Examining The Financial Risks Of Public Sector Pension Plans
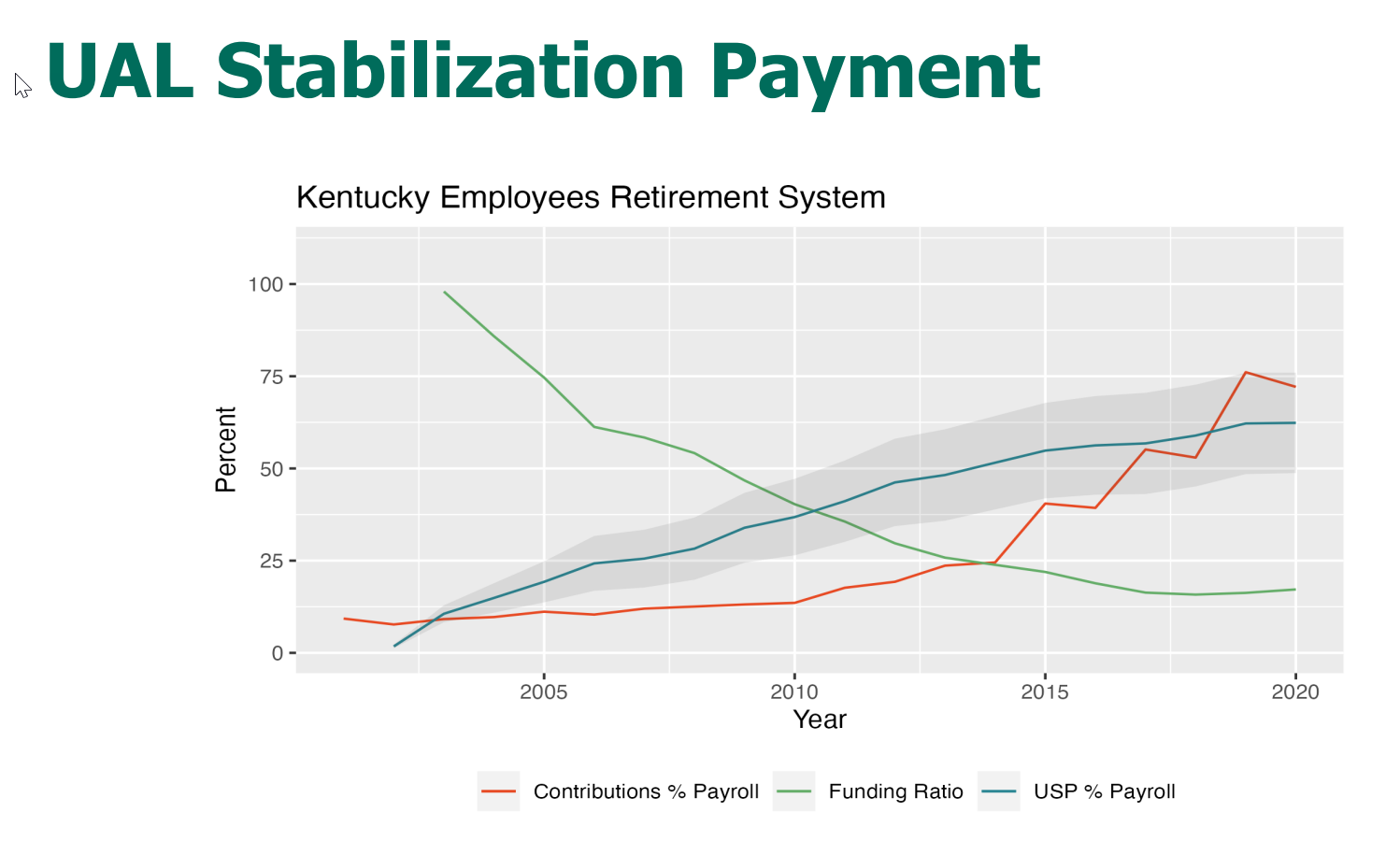
Table of Contents
Understanding the Funding Mechanisms of Public Sector Pension Plans
Public sector pension plans utilize various funding mechanisms, each with its own set of inherent risks. A key distinction lies between defined benefit (DB) and defined contribution (DC) plans.
