China's Trade War Losses: The Unseen Impact On Beijing's Economy
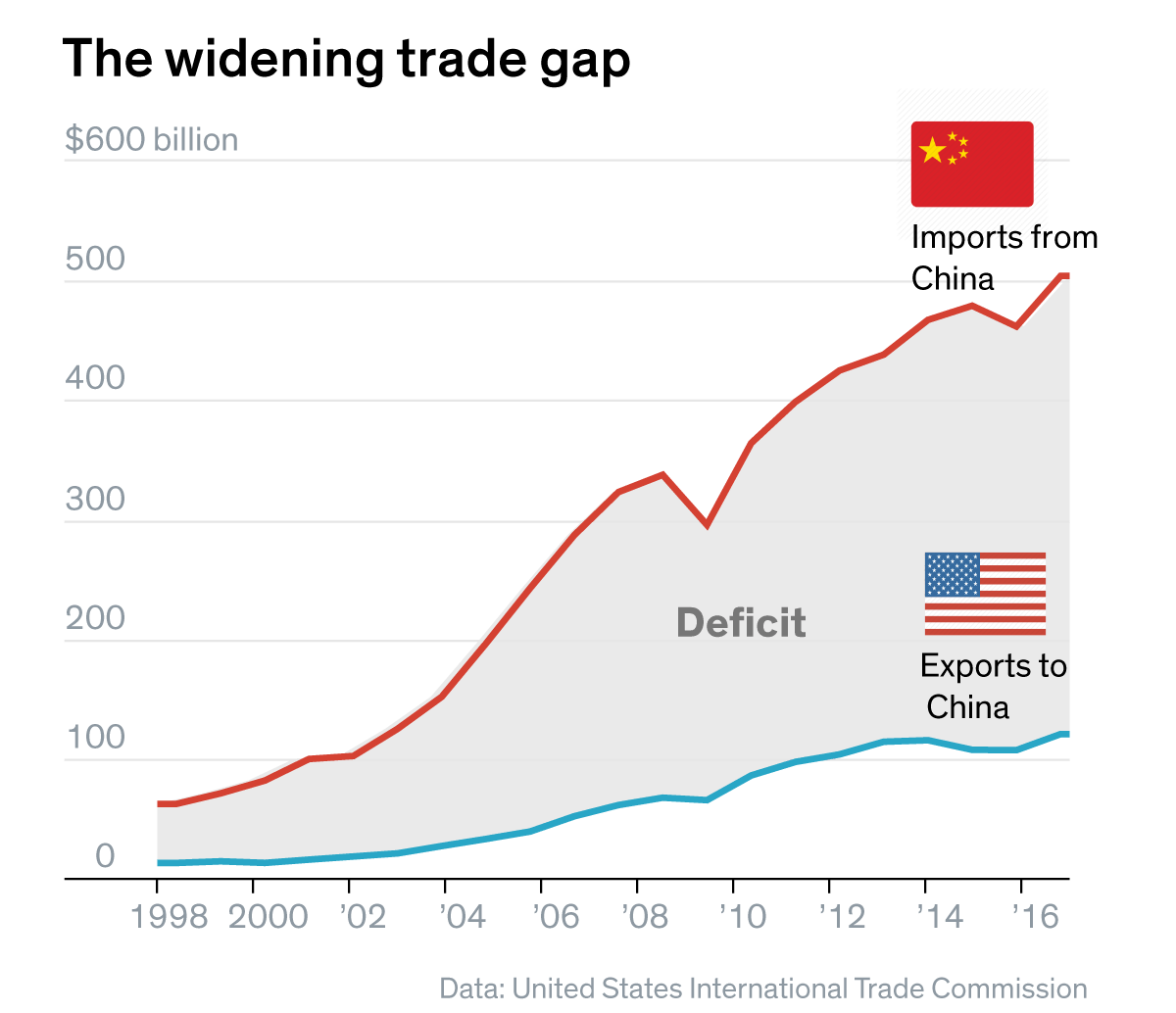
Table of Contents
The US-China trade war, while seemingly relegated to the history books, left indelible scars on Beijing's economy. While headlines focused on headline-grabbing tariff battles and immediate trade disruptions, a deeper analysis reveals a more nuanced and far-reaching impact. This article delves into the unseen consequences of the trade war on China's economic landscape, exploring its effects on various sectors and the long-term implications for Beijing's economic strategies. We'll move beyond the simple export figures, examining the ripple effects on innovation, foreign investment, and China's overall global economic standing. Understanding these "unseen" losses is crucial to grasping the full extent of the trade war's legacy and its continuing influence on China's economic future. We will explore the key areas where the trade war significantly impacted China's economy, shedding light on the lasting effects felt by Beijing and the broader global economy.
H2: Disrupted Supply Chains and Manufacturing Slowdown
The trade war inflicted significant damage on China's intricate manufacturing ecosystem. The imposition of tariffs and retaliatory measures triggered a chain reaction throughout the global supply chain, leading to substantial economic consequences for China.
H3: The Impact on Export-Oriented Industries
- Disruption of global supply chains: The trade war led to significant disruptions in global supply chains, causing production delays and increased costs for Chinese manufacturers. Companies struggled to source raw materials and components, leading to production bottlenecks and increased uncertainty.
- Decline in exports of specific goods: Tariffs imposed by the US directly impacted the export of numerous Chinese goods, leading to a decline in sales and revenue for many export-oriented industries. This decline was particularly acute in sectors like electronics, textiles, and agriculture.
