Earth - Series 1: Inferno - A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
The Science of Volcanoes: Understanding Earth's Inner Fury
Plate Tectonics and Volcanic Activity
Volcanic activity is intrinsically linked to the movement of Earth's tectonic plates. Understanding plate tectonics is key to comprehending why volcanoes erupt where they do. The vast majority of volcanoes are found along plate boundaries, areas where tectonic plates collide, pull apart, or slide past each other.
- Convergent Boundaries: Where plates collide, one plate often slides beneath the other in a process called subduction. This subducting plate melts, forming magma that rises to the surface, creating volcanic arcs like the Ring of Fire encircling the Pacific Ocean. Keywords: subduction zones, volcanic arcs, magma chambers.
- Divergent Boundaries: At mid-ocean ridges, plates move apart, allowing magma to well up from the mantle, forming new crust and underwater volcanoes. Keywords: mid-ocean ridges, seafloor spreading.
- Transform Boundaries: While less directly related to volcanism, transform boundaries can create friction and stress that can indirectly influence volcanic activity in nearby areas. Keywords: transform faults, tectonic stress.
The process of magma formation and ascent is complex. As the mantle rock melts, it becomes less dense and rises buoyantly towards the surface. The magma may accumulate in magma chambers before eventually erupting. The composition of the magma, its gas content, and the surrounding rock formations all influence the style of eruption. Examples of volcanoes formed at different plate boundaries include the Andes Mountains (convergent), Iceland (divergent), and the San Andreas Fault (transform, indirectly influencing nearby volcanism).
Types of Volcanic Eruptions
Volcanic eruptions are not all created equal. They vary dramatically in their style and intensity, determined by factors such as the viscosity of the magma (its resistance to flow), its gas content, and the surrounding geology.
- Effusive Eruptions: These eruptions involve the relatively gentle outpouring of lava flows. The lava is typically basaltic, low in silica, and flows relatively easily. Keywords: lava flows, shield volcanoes, basalt.
- Explosive Eruptions: These eruptions are far more violent, characterized by the explosive ejection of pyroclastic materials—fragments of rock, ash, and volcanic gases. This is often associated with more viscous, silica-rich magma. Keywords: pyroclastic flows, volcanic ash, eruption column, Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI).
- Pyroclastic flows are incredibly dangerous, representing fast-moving currents of hot gas and volcanic debris that can incinerate everything in their path.
- Volcanic ash clouds can disrupt air travel and cause respiratory problems. The Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) is a logarithmic scale used to measure the intensity of volcanic eruptions.
Famous examples include the effusive eruptions of Kilauea in Hawaii and the explosive eruptions of Mount Vesuvius and Mount St. Helens.
The Impact of Volcanic Activity on Earth's History and Environment
Shaping the Landscape
Volcanic activity has profoundly shaped Earth's geography over millions of years. Volcanoes have built islands, mountain ranges, and vast plateaus. Keywords: volcanic landforms, island arcs, shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes, caldera.
- Island Arcs: Chains of volcanic islands, like Japan and the Philippines, are formed at convergent plate boundaries.
- Shield Volcanoes: These broad, gently sloping volcanoes are built up by successive lava flows, like those found in Hawaii.
- Stratovolcanoes: These steep-sided volcanoes are formed by alternating layers of lava and pyroclastic materials, like Mount Fuji.
- Calderas: Large, basin-shaped depressions formed by the collapse of a volcano after a massive eruption.
Volcanoes also play a crucial role in soil fertility. Volcanic ash and rock weather down to create rich, nutrient-rich soil, supporting vibrant ecosystems. The weathering of volcanic rocks also influences the chemical composition of rivers and oceans.
Volcanoes and Mass Extinctions
Supervolcanoes, capable of producing eruptions many orders of magnitude larger than typical volcanoes, have played a significant role in shaping life on Earth, potentially triggering mass extinction events. Keywords: supervolcanoes, Yellowstone Caldera, Deccan Traps, climate disruption.
- The environmental consequences of super-eruptions are catastrophic. Massive amounts of ash and gases are ejected into the atmosphere, blocking sunlight, causing widespread cooling, and disrupting the global climate.
