Dealerships Intensify Opposition To Mandatory Electric Vehicle Sales
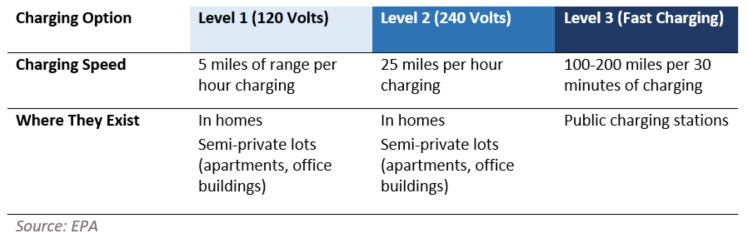
Table of Contents
Economic Concerns Fueling Dealer Opposition
The transition to selling and servicing EVs presents substantial financial challenges for dealerships. The high upfront investment required for EV infrastructure is a major concern. This includes the cost of installing charging stations, acquiring specialized tools for EV repair and maintenance, and upgrading existing facilities to accommodate the unique needs of electric vehicles. These costs can be substantial, especially for smaller dealerships with limited resources.
- High Upfront Investment Costs: Installing Level 2 and DC fast chargers requires significant capital expenditure, and the return on investment may be uncertain in the short term.
- Extensive Employee Retraining: EV mechanics need specialized training to diagnose and repair electric motors, batteries, and other components. This training can be expensive and time-consuming.
- Lower Profit Margins on EVs: Dealers often report lower profit margins on EVs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles, due to factors such as lower service revenue and increased competition.
- Inventory Management Challenges: The supply chain for EVs can be less predictable than for gasoline cars, leading to inventory management difficulties and potential stockouts. Longer lead times also impact sales cycles.
- Regional Variations in Demand: Consumer adoption rates for EVs vary significantly across regions, and dealerships in areas with lower demand face greater challenges in managing their EV inventory.
Logistical Challenges and Lack of Readiness
Beyond the economic hurdles, dealerships face significant logistical challenges in adapting to mandatory EV sales. The current infrastructure is not always adequate to support a rapid transition to widespread EV adoption.
- Inadequate Charging Infrastructure: The lack of sufficient public charging stations, especially in rural areas, remains a major barrier to EV adoption and creates range anxiety for potential buyers.
- Challenges in Securing a Reliable EV Supply: Dealerships often struggle to secure a steady supply of electric vehicles from manufacturers, leading to frustrated customers and missed sales opportunities. The ongoing supply chain issues exacerbate this problem.
- Showroom Adaptation: Showrooms need to be adapted to showcase EVs effectively and accommodate charging infrastructure. This may require costly renovations or new construction.
- Lack of Consumer Awareness and Education: Many consumers lack a full understanding of EV technology, charging infrastructure, and the associated costs, hindering the widespread adoption of EVs.
- Insufficient Government Support: Many dealerships argue that government support for dealer transition programs, including financial incentives and assistance with infrastructure development, is insufficient.
Concerns about Consumer Choice and Market Impact
A core argument against mandatory EV sales is that it restricts consumer choice and potentially distorts the free market.
- Reduced Availability of Gasoline-Powered Vehicles: Mandatory EV sales quotas could lead to a reduction in the availability of gasoline-powered vehicles, limiting consumer options.
- Potential Price Increases: Reduced competition due to fewer gasoline car options could potentially lead to higher prices for both gasoline and electric vehicles.
- Impact on Lower-Income Consumers: Not all consumers can afford the higher upfront cost of an EV, and mandatory sales mandates could disproportionately impact lower-income households.
- Government Intervention in the Free Market: Critics argue that government mandates interfere with the natural forces of supply and demand and stifle innovation.
- Need for a Gradual Transition: A phased approach, aligning with market demand and technological advancements, would allow for a more manageable transition to electric mobility.
The Dealers' Proposed Solutions and Counterarguments
Dealerships are not simply opposed to EVs; they are advocating for a more pragmatic approach to the transition.
- Phased Approach to EV Mandates: A gradual increase in EV sales quotas over time would give dealerships and consumers more time to adapt.
- Government Incentives: Increased government incentives for dealers to invest in EV infrastructure and training would ease the financial burden.
- Consumer Education Campaigns: Government-funded campaigns aimed at educating consumers about the benefits and practicality of EVs are crucial.
- Government Partnerships: Stronger collaboration between government and dealerships would facilitate a smoother transition and address logistical challenges collaboratively.
Conclusion
The debate surrounding mandatory electric vehicle sales is complex, with strong arguments on both sides. Dealerships' concerns regarding economic viability, logistical readiness, and consumer choice are significant and cannot be ignored. A balanced approach is needed—one that acknowledges the environmental imperative of transitioning to electric vehicles while addressing the legitimate concerns of automotive dealerships and consumers. Ignoring the voices of dealerships could lead to a disruptive and potentially ineffective transition to electric mobility. The opposition to mandatory electric vehicle sales highlights the need for a productive dialogue involving all stakeholders. Let's continue the discussion on finding a workable solution for mandatory electric vehicle sales to ensure a smooth and sustainable shift towards a greener automotive future.

Featured Posts
-
 Jack White Joins Detroit Tigers Broadcast Hall Of Fame Discussion And Baseball Insights
May 31, 2025
Jack White Joins Detroit Tigers Broadcast Hall Of Fame Discussion And Baseball Insights
May 31, 2025 -
 Bodensee Katastrophenuebung Einsatzkraefte Trainieren In Hard Fuer Den Ernstfall
May 31, 2025
Bodensee Katastrophenuebung Einsatzkraefte Trainieren In Hard Fuer Den Ernstfall
May 31, 2025 -
 Samsung Galaxy Tab Undercuts I Pad 101 Bargain
May 31, 2025
Samsung Galaxy Tab Undercuts I Pad 101 Bargain
May 31, 2025 -
 Trumps Iran Deal Is Israel Facing Encirclement
May 31, 2025
Trumps Iran Deal Is Israel Facing Encirclement
May 31, 2025 -
 Persistent Rain In Seattle Forecast For The Weekend
May 31, 2025
Persistent Rain In Seattle Forecast For The Weekend
May 31, 2025