Defined Benefit vs. Defined Contribution Plans
- Defined Benefit (DB) Plans: These plans promise a specific monthly payment upon retirement, calculated based on factors like salary and years of service. Public sector plans often utilize this model.
- Advantages: Provides guaranteed income in retirement.
- Disadvantages: High risk for sponsoring entities due to potential underfunding and vulnerability to market fluctuations. Long-term financial projections are significantly impacted by changing demographics, investment returns, and longevity.
- Defined Contribution (DC) Plans: These plans require contributions from both the employer and employee, with the final retirement benefit depending on the total accumulated funds and investment performance.
- Advantages: Lower risk for the sponsoring entity; the risk is shifted to the employee.
- Disadvantages: Retirement income is not guaranteed and depends on market performance and individual investment choices.
Actuarial Valuations and Their Importance
Actuarial valuations are crucial for assessing the financial health of pension plans. These valuations project future liabilities based on various assumptions, including:
- Discount rates: The rate used to discount future benefit payments to their present value.
- Salary growth: Projected increases in employee salaries.
- Mortality rates: The expected lifespan of retirees.
Inaccurate assumptions can significantly impact the valuation's accuracy, potentially underestimating future liabilities and creating a false sense of security. Regular, independent actuarial valuations are essential for identifying potential shortfalls and informing proactive management strategies. Ideally, valuations should be performed annually to capture changing economic conditions and demographic trends affecting public sector pension plans.
Investment Strategies and Risk Management
Public sector pension plans employ various investment strategies to generate returns needed to cover future liabilities. However, these strategies are not without risk:
- Market volatility: Fluctuations in the stock market can significantly impact investment returns.
- Interest rate risk: Changes in interest rates can affect the value of fixed-income investments.
- Inflation risk: Inflation can erode the purchasing power of future benefit payments.
Diversification is a key risk management technique, spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce overall portfolio volatility. However, even well-diversified portfolios are susceptible to economic downturns. Careful monitoring of investment performance and regular adjustments to the investment strategy are necessary to adapt to changing market conditions and maintain the long-term financial health of pension plans.
Key Financial Risks Facing Public Sector Pension Plans
Several key financial risks threaten the solvency of public sector pension plans:
Unfunded Liabilities and Their Implications
Unfunded liabilities represent the difference between a pension plan's projected liabilities and its assets. This shortfall creates a significant financial burden on taxpayers and public sector entities. Causes of unfunded liabilities include:
- Demographic shifts: Increasing life expectancy and declining birth rates contribute to higher benefit payments.
- Underfunding: Insufficient contributions from employers and employees.
- Poor investment returns: Lower-than-expected investment returns exacerbate existing funding shortfalls.
Addressing unfunded liabilities requires a multi-pronged approach, potentially involving increased contribution rates, benefit reductions, or government bailouts. Each option has significant political and economic implications.
Longevity Risk and Increasing Life Expectancy
Increasing life expectancy is a major driver of rising pension liabilities. People are living longer, resulting in longer periods of benefit payments. Strategies for mitigating longevity risk include:
- Adjusting benefit formulas: Modifying benefit calculations to reflect increased life expectancy.
- Investing in longevity risk hedging products: Using financial instruments to transfer longevity risk to other parties.
Economic Downturns and Their Effect on Pension Funding
Economic recessions can severely impact pension funding. Decreased investment returns during downturns can widen the gap between assets and liabilities, potentially necessitating government intervention to prevent plan insolvency. This places a significant strain on public finances and can lead to increased taxation or cuts in other public services.
Strategies for Mitigating Pension Risk
Several strategies can help mitigate the financial risks associated with public sector pension plans:
Pension Reform and Policy Changes
Pension reform is crucial for addressing the long-term sustainability of public sector pension plans. Options include:
- Increasing contribution rates: Higher contributions from employees and/or employers.
- Reducing benefits: Lowering the level of benefits paid to retirees.
- Shifting to defined contribution plans: Transferring some or all of the investment risk to employees.
Pension reform often faces significant political and social challenges, as it involves difficult trade-offs between the interests of current and future retirees, taxpayers, and government budgets.