- The Deccan Traps in India, a massive volcanic province, is thought to have contributed to the extinction event that wiped out the dinosaurs.
- The Yellowstone Caldera is a supervolcano that poses a significant albeit low probability threat in the future.
The link between volcanic eruptions and climate change is complex. While large eruptions can cause short-term cooling, the long-term effects are more nuanced and depend on the type and amount of gases released.
Living with Volcanoes: Human Stories from the Ring of Fire
Communities at Risk
Millions of people live near active volcanoes, facing the constant threat of eruptions. Keywords: risk assessment, volcanic hazard maps, early warning systems, disaster preparedness.
- Communities living in volcanic regions face a range of challenges, including the risk of lava flows, pyroclastic flows, lahars (volcanic mudflows), and ashfall.
- Volcanic monitoring and prediction are crucial for mitigating risks. Scientists use a variety of techniques, including seismic monitoring, gas measurements, and ground deformation measurements, to track volcanic activity and issue warnings.
- Disaster preparedness measures include evacuation plans, community education programs, and the construction of protective structures.
Examples of communities living in volcanic regions include those around Mount Vesuvius in Italy, Mount Merapi in Indonesia, and Mount Fuji in Japan.
Volcanic Tourism and Geothermal Energy
Volcanic regions also offer significant opportunities for sustainable development. Keywords: geothermal energy, sustainable energy, volcanic tourism, ecotourism.
- Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from Earth's interior to generate electricity and provide heating. This is a clean and renewable energy source.
- Volcanic tourism can be a significant source of income for local communities, but it's crucial to practice responsible tourism to minimize environmental impact.
- Ecotourism focuses on minimizing the environmental and social impact of tourism, ensuring that it benefits local communities and protects the environment.
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide to "Earth - Series 1: Inferno" has explored the science, history, and human impact of volcanic activity. From the fiery spectacle of eruptions to the geological forces that shape our planet, we've journeyed into the heart of Earth's inner furnace. Understanding the power and potential dangers of volcanoes is crucial for mitigating risks and harnessing their potential benefits. Continue your exploration of the Earth’s dynamic forces by learning more about Earth Series 1 Inferno and related documentaries. Further your knowledge and appreciation for our planet’s incredible power with continued research on the subject of Earth Series 1 Inferno.

Featured Posts
-
 Schools In Manila Closed Because Of Intense Heat Bangkok Post
May 13, 2025
Schools In Manila Closed Because Of Intense Heat Bangkok Post
May 13, 2025 -
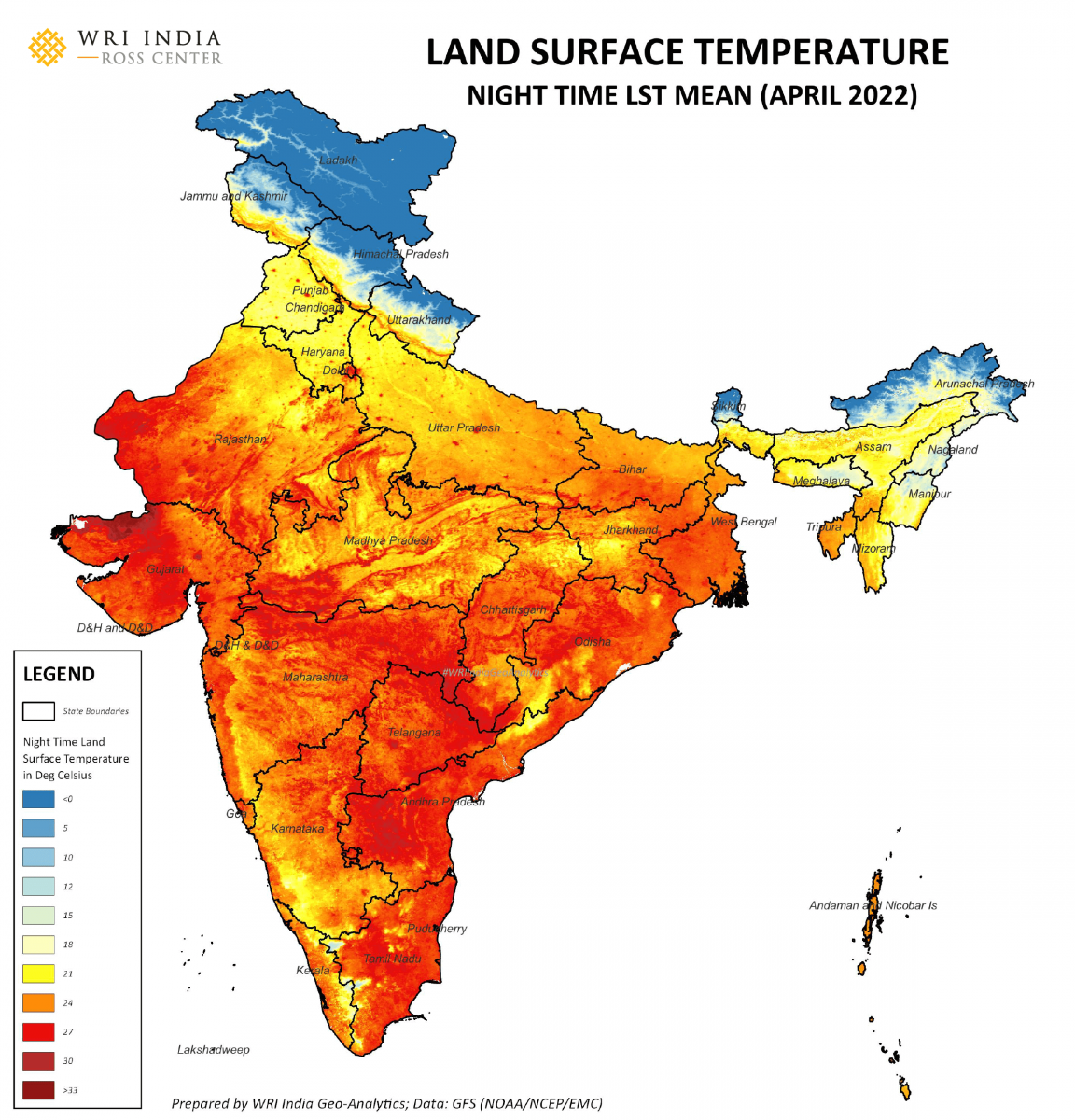 India Heatwave Central Government Issues Alert States On High Alert
