End Of A School Desegregation Order: The Justice Department's Decision And Its Ripple Effects

Table of Contents
The Justice Department's Rationale for Ending the School Desegregation Order
The Justice Department's decision to terminate the school desegregation order in the United States v. School District of Indianapolis case, a decades-long order impacting several Indiana schools, has been met with mixed reactions. This specific order, implemented in 1971, mandated busing and other measures to address racial imbalances within the district. The Department's stated rationale rests on several pillars. They argue that the initial goals of the order – achieving racial balance and eliminating discriminatory practices – have largely been met. Further, they cite changed circumstances within the school district, including improved infrastructure, desegregated student populations in many schools, and the implementation of successful diversity initiatives.
- Legal Precedents: The decision references Parents Involved in Community Schools v. Seattle School Dist. No. 1, a Supreme Court case that limited the use of race as a primary factor in assigning students to schools.
- Data and Statistics: The Justice Department presented data indicating a significant reduction in racial disparities within the Indianapolis school system, including decreased achievement gaps in certain areas and more balanced school demographics in many schools. However, critics argue that this data does not tell the full story and ignores persistent inequalities.
- Political Considerations: The timing of the decision and the administration's broader stance on affirmative action have fueled accusations of political motivations influencing the legal arguments.
Potential Negative Consequences of Ending the School Desegregation Order
Ending the school desegregation order carries significant risks. The most pressing concern is the potential for a resurgence of school segregation. Without the mandated measures, schools may revert to reflecting the racial demographics of their surrounding neighborhoods, potentially leading to highly segregated learning environments. This re-segregation could severely impact minority student achievement.
- Re-segregation Scenarios: In the affected districts, we could see a return to predominantly minority schools with fewer resources and opportunities compared to predominantly white schools. This exacerbates the existing achievement gap.
- Impact on Academic Outcomes: Extensive research demonstrates a strong correlation between school segregation and lower academic achievement for minority students. The end of this order risks widening this gap, potentially impacting future opportunities for these students.
- Legal Challenges: The decision is likely to face legal challenges from civil rights organizations and concerned parents who argue that the order's termination is premature and undermines the ongoing fight for educational equality.
Impact on Specific Student Demographics
The impact will disproportionately affect African American and Hispanic students. Data indicates these groups already face significant achievement gaps compared to their white peers. The termination of this order risks widening these gaps significantly, perpetuating cycles of inequality and limiting opportunities for upward mobility. Specific data on the expected increase in achievement gaps needs to be closely monitored and assessed in the post-order period.
Positive Aspects (if any) and Counterarguments
Proponents of ending the order argue that it represents a step towards greater local control over education, enabling communities to develop their own solutions to address diversity and integration. Some believe that community-based initiatives can be more effective than mandated busing and other top-down approaches.
- Local Control and Community Solutions: Supporters highlight the potential for local school boards and communities to implement innovative programs and strategies tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
- Alternative Strategies: Instead of mandated busing, alternatives such as magnet schools, open enrollment policies, and targeted investments in underserved communities could be explored to achieve integration goals.
- Different Viewpoints: However, critics argue that relying solely on local initiatives risks neglecting the systemic inequalities that continue to drive segregation. They emphasize the need for continued federal oversight to ensure equal access to quality education for all students.
Long-Term Implications and Future of School Desegregation Efforts
The decision’s long-term implications are far-reaching. It sets a precedent for other desegregation cases and raises questions about the federal government’s continued role in ensuring equal educational opportunities. The decision also challenges the ongoing debate surrounding the effectiveness of various desegregation strategies.
- Future Desegregation Cases: This decision could embolden challenges to other remaining desegregation orders, potentially leading to their termination.
- Federal Role in Education: The decision raises concerns about the federal government's commitment to addressing systemic racism in education.
- Legislative and Policy Responses: The decision could spur legislative efforts to either strengthen or weaken federal oversight of school desegregation.
Conclusion:
The Justice Department's decision to end this school desegregation order represents a significant turning point in the ongoing struggle for racial equality in American education. While the Department points to progress in achieving integration goals and changed circumstances, the potential for re-segregation and the exacerbation of achievement gaps pose significant challenges. The decision highlights the complexities of achieving truly equitable access to quality education for all students, regardless of race or background. The ending of this school desegregation order necessitates ongoing vigilance and advocacy. Continued discussion and engagement regarding school desegregation orders are crucial to prevent a return to segregated schooling and promote true educational equality for all children. We must remain committed to fighting for equal opportunities and ensuring that all students, regardless of race or background, have access to a quality education. Let's continue the conversation on the implications of this decision and work together toward a more just and equitable future for our schools.