Improved Investment Management and Risk Control
Improved investment management practices can enhance the long-term financial health of pension plans. Strategies include:
- Adopting more conservative investment strategies: Reducing exposure to higher-risk investments.
- Enhancing risk management frameworks: Implementing robust processes for identifying, assessing, and managing risks.
- Diversifying investments: Spreading investments across a wider range of asset classes.
Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are vital for ensuring the responsible management of public sector pension plans. This includes:
- Regular reporting of plan finances: Providing regular updates on the financial health of the plan.
- Independent audits: Conducting regular audits to verify the accuracy of financial statements.
- Public access to information: Making key plan information readily available to the public.
Conclusion
The financial risks associated with public sector pension plans are significant and multifaceted. Underfunding, demographic shifts, economic downturns, and longevity risk all contribute to the challenge of ensuring the long-term solvency of these vital retirement systems. Proactive strategies, including pension reform, improved investment management, and enhanced transparency and accountability, are crucial for mitigating these risks and securing a stable financial future for both public sector employees and taxpayers. Understanding the financial risks of public sector pension plans is crucial for securing a stable financial future. Further research into public pension funding analysis, pension risk management strategies, and public sector pension reform initiatives is highly encouraged.

Featured Posts
-
 Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets The Official Buying Guide
Apr 29, 2025
Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets The Official Buying Guide
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Trump To Pardon Pete Rose After His Death Fact Or Fiction
Apr 29, 2025
Trump To Pardon Pete Rose After His Death Fact Or Fiction
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Porsche 911 W Polsce 1 33 Mln Zl Cena Hitu Sprzedazy
Apr 29, 2025
Porsche 911 W Polsce 1 33 Mln Zl Cena Hitu Sprzedazy
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Egyedi Porsche F1 Motorral Felszerelt Koezuti Szuperauto
Apr 29, 2025
Egyedi Porsche F1 Motorral Felszerelt Koezuti Szuperauto
Apr 29, 2025 -
 First Look Adidas Anthony Edwards 2 Basketball Shoes
Apr 29, 2025
First Look Adidas Anthony Edwards 2 Basketball Shoes
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
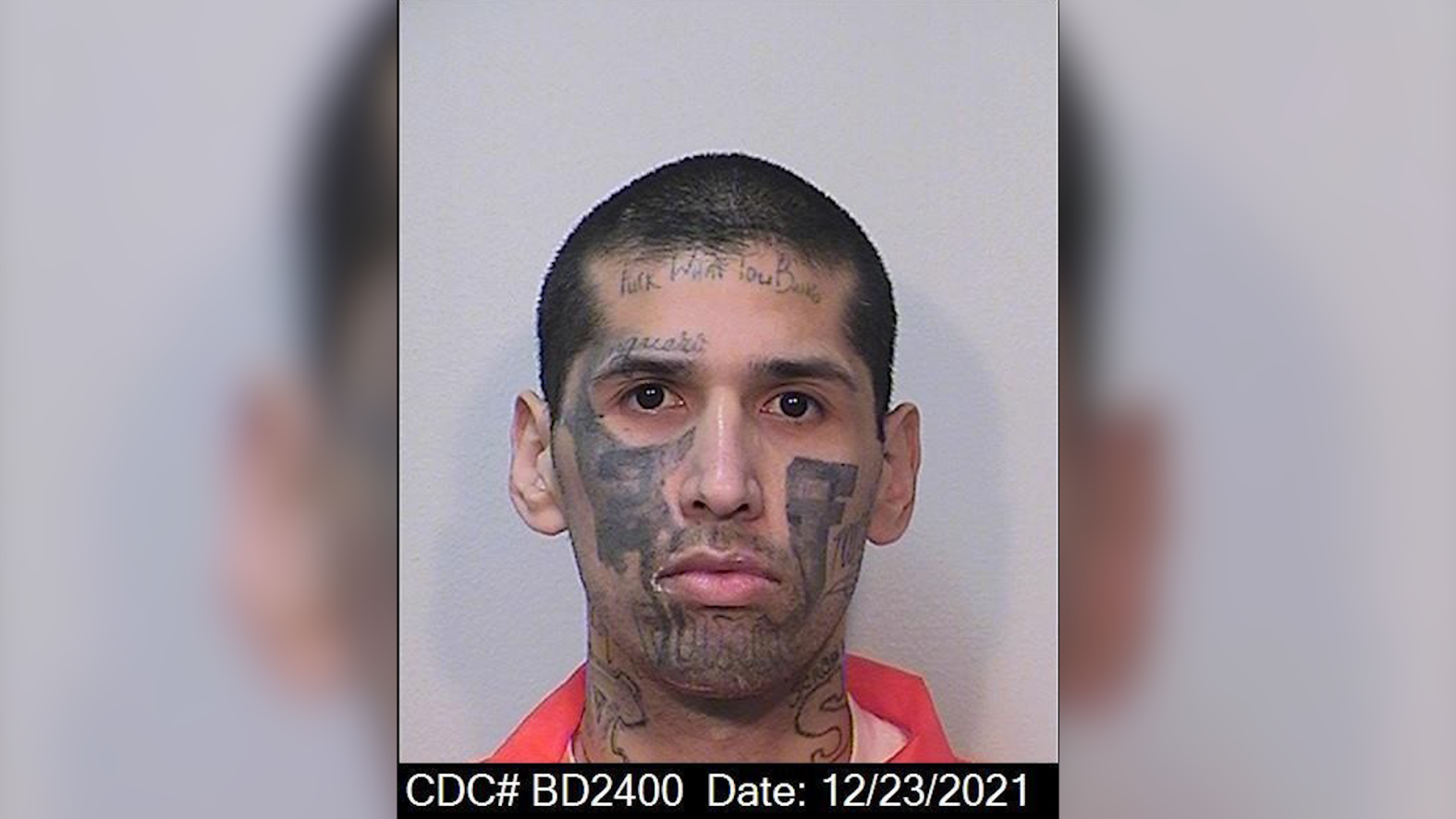 Inmates Death In San Diego County Jail Prompts Lawsuit By Family Over Alleged Torture And Murder
