Desjardins Forecasts Three Further Bank Of Canada Interest Rate Cuts

Table of Contents
Desjardins' Rationale Behind the Prediction
Desjardins' forecast rests on several key economic indicators and factors suggesting a need for further monetary easing. Their analysis points to a weakening Canadian economy requiring stimulus through lower interest rates.
-
Weakening Consumer Spending: Consumer confidence has declined significantly in recent months, with rising inflation eroding purchasing power. This reduced consumer spending is a major drag on economic growth and a key reason Desjardins anticipates further rate cuts. Data released by Statistics Canada showing a decline in retail sales supports this assessment. Lower interest rates aim to boost consumer confidence and spending.
-
Slowing Economic Growth: Canada's economic growth has decelerated considerably, falling below expectations in the last quarter. This economic slowdown, coupled with weakening global economic conditions, increases the likelihood of a recession, prompting Desjardins to advocate for lower interest rates. GDP figures paint a concerning picture requiring proactive monetary policy adjustments.
-
High Inflation Persistent Despite Previous Rate Hikes: While the inflation rate has shown signs of easing, it remains stubbornly above the Bank of Canada's target of 2%. Despite previous interest rate hikes aimed at curbing inflation, the persistence of elevated prices suggests further action is needed, but possibly in a different direction than further increases. This persistent inflation may be more responsive to measures addressing supply chain issues rather than further interest rate hikes.
-
Impact of Global Economic Uncertainty: The global economic landscape is fraught with uncertainty, with geopolitical tensions and persistent inflationary pressures in major economies impacting Canada. This global economic uncertainty further weakens the case for maintaining or raising interest rates.
-
Housing Market Downturn: The Canadian housing market has experienced a significant downturn, with prices falling and sales activity declining. Lower interest rates are seen as a potential way to stimulate demand and prevent a deeper correction in the housing sector, though this carries risks to already high housing debt.
Potential Impact of Further Interest Rate Cuts
Three additional Bank of Canada interest rate cuts would likely have significant consequences for the Canadian economy:
-
Effect on Borrowing Costs (Mortgages, Loans): Lower interest rates would translate to lower borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. This would make mortgages and other loans more affordable, potentially stimulating spending and investment. Lower mortgage rates, in particular, could provide a boost to the housing market, though this could also increase already inflated housing prices.
-
Stimulus to Economic Activity: Reduced borrowing costs are intended to spur economic activity by encouraging investment and consumer spending. This stimulus is aimed at countering the economic slowdown and potentially preventing a recession. However, the effectiveness of this stimulus depends on several factors, including consumer confidence and business sentiment.
-
Potential Impact on Inflation: While lower interest rates are meant to stimulate the economy, there's a risk they could also fuel inflation. This is a key concern, as the Bank of Canada's primary mandate is price stability. The effectiveness of rate cuts in stimulating the economy without reigniting inflation will be a key factor in determining the overall success of the policy change.
-
Influence on the Canadian Dollar Exchange Rate: Lower interest rates could weaken the Canadian dollar against other currencies, making Canadian exports more competitive but potentially increasing the cost of imports. This impact on the currency exchange rate is an important consideration for the Bank of Canada.
-
Risks Associated with Further Rate Cuts (e.g., Fueling Inflation): A significant risk is that lower interest rates could lead to increased inflation, negating the intended benefits of stimulating the economy. This trade-off between economic growth and price stability is a critical challenge for the Bank of Canada.
Market Reaction and Expert Opinions
The market's reaction to Desjardins' forecast has been mixed. Some analysts see it as a plausible scenario given the current economic climate, while others express skepticism.
-
Stock Market Reaction: Stock markets generally responded positively to the news, reflecting investor anticipation of lower borrowing costs and potentially stronger economic growth. However, this positive reaction may also reflect a shift in investor sentiment towards a less aggressive interest rate environment.
-
Bond Market Reaction: Bond yields have generally fallen, reflecting investor expectations of lower interest rates in the future. This is a typical reaction to predictions of lower borrowing costs.
-
Opinions of Other Financial Institutions: Other financial institutions have offered varying opinions. While some agree with Desjardins' assessment, others remain cautious, pointing to the risks of further inflation. The divergence of opinions highlights the uncertainty surrounding the future path of interest rates.
-
Differing Predictions and Their Reasoning: The range of predictions emphasizes the complexities of economic forecasting and the many factors impacting the Bank of Canada's decision-making. These differing predictions underscore the fact that even among experts, there's no consensus on the optimal monetary policy path.
Comparison with Bank of Canada's Stance
Desjardins' prediction currently contrasts with the Bank of Canada's recent public statements. While the Bank acknowledges economic challenges, it hasn't explicitly signaled its intention to cut interest rates further. The divergence highlights the ongoing debate among economists regarding the appropriate monetary policy response to the current economic climate. However, the Bank of Canada's forward guidance may shift, especially if economic data aligns with Desjardins' forecast.