May 13, 2025
India Heatwave Central Government Issues Alert States On High Alert
May 13, 2025 -
 Culinary Diplomacy India And Myanmars Food Festival
May 13, 2025
Culinary Diplomacy India And Myanmars Food Festival
May 13, 2025 -
 Boj Proti Diskriminacii Reagovanie Na Statistiku 74 Pri Prenajme Nehnutelnosti Romov
May 13, 2025
Boj Proti Diskriminacii Reagovanie Na Statistiku 74 Pri Prenajme Nehnutelnosti Romov
May 13, 2025 -
 Tindakan Hukum Terbaru Untuk Mengatasi Judi Online Dan Penipuan Di Myanmar
May 13, 2025
Tindakan Hukum Terbaru Untuk Mengatasi Judi Online Dan Penipuan Di Myanmar
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Gibraltar Et L Ue Progres Significatifs Vers Un Accord Post Brexit
May 13, 2025
Gibraltar Et L Ue Progres Significatifs Vers Un Accord Post Brexit
May 13, 2025 -
 Gibraltar Sovereignty Crisis Analysis Of Keir Starmers Unwavering Approach
May 13, 2025
Gibraltar Sovereignty Crisis Analysis Of Keir Starmers Unwavering Approach
May 13, 2025 -
 Accord Post Brexit Gibraltar Les Dernieres Nouvelles
May 13, 2025
Accord Post Brexit Gibraltar Les Dernieres Nouvelles
May 13, 2025 -
 Keir Starmers Firm Gibraltar Position A Deeper Dive Into The Sovereignty Dispute
May 13, 2025
Keir Starmers Firm Gibraltar Position A Deeper Dive Into The Sovereignty Dispute
May 13, 2025 -
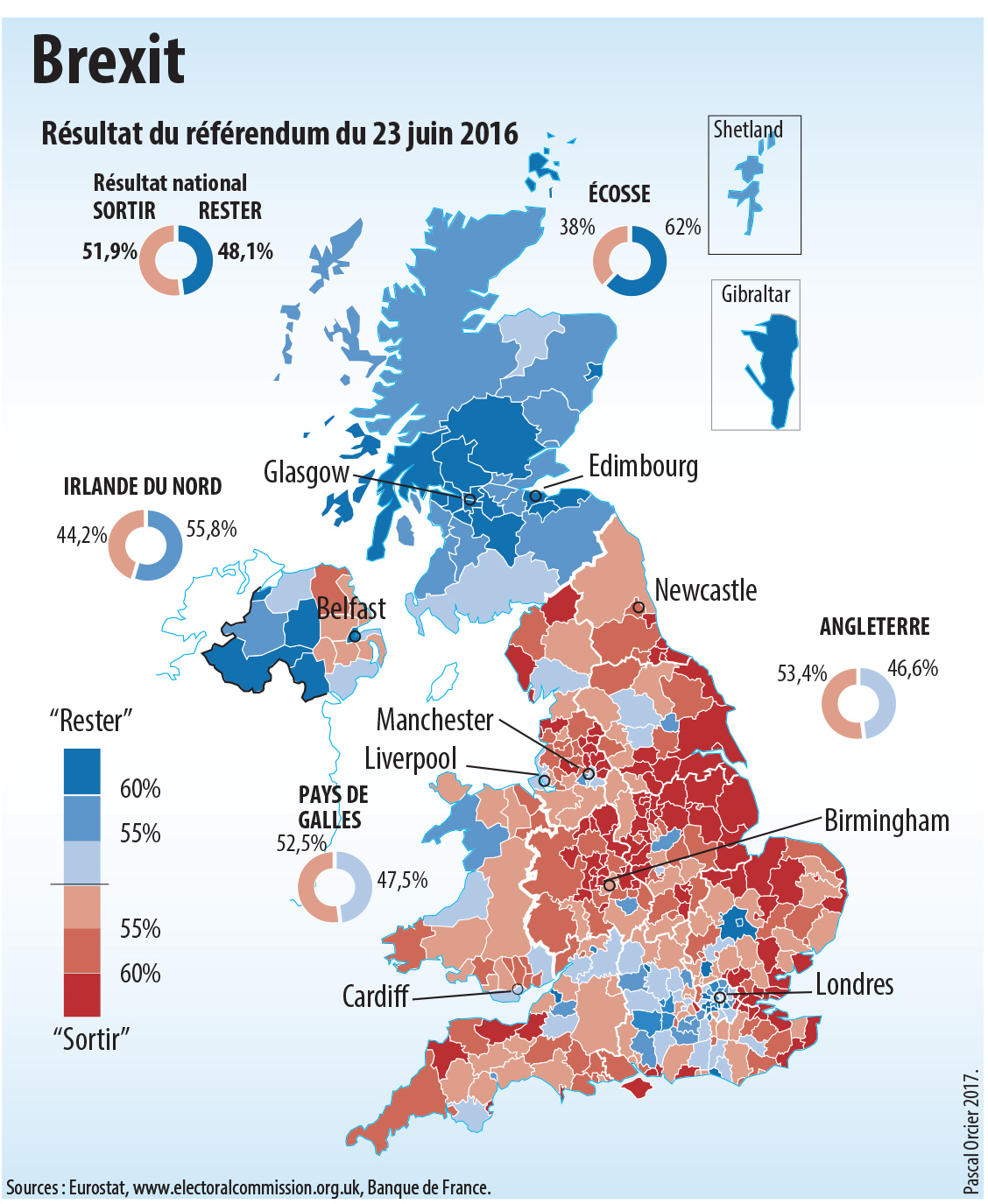 Accord Post Brexit A Gibraltar Perspectives Et Defis
May 13, 2025
Accord Post Brexit A Gibraltar Perspectives Et Defis
May 13, 2025
