Bilateral Anophthalmia: A Comprehensive Guide For Parents And Caregivers

Table of Contents
What is Bilateral Anophthalmia? Causes and Diagnosis
Bilateral anophthalmia is a rare congenital condition characterized by the complete absence of both eyes at birth. This absence of eyes, also known as ocular aplasia, is a significant developmental anomaly impacting vision and overall development. Unlike conditions involving underdeveloped eyes (microphthalmia), bilateral anophthalmia signifies a complete lack of eye structures.
Several factors may contribute to bilateral anophthalmia. Genetic mutations play a significant role, with various genes implicated in eye development. Prenatal factors, such as exposure to teratogens (substances that can cause birth defects) during pregnancy, are also considered potential causes. Developmental anomalies during early embryonic development can also disrupt the formation of the eyes.
Diagnosis often begins with prenatal ultrasound, which may detect the absence of eyeballs. Postnatal examinations by an ophthalmologist confirm the diagnosis. Genetic testing may be recommended to identify any underlying genetic causes and assess the risk of recurrence in future pregnancies. Advanced imaging techniques may also be used to rule out other associated conditions.
- Types of Anophthalmia: While bilateral anophthalmia refers to the absence of both eyes, the severity can vary slightly, with some individuals exhibiting rudimentary eye structures.
- Associated Syndromes: Bilateral anophthalmia can be associated with other genetic syndromes, requiring a comprehensive evaluation to determine any co-occurring conditions.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis: Early diagnosis is crucial for initiating appropriate management and support services, optimizing the child's development.
Managing Bilateral Anophthalmia: Providing Optimal Care and Support
Early intervention is paramount in managing bilateral anophthalmia. A focus on developmental milestones, particularly sensory integration, is critical for healthy development. Vision rehabilitation, though not restoring sight, focuses on developing other senses and improving overall sensory awareness. Early childhood development programs specializing in visual impairments can provide valuable support.
Treatment options include the fitting of ocular prostheses (artificial eyes). These can be purely cosmetic or provide a degree of functionality, improving the fit of glasses or other assistive devices. Adaptive equipment, such as specialized toys and assistive technology, may also be necessary. Therapeutic interventions, including vision stimulation techniques, aim to improve sensory awareness and processing.
A multidisciplinary team approach is essential. This team typically includes an ophthalmologist, developmental pediatrician, orthoptist (specializing in eye muscle alignment), social worker, and occupational therapist. Each professional plays a crucial role in addressing the child's physical, developmental, and emotional needs.
- Prosthetic Eyes: Cosmetic prostheses aim to provide a natural appearance, while some functional prostheses might aid in the fitting of glasses or other devices.
- Social-Emotional Development: Strategies to foster social-emotional development include positive reinforcement, creating a nurturing environment, and promoting social interaction.
- Resources: Local support groups, online communities, and organizations dedicated to visual impairments can offer invaluable resources and support networks.
Emotional and Psychological Well-being for Children and Families
The diagnosis of bilateral anophthalmia presents significant emotional challenges for both the child and their family. Parental adjustment to the diagnosis and the lifelong implications requires emotional support and coping mechanisms. Family therapy can play a significant role in navigating these complex emotions and strengthening family bonds. The psychological well-being of the child is paramount, necessitating strategies to promote self-esteem and a positive self-image.
Building self-esteem and confidence requires a supportive and understanding environment. Social skills training can help children navigate social situations and interact with peers effectively. Peer support groups can provide a sense of belonging and understanding. Open communication about the condition is vital.
Access to mental health professionals specializing in developmental disabilities can provide counseling and support for the entire family. Online resources and support networks offer additional channels for information and emotional support.
- Communication: Open and honest conversations with the child about their condition, tailored to their developmental age, are crucial.
- Independence: Encouraging independence and self-reliance in age-appropriate ways builds confidence and self-esteem.
- Bullying Prevention: Proactive strategies to address potential bullying or social isolation, such as education and peer support, are essential.
Long-Term Considerations and Ongoing Care
Long-term care for children with bilateral anophthalmia necessitates regular follow-up appointments with specialists to monitor development and address any emerging concerns. Ongoing support is critical throughout the child's life. Medical management focuses on addressing any associated conditions and ensuring the child's overall health and well-being.
Adapting to developmental changes and life transitions requires ongoing support and flexibility. Strategies for successful integration into school and community life are essential. Age-appropriate care ensures that the child receives the necessary support at every stage of life. Advocating for the child's needs in education and other settings is crucial for successful integration.
The future outlook for children with bilateral anophthalmia is positive. With comprehensive care and support, they can achieve a high quality of life, actively participate in society, and develop their full potential.
- Education: Advocating for inclusive educational settings and appropriate support services is crucial for the child's educational success.
- Associated Conditions: Long-term management of any associated conditions requires regular monitoring and treatment.
- Future Planning: Planning for the future, including access to appropriate resources and support throughout adulthood, is a key aspect of long-term care.
