffs: The automotive, manufacturing, and construction sectors are particularly vulnerable to tariff-related uncertainties.
- Reduced investment in expansion or new projects: Businesses postpone expansion plans, delay hiring, and reduce capital expenditures due to the unpredictable business environment.
"The current tariff environment creates significant headwinds for business investment," says [Name], Chief Economist at [Institution]. "Uncertainty about future trade costs makes it difficult for businesses to plan for the long term."
Job Market Weakness and its Implications for Monetary Policy
The Canadian job market has shown signs of weakness, which further complicates the Bank of Canada's decision-making process regarding interest rates.
Unemployment Rate and its Trends
Recent trends in Canadian unemployment rates indicate a slowdown in job creation, particularly in certain sectors. Regional disparities also exist, with some provinces experiencing higher unemployment than others.
- Unemployment figures broken down by sector: [Insert data on unemployment rates broken down by sector, e.g., manufacturing, retail, etc.]
- Regional disparities in job losses: [Insert data on unemployment rates in different provinces and regions.]
[Insert a chart or graph visually representing the unemployment data over time.]
Wage Growth and its Correlation with Interest Rates
Slow wage growth, or wage stagnation, poses a challenge for the Bank of Canada. Low wage growth, combined with inflation driven by tariffs, can squeeze consumer spending and overall economic growth.
- Connection between wage stagnation and inflation: When wages fail to keep pace with inflation, consumers have less disposable income, leading to reduced demand and potential economic slowdown.
- How it affects monetary policy decisions: The Bank of Canada must carefully consider the impact of interest rate changes on both inflation and employment when wage growth is sluggish.
Statistics Canada reported average wage growth of X% in [Month, Year], significantly lower than the inflation rate of Y%. This wage-inflation gap puts pressure on consumer spending and economic growth.
Potential Scenarios and the Bank of Canada's Response
The Bank of Canada faces several potential scenarios in its upcoming decision, each with different implications for the Canadian economy.
Scenario 1: Interest Rate Hike
An interest rate hike could be considered if inflationary pressures outweigh concerns about job market weakness. This would aim to control inflation but risks slowing down economic growth further.
- Potential consequences of a rate hike: Higher borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially dampening investment and spending.
- Impact on borrowing costs: Increased interest rates on mortgages, loans, and credit cards.
- Effect on the economy: A potential slowdown in economic activity.
Scenario 2: Interest Rate Hold
Maintaining the current interest rate could be a strategic choice if the Bank of Canada believes the current economic conditions warrant a wait-and-see approach.
- Arguments supporting a rate hold: A cautious approach to avoid further economic slowdown, given the weak job market.
- Potential risks and benefits: The risk of allowing inflation to rise further, versus the benefit of supporting employment.
Scenario 3: Interest Rate Cut
An interest rate cut is a possibility if the job market weakens significantly and deflationary pressures emerge.
- Circumstances that would necessitate a rate cut: A sharp rise in unemployment, coupled with falling inflation.
- Potential economic consequences: Stimulating economic activity, but potentially increasing inflation in the longer term.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada's Interest Rate Decision is a complex balancing act, heavily influenced by the interplay of tariffs, which fuel inflation, and job market weakness, which threatens economic growth. The impact of tariffs on inflation and business investment is undeniable, while the sluggish job market adds another layer of complexity. Understanding these factors is critical for predicting the Bank's response. The potential scenarios – a rate hike, a hold, or a cut – each carry significant implications for the Canadian economy and individuals' financial well-being. Stay updated on the next Bank of Canada Interest Rate Decision to make informed financial decisions. Understanding the Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions is crucial for navigating the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Aaron Judges Early Power Surge Vs Atlantas Cold Start
May 12, 2025
Aaron Judges Early Power Surge Vs Atlantas Cold Start
May 12, 2025 -
 Analysis Of Progress In Us China Trade Discussions
May 12, 2025
Analysis Of Progress In Us China Trade Discussions
May 12, 2025 -
 Thomas Mueller Till Mls Senaste Nytt Och Rykten
May 12, 2025
Thomas Mueller Till Mls Senaste Nytt Och Rykten
May 12, 2025 -
 The Bce Inc Dividend Cut What It Means For Your Investments
May 12, 2025
The Bce Inc Dividend Cut What It Means For Your Investments
May 12, 2025 -
 Revisitando A Adaptacao Em Quadrinhos De Stallone Uma Avaliacao
May 12, 2025
Revisitando A Adaptacao Em Quadrinhos De Stallone Uma Avaliacao
May 12, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Noida And Ghaziabad Heatwave Warning For Outdoor Workers
May 13, 2025
Noida And Ghaziabad Heatwave Warning For Outdoor Workers
May 13, 2025 -
 Ghaziabads Heat Advisory Safety Guidelines For Outdoor Workers In Noida
May 13, 2025
Ghaziabads Heat Advisory Safety Guidelines For Outdoor Workers In Noida
May 13, 2025 -
 Ghaziabad Issues Advisory For Outdoor Workers Noida News
May 13, 2025
Ghaziabad Issues Advisory For Outdoor Workers Noida News
May 13, 2025 -
 Extreme Heat Warning Record Breaking Temperatures In La And Orange Counties
May 13, 2025
Extreme Heat Warning Record Breaking Temperatures In La And Orange Counties
May 13, 2025 -
 Record High Temperatures La And Orange County Heatwave
May 13, 2025
Record High Temperatures La And Orange County Heatwave
May 13, 2025
