EU Targets Russian Gas: Spot Market Phaseout Under Discussion
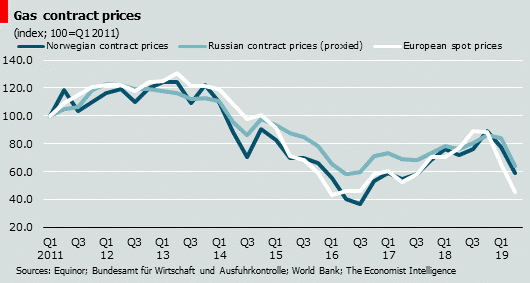
Table of Contents
The Urgency of Reducing Russian Gas Reliance
The continued reliance on Russian gas presents significant and multifaceted risks to the EU.
Geopolitical Risks
The geopolitical risks associated with continued reliance on Russian gas are substantial. Russia has repeatedly demonstrated its willingness to weaponize energy supplies, using gas exports as a tool of political leverage.
- Examples of supply disruptions: Past instances, such as the 2006 and 2009 gas crises, demonstrated the severe economic consequences of disruptions to Russian gas supplies, leading to energy shortages and price spikes across Europe.
- Price volatility: Russia's control over gas supplies allows it to manipulate prices, creating instability in the European energy market and impacting businesses and consumers alike.
- Geopolitical leverage by Russia: The EU's dependence on Russian gas gives Russia significant leverage in geopolitical negotiations, undermining the EU's strategic autonomy. Keywords: energy security, geopolitical risks, Russian gas supply, price volatility.
Environmental Concerns
Beyond the geopolitical considerations, continued reliance on natural gas presents significant environmental challenges, directly conflicting with the EU's ambitious climate goals.
- Greenhouse gas emissions from natural gas: Natural gas, while often presented as a "cleaner" fossil fuel, still contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, hindering the EU's efforts to achieve carbon neutrality.
- EU climate targets: The EU's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to a low-carbon economy necessitates a rapid decrease in its reliance on fossil fuels, including natural gas.
- Transition to renewable energy: A phaseout of Russian gas provides a crucial impetus for accelerating the transition to renewable energy sources, fostering a more sustainable and resilient energy system. Keywords: climate change, greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy, EU climate targets.
Challenges of a Spot Market Phaseout
While the benefits of reducing Russian gas reliance are clear, transitioning away from Russian spot market purchases presents several significant challenges.
Supply Gaps
Replacing Russian gas supplies will require a multifaceted approach involving diversification of sources and substantial infrastructure investment.
- LNG imports: Increasing imports of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is crucial, but requires expansion of LNG terminal capacity and efficient transportation infrastructure.
- Pipeline diversification: Strengthening existing pipeline connections with alternative gas suppliers and exploring new pipeline projects are necessary to ensure a reliable and diverse supply.
- Renewable energy expansion: A significant expansion of renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydro, is essential to fill the gap left by reduced gas imports.
- Energy storage solutions: Investing in energy storage technologies, such as pumped hydro storage and battery storage, is crucial to manage the intermittency of renewable energy sources. Keywords: LNG imports, pipeline infrastructure, renewable energy sources, energy storage, gas supply diversification.
Economic Impacts
The phaseout of Russian gas will undoubtedly have economic consequences, potentially leading to price increases and impacting various industries.
- Potential price increases: The transition may lead to short-term increases in energy prices, particularly for energy-intensive industries.
- Impact on energy-intensive industries: Sectors heavily reliant on natural gas, such as manufacturing and chemicals, may face significant challenges during the transition.
- Government support measures: Governments will need to implement targeted support measures to mitigate the economic impact on vulnerable businesses and households.
- Consumer protection: Protecting consumers from excessive price increases and ensuring energy affordability will be crucial. Keywords: economic impact, energy prices, inflation, government subsidies, energy transition.
Potential Solutions and Alternatives
Overcoming the challenges requires a comprehensive strategy focused on diversification and a rapid acceleration of the energy transition.
Diversification of Gas Sources
The EU must actively explore alternative gas suppliers and develop new infrastructure to secure diverse and reliable gas supplies.