Featured Posts
-
 Play Station Beta Program Requirements And How To Apply
May 02, 2025
Play Station Beta Program Requirements And How To Apply
May 02, 2025 -
 Is Fortnite Experiencing Server Issues Update 34 30 Downtime And New Content
May 02, 2025
Is Fortnite Experiencing Server Issues Update 34 30 Downtime And New Content
May 02, 2025 -
 2024 Open Ai Developer Event New Tools For Voice Assistant Development
May 02, 2025
2024 Open Ai Developer Event New Tools For Voice Assistant Development
May 02, 2025 -
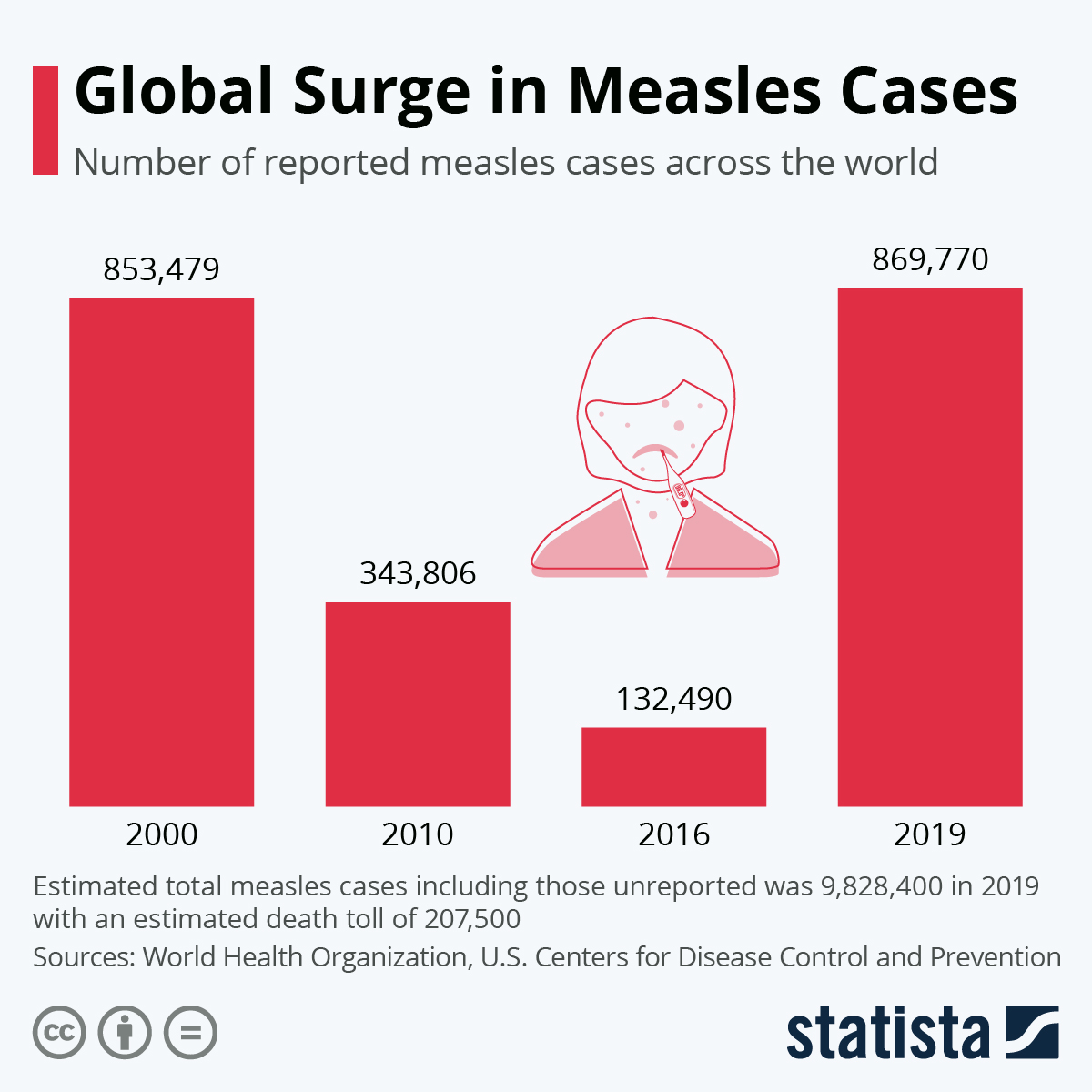 Us Vaccine Watchdog Monitoring The Measles Surge
May 02, 2025
Us Vaccine Watchdog Monitoring The Measles Surge
May 02, 2025 -
 Kashmirs Cat Owners Respond To Disturbing Online Content
May 02, 2025
Kashmirs Cat Owners Respond To Disturbing Online Content
May 02, 2025