Conclusion
Desjardins' forecast of three further Bank of Canada interest rate cuts presents a significant shift in the outlook for the Canadian economy. The prediction is grounded in weakening consumer spending, slowing economic growth, persistent inflation despite previous rate hikes, global economic uncertainty, and the housing market downturn. While lower interest rates could stimulate economic activity and reduce borrowing costs, they also carry the risk of fueling inflation. The market's reaction has been mixed, reflecting the uncertainty surrounding this bold prediction. Understanding the potential implications of these Bank of Canada interest rate cuts is crucial for navigating the complexities of the current economic landscape. Stay tuned for further updates on the Bank of Canada’s monetary policy decisions and their implications. Understanding the nuances of Bank of Canada interest rate cuts and their potential consequences is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Consult with a financial advisor for personalized advice.

Featured Posts
-
 Guccis Massimo Vian Departs Supply Chain Officer Exit Explained
May 24, 2025
Guccis Massimo Vian Departs Supply Chain Officer Exit Explained
May 24, 2025 -
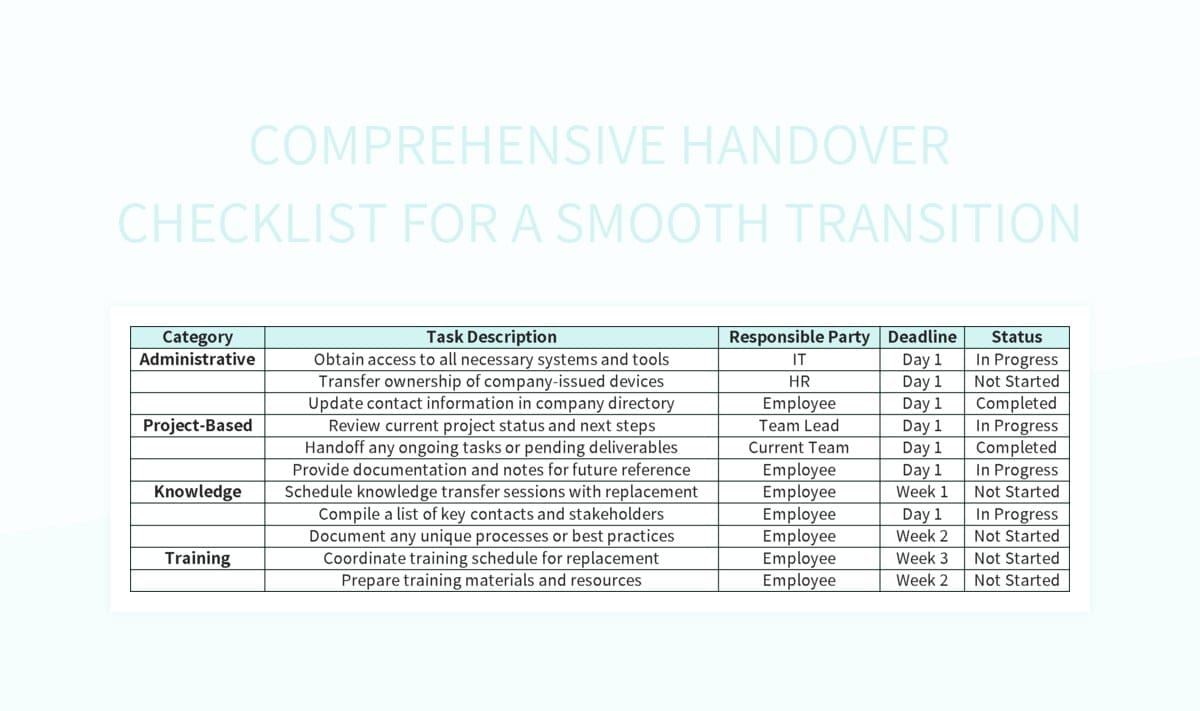 Country Escape The Ultimate Checklist For A Smooth Transition
May 24, 2025
Country Escape The Ultimate Checklist For A Smooth Transition
May 24, 2025 -
 Brest Urban Trail L Importance Des Benevoles Artistes Et Partenaires
May 24, 2025
Brest Urban Trail L Importance Des Benevoles Artistes Et Partenaires
May 24, 2025 -
 Are Thames Waters Executive Bonuses Acceptable A Critical Examination
May 24, 2025
Are Thames Waters Executive Bonuses Acceptable A Critical Examination
May 24, 2025 -
 Escape To The Country Financing Your Rural Property Purchase
May 24, 2025
Escape To The Country Financing Your Rural Property Purchase
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Jonathan Groff On Asexuality Instinct Magazine Interview
May 24, 2025
Jonathan Groff On Asexuality Instinct Magazine Interview
May 24, 2025 -
 Jonathan Groffs Past An Open Discussion Of Asexuality
May 24, 2025
Jonathan Groffs Past An Open Discussion Of Asexuality
May 24, 2025 -
 Broadway Buzz Jonathan Groffs Performance In Just In Time And His Connection To Bobby Darin
May 24, 2025
Broadway Buzz Jonathan Groffs Performance In Just In Time And His Connection To Bobby Darin
May 24, 2025 -
 Jonathan Groff Channels Bobby Darin A Deep Dive Into Just In Time
May 24, 2025
Jonathan Groff Channels Bobby Darin A Deep Dive Into Just In Time
May 24, 2025 -
 Etoile A Spring Awakening Reunion Brings Laughter With Gideon Glick And Jonathan Groff
May 24, 2025
Etoile A Spring Awakening Reunion Brings Laughter With Gideon Glick And Jonathan Groff
May 24, 2025