Conclusion: Supporting Children with Bilateral Anophthalmia
This guide highlights the importance of early diagnosis, comprehensive care, and emotional support for children with bilateral anophthalmia and their families. A multidisciplinary team approach, coupled with the utilization of available resources, significantly impacts the child’s development and well-being. Remember, understanding bilateral anophthalmia and actively participating in your child's care is key to ensuring a fulfilling life.
We encourage parents and caregivers to connect with support organizations like [insert relevant organization links here] to learn more about bilateral anophthalmia, access valuable resources, and join a supportive community. By working together, we can empower children with bilateral anophthalmia to thrive and reach their full potential.

Featured Posts
-
 Last Chance To Win Tales From The Track Tickets
May 12, 2025
Last Chance To Win Tales From The Track Tickets
May 12, 2025 -
 Jamaica Observer Grand Slam Delight
May 12, 2025
Jamaica Observer Grand Slam Delight
May 12, 2025 -
 37 Point Loss Highlights Knicks Resolve Issues Thibodeaus Reaction
May 12, 2025
37 Point Loss Highlights Knicks Resolve Issues Thibodeaus Reaction
May 12, 2025 -
 Mtv Cribs A Look Inside The Homes Of Rich Kids
May 12, 2025
Mtv Cribs A Look Inside The Homes Of Rich Kids
May 12, 2025 -
 Royal Familys Divorce Princess Beatrice Shares Her Perspective On Prince Andrew And Fergies Split
May 12, 2025
Royal Familys Divorce Princess Beatrice Shares Her Perspective On Prince Andrew And Fergies Split
May 12, 2025
Latest Posts
-
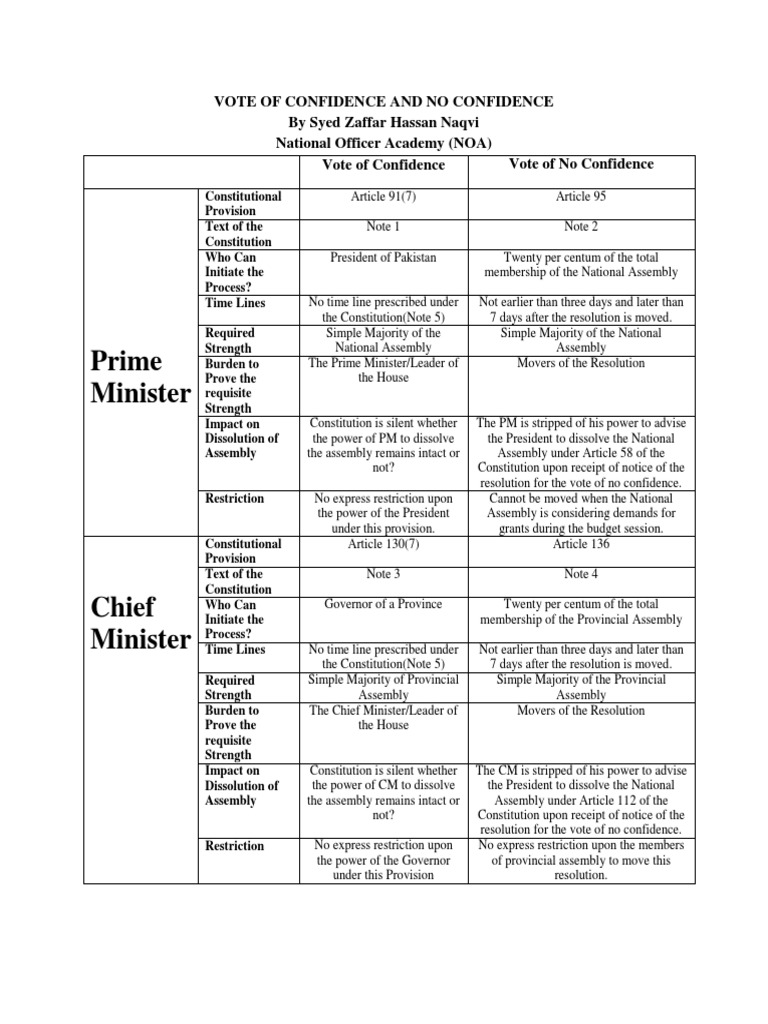 Faber Retains Position After No Confidence Vote
May 12, 2025
Faber Retains Position After No Confidence Vote
May 12, 2025 -
 Asylum Volunteer Royal Honors Fabers Complete Policy Reversal
May 12, 2025
Asylum Volunteer Royal Honors Fabers Complete Policy Reversal
May 12, 2025 -
 Potenziale Zur Kostensenkung In Asylunterkuenften Ein Bericht Der Beiraete
May 12, 2025
Potenziale Zur Kostensenkung In Asylunterkuenften Ein Bericht Der Beiraete
May 12, 2025 -
 Marjolein Faber Considers Legal Action After Hitler Mustache Photo Surfaces
May 12, 2025
Marjolein Faber Considers Legal Action After Hitler Mustache Photo Surfaces
May 12, 2025 -
 Faber Backtracks On Asylum Volunteer Awards 100 Support Confirmed
May 12, 2025
Faber Backtracks On Asylum Volunteer Awards 100 Support Confirmed
May 12, 2025