- Shift in global sourcing: The trade war accelerated a pre-existing trend of companies diversifying their supply chains and moving production away from China to mitigate risks associated with trade disputes. This shift poses a long-term challenge to China's competitiveness.
- Examples: Specific sectors like consumer electronics, where tariffs significantly impacted the cost of components, experienced a steep decline in exports. Similarly, the agricultural sector faced challenges due to retaliatory tariffs on Chinese agricultural products.
H3: Increased Input Costs and Reduced Profit Margins
- Higher costs for raw materials: Tariffs and trade restrictions increased the cost of raw materials and intermediate goods for Chinese manufacturers, squeezing profit margins. This impact was especially significant for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited resources to absorb these cost increases.
- Reduced profitability: The combination of decreased export demand and increased input costs significantly reduced profitability for many Chinese businesses. This led to job losses, factory closures, and a slowdown in investment.
- Impact on SMEs: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which form the backbone of China's manufacturing sector, were disproportionately affected by the increased costs and reduced demand. Many SMEs struggled to survive, leading to business failures and job losses.
- Government intervention: The Chinese government implemented various support packages and stimulus measures to mitigate the negative impact of the trade war on businesses, particularly SMEs. These measures included tax breaks, subsidies, and loan guarantees.
H2: Foreign Investment Slowdown and Capital Flight
The trade war created considerable uncertainty in the global investment landscape, significantly impacting foreign direct investment (FDI) in China.
H3: Decreased FDI Inflows
- Uncertainty and decreased confidence: The trade war created considerable uncertainty, discouraging foreign direct investment (FDI) in China. Companies were hesitant to invest in a market perceived as politically unstable and subject to unpredictable trade policies.
- Comparison of FDI inflows: A clear comparison of FDI inflows before, during, and after the trade war reveals a substantial decline during the period of heightened trade tensions. This slowdown had significant implications for China's economic growth and development.
H3: Increased Capital Outflows
- Seeking safer investments: Chinese businesses and investors, fearing further economic instability, sought safer investment opportunities outside of China, leading to a significant increase in capital outflows.
- Impact on the Yuan: Capital flight put downward pressure on the value of the Chinese Yuan, adding another layer of economic uncertainty.
- Government policies to curb capital flight: The Chinese government implemented various measures to curb capital flight and stabilize the Yuan, including restrictions on capital transfers and interventions in the foreign exchange market.
H2: Technological Dependence and Innovation Challenges
The trade war exposed and exacerbated China's reliance on foreign technology, prompting a renewed focus on domestic technological innovation.
H3: Increased reliance on domestic technology
- Accelerated domestic innovation: The trade war forced China to accelerate efforts in domestic technological innovation, particularly in areas where it faced restrictions on access to foreign technology.
- Challenges in competing: However, Chinese companies still face significant challenges in competing with established foreign technology companies in terms of innovation and market share.
- Government initiatives: The Chinese government launched numerous initiatives to promote technological self-reliance, including substantial investments in research and development, support for domestic technology companies, and policies aimed at reducing reliance on foreign technology.
H3: Impact on the development of key technologies
- Slowdown in key technology development: Restrictions on access to foreign technologies, particularly in sensitive areas like semiconductors and artificial intelligence (AI), likely slowed the development of 5G, AI, and other key technologies in China.
- Long-term implications: The trade war's impact on the development of key technologies has long-term implications for China's technological advancement and global competitiveness.
H2: Shifting Geopolitical Landscape and Economic Relationships
The trade war significantly altered China's geopolitical landscape and its economic relationships with other countries.
H3: Diversification of Trade Partners
- Reduced reliance on the US: The trade war prompted China to actively diversify its trade partners and reduce its reliance on the US market. This involved strengthening trade relationships with countries in the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and other regions.
- Challenges in establishing new relationships: While China made progress in diversifying its trade relationships, establishing new, reliable trade partners and supply chains requires significant time and investment.
H3: Strained US-China relations
- Long-term impact on cooperation: The trade war severely strained US-China relations, impacting bilateral economic cooperation and trust. This has wider implications for global economic stability and cooperation.
Conclusion:
The US-China trade war inflicted significant, often unseen, damage on Beijing's economy. While the immediate impact was focused on trade tariffs, a deeper analysis reveals substantial disruptions to supply chains, reduced foreign investment, challenges to technological advancement, and a reshaped geopolitical landscape. Understanding the long-term implications of these "unseen" losses is crucial for comprehending China's future economic trajectory. Beijing's response, characterized by efforts to increase self-reliance and diversify trade partners, highlights the enduring impact of this trade conflict. To gain a more complete understanding of the economic ramifications, further research into specific sectors and long-term data analysis is critical. Continue exploring the lasting effects of China's trade war losses to gain a comprehensive understanding of the complex economic shifts impacting Beijing and the global economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Daily Lotto Tuesday 15th April 2025 Winning Numbers
May 02, 2025
Daily Lotto Tuesday 15th April 2025 Winning Numbers
May 02, 2025 -
 Mental Health Literacy Education Strategies For Effective Training And Implementation
May 02, 2025
Mental Health Literacy Education Strategies For Effective Training And Implementation
May 02, 2025 -
 High Cost And Stigma Barriers To Mental Healthcare Access
May 02, 2025
High Cost And Stigma Barriers To Mental Healthcare Access
May 02, 2025 -
 Spotlight On Splice A Cay Fest Film Review
May 02, 2025
Spotlight On Splice A Cay Fest Film Review
May 02, 2025 -
 Florida And Wisconsins Election Turnout Signals For The Next Political Cycle
May 02, 2025
Florida And Wisconsins Election Turnout Signals For The Next Political Cycle
May 02, 2025