Apr 30, 2025
Inmates Death In San Diego County Jail Prompts Lawsuit By Family Over Alleged Torture And Murder
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Finding The Perfect Summer Slides 2025s Top Choices
Apr 30, 2025
Finding The Perfect Summer Slides 2025s Top Choices
Apr 30, 2025 -
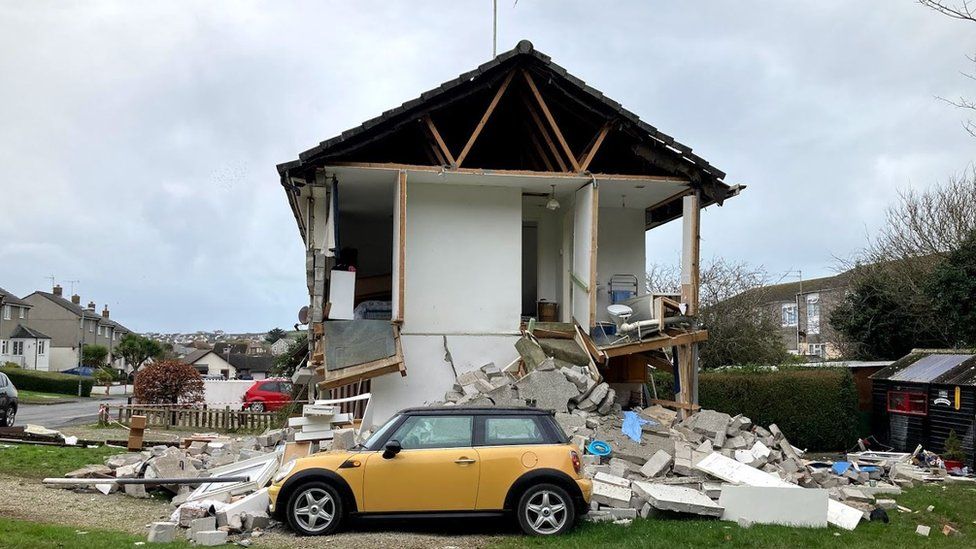 Gas Explosion In Yate Bristol Three People Injured
Apr 30, 2025
Gas Explosion In Yate Bristol Three People Injured
Apr 30, 2025 -
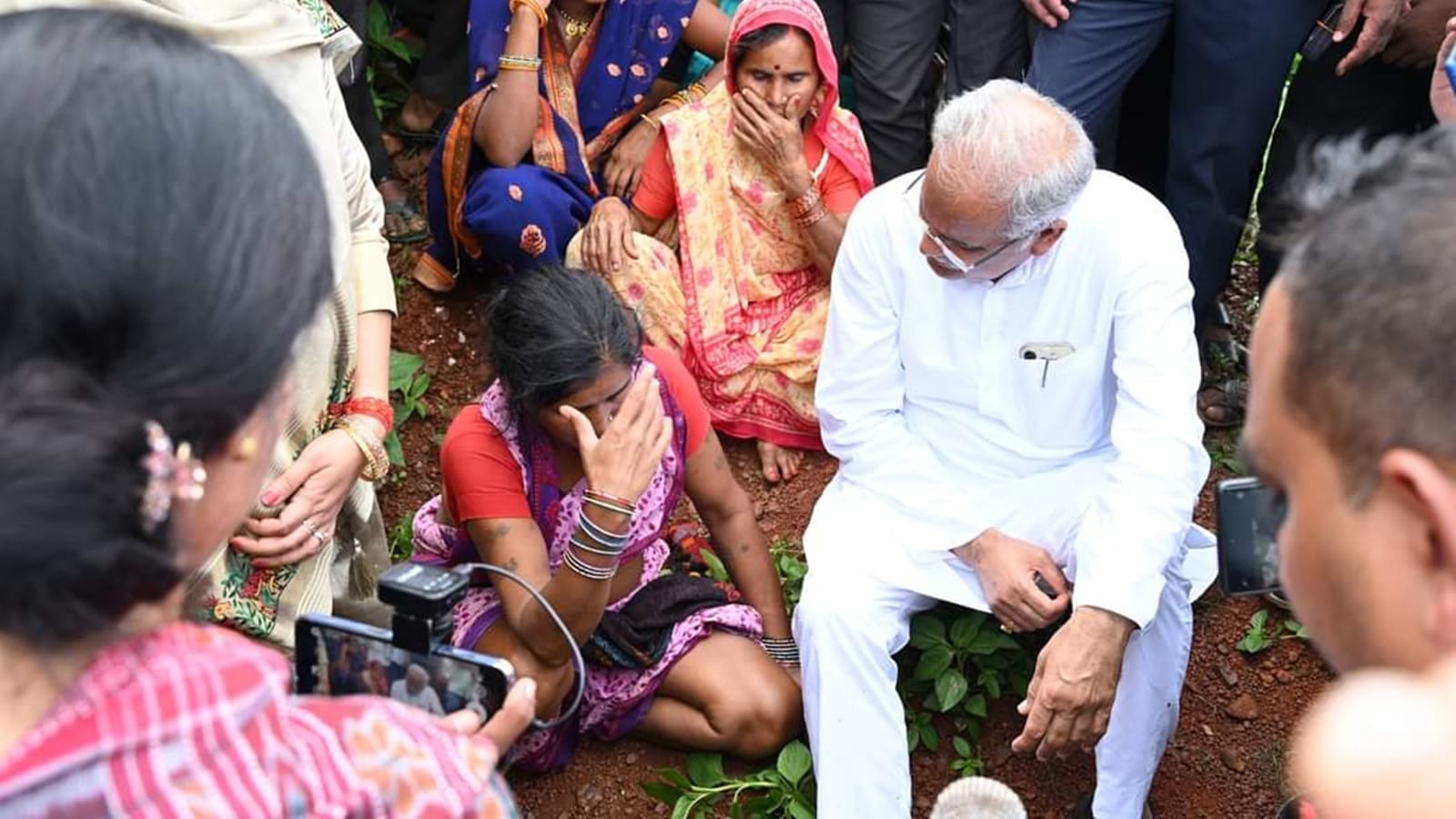 San Diego County Jail Lawsuit Family Alleges Torture And Murder Of Inmate By Cellmate
Apr 30, 2025
San Diego County Jail Lawsuit Family Alleges Torture And Murder Of Inmate By Cellmate
Apr 30, 2025 -
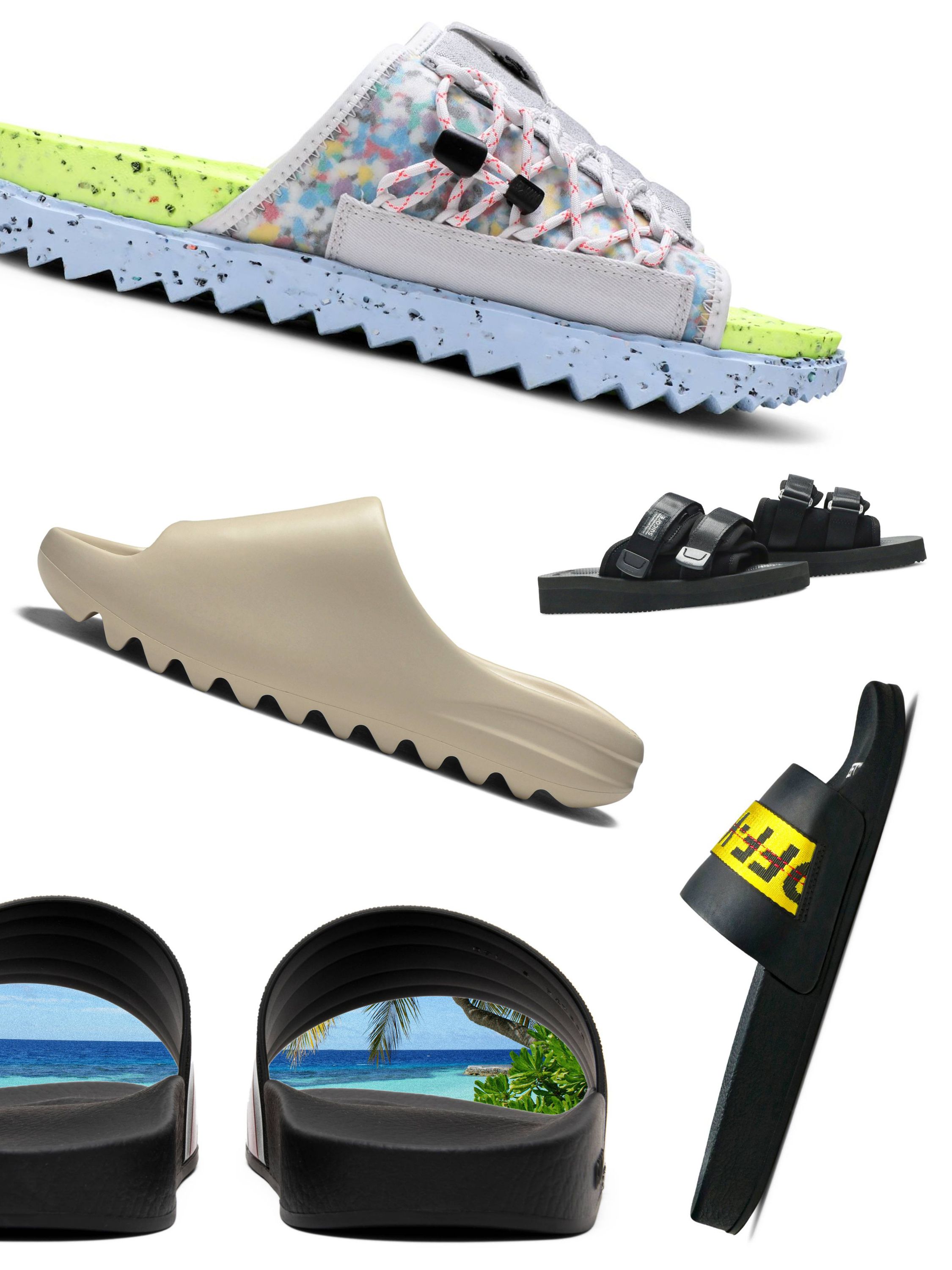 Best Summer Slides 2025 Features Prices And Comparisons
Apr 30, 2025
Best Summer Slides 2025 Features Prices And Comparisons
Apr 30, 2025