- Specific examples of alternative gas suppliers: Norway, Algeria, and other reliable suppliers can help fill the gap left by reduced Russian imports.
- LNG terminal expansion: Significant investments in LNG import terminals are crucial to handle the increased demand for LNG.
- Pipeline projects: New pipeline projects connecting the EU to alternative gas suppliers will enhance energy security and reduce dependence on a single supplier. Keywords: LNG, pipeline projects, gas diversification, alternative gas suppliers, energy infrastructure.
Accelerated Renewable Energy Transition
The most sustainable long-term solution is to significantly accelerate the transition to renewable energy sources.
- Investment in renewable energy infrastructure: Massive investments in renewable energy infrastructure, including wind farms, solar power plants, and hydropower projects, are necessary.
- Policy incentives for renewables: Supportive policy measures, such as subsidies and tax breaks, can stimulate private investment in renewable energy.
- Grid modernization: Upgrading the electricity grid to handle the increased integration of renewable energy sources is critical for ensuring grid stability and reliability. Keywords: renewable energy, solar energy, wind energy, energy transition, green energy.
Conclusion
The EU's consideration of a phaseout of Russian gas from the spot market is a momentous decision, representing a crucial step toward achieving genuine energy independence and substantially enhancing its energy security. While the transition presents undeniable challenges, including potential short-term economic impacts and the need for massive investments in alternative energy sources and infrastructure, the urgency of decoupling from a politically volatile supplier outweighs the difficulties. A swift and well-coordinated effort to diversify gas sources, dramatically accelerate the renewable energy transition, and implement effective mitigation strategies is paramount to a successful outcome. This transition demands a comprehensive, multi-pronged approach, and the long-term benefits – enhanced energy security, reduced climate impact, and increased strategic autonomy – make it a vital undertaking for the EU's future.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the EU's progress in phasing out Russian gas from the spot market. Follow updates on EU energy policy and actively support initiatives promoting energy independence and sustainable energy solutions. Keywords: EU Russian gas, spot market phaseout, energy independence, energy security, renewable energy transition.

Featured Posts
-
 The Zuckerberg Trump Dynamic Implications For The Tech Industry
Apr 24, 2025
The Zuckerberg Trump Dynamic Implications For The Tech Industry
Apr 24, 2025 -
 The Countrys Best New Business Locations A Detailed Overview
Apr 24, 2025
The Countrys Best New Business Locations A Detailed Overview
Apr 24, 2025 -
 John Travoltas Miami Steakhouse Adventure A Pulp Fiction Inspired Meal
Apr 24, 2025
John Travoltas Miami Steakhouse Adventure A Pulp Fiction Inspired Meal
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Five Point Plan From Canadian Auto Dealers To Counter Us Trade Threats
Apr 24, 2025
Five Point Plan From Canadian Auto Dealers To Counter Us Trade Threats
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Governor Newsoms Urgent Call For Action On Californias High Gas Prices
Apr 24, 2025
Governor Newsoms Urgent Call For Action On Californias High Gas Prices
Apr 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Bayern Legend Thomas Mueller Bids Emotional Farewell After 25 Years
May 12, 2025
Bayern Legend Thomas Mueller Bids Emotional Farewell After 25 Years
May 12, 2025 -
 The Thomas Mueller Situation Bayern Munichs Response And Fan Sentiment
May 12, 2025
The Thomas Mueller Situation Bayern Munichs Response And Fan Sentiment
May 12, 2025 -
 Bayern Exit Mueller Weighs Up His Future League Options
May 12, 2025
Bayern Exit Mueller Weighs Up His Future League Options
May 12, 2025 -
 Analyse Du Quart De Finale C1 Bayern Munich Vs Inter Milan Le Role Decisif De Mueller
May 12, 2025
Analyse Du Quart De Finale C1 Bayern Munich Vs Inter Milan Le Role Decisif De Mueller
May 12, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Fallout Public Reaction To Thomas Muellers Possible Bayern Exit
May 12, 2025
Analyzing The Fallout Public Reaction To Thomas Muellers Possible Bayern Exit
May 12, 2025
