Federal Reserve Goals At Risk Amidst Rising Tariffs: Powell's Assessment
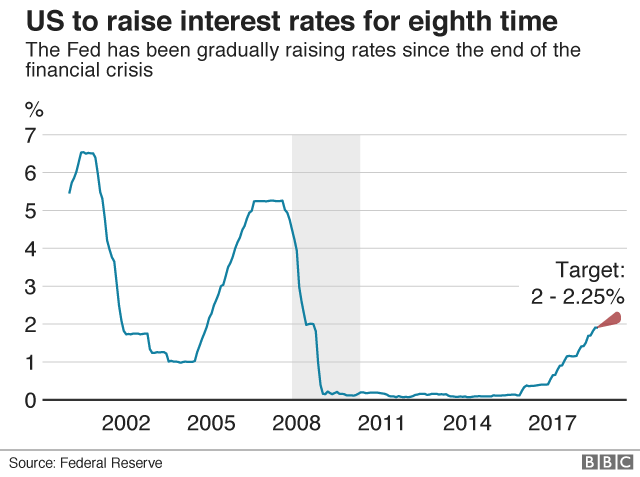
Table of Contents
Inflationary Pressures from Tariffs
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, exert significant upward pressure on prices, directly challenging the Federal Reserve's mandate of price stability.
Increased Import Costs
Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers and businesses. This inflationary effect ripples throughout the economy.
- Examples: Tariffs on steel and aluminum have increased the cost of construction materials and automobiles. Tariffs on consumer electronics have raised the prices of smartphones, televisions, and other popular goods.
- Data: The Consumer Price Index (CPI) has shown a noticeable increase in the prices of goods subject to tariffs, exceeding the Fed's target inflation rate in several periods.
- Explanation: These increased import costs contribute to inflation in two main ways. First, businesses pass on the increased costs to consumers through higher prices. Second, increased production costs can lead to a wage-price spiral, where businesses raise wages to compensate for inflation, leading to further price increases. This puts significant strain on the Federal Reserve's ability to maintain its target inflation rate, directly impacting its Federal Reserve goals.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Beyond direct cost increases, tariffs disrupt global supply chains, creating shortages and further exacerbating inflationary pressures.
- Examples: Tariffs have led to delays in the delivery of goods, forcing businesses to seek alternative (and often more expensive) suppliers. Some businesses have even been forced to halt production due to a lack of essential imported components.
- Impact: Supply chain bottlenecks lead to higher prices due to scarcity. Businesses face difficulties accurately predicting costs, adding to uncertainty and hindering long-term planning. This uncertainty significantly affects investment decisions and the overall economic outlook, threatening the Federal Reserve goals.
- Explanation: The ripple effect through the economy is significant, impacting various sectors and contributing to overall inflation. The resulting uncertainty makes it harder for businesses to plan effectively, leading to reduced investment and potentially impacting job creation, thus directly affecting the Federal Reserve goals.
Impact on Economic Growth and Employment
The inflationary pressures caused by tariffs have a direct impact on economic growth and employment, further complicating the Federal Reserve's objectives.
Reduced Consumer Spending
Higher prices due to tariffs reduce consumer purchasing power, potentially slowing economic growth. Consumers have less disposable income to spend on goods and services.
- Data: Data on consumer spending shows a decline in certain sectors following the imposition of tariffs. This reduction is particularly noticeable in sectors heavily reliant on imported goods.
- Impact: Reduced consumer spending leads to a decrease in demand, forcing businesses to reduce production and potentially leading to layoffs. This can trigger a negative feedback loop, further slowing economic growth. This represents a significant deviation from the Federal Reserve goals of robust and sustainable economic expansion.
- Explanation: This is the multiplier effect in action: decreased consumer spending leads to decreased business revenue, impacting employment, investment, and ultimately, GDP growth. The risk of a recessionary scenario becomes more pronounced under these conditions.
Job Losses and Uncertainty
Businesses may respond to higher costs by reducing investment, hiring, or even relocating operations, leading to job losses and increased economic uncertainty.
- Examples: Some businesses have announced layoffs or plant closures due to increased costs associated with tariffs. This negatively impacts employment numbers and worker confidence.
- Data: Unemployment claims may rise in sectors heavily affected by tariff-related price increases. Shifts in employment from manufacturing to services may also be observed.
- Explanation: The uncertainty created by tariffs discourages business investment, further slowing economic growth and jeopardizing job creation. This undermines the Federal Reserve's goal of full employment, a core pillar of its mandate.
The Federal Reserve's Response and Policy Challenges
The Federal Reserve faces a difficult balancing act in responding to the economic challenges posed by rising tariffs.
Balancing Act
The Fed must manage inflation without triggering a recession. This requires a delicate approach to monetary policy.
- Possible Responses: The Fed might raise interest rates to curb inflation, but this could also slow economic growth and increase unemployment. Quantitative easing might be less effective given the supply-side nature of tariff-induced inflation.
- Limitations: Monetary policy tools are not always effective in addressing supply-side shocks like tariffs. The effectiveness of monetary policy in this instance is constrained by the nature of the problem. This limits the Federal Reserve's ability to achieve its stated goals.
- Explanation: The Fed faces a trade-off between controlling inflation and supporting economic growth. Finding the optimal policy response is challenging, especially given the uncertainty surrounding the future impact of tariffs.
Limited Influence
The Fed's ability to mitigate the impact of tariffs is limited because tariffs are primarily a fiscal policy issue.
- Monetary vs. Fiscal Policy: Monetary policy (controlled by the Fed) focuses on interest rates and money supply. Fiscal policy (controlled by Congress and the executive branch) involves government spending and taxation.
- Role of Congress: Congress has the power to alter tariff policies, making fiscal policy adjustments crucial in addressing the root cause of the problem.
- Explanation: The Fed's influence is limited to mitigating the effects of tariffs through monetary policy, but it cannot directly address the cause. This highlights the need for coordinated fiscal and monetary policy responses to effectively manage the economic consequences of tariffs.
Conclusion
Rising tariffs pose a significant threat to the Federal Reserve's goals of price stability and full employment. Chairman Powell's assessment underscores the serious challenges posed by these trade policies, highlighting the inflationary pressures, potential for reduced economic growth, and increased job uncertainty. While the Fed can employ monetary policy tools, its influence is limited, emphasizing the need for coordinated policy responses. Understanding the impact of rising tariffs on the Federal Reserve goals is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers. Stay informed about the latest developments and their effect on the Federal Reserve goals and the broader economy. Understanding the impact of tariffs on the Fed's objectives is crucial for navigating the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Ovde Penzioneri Uzivaju Luksuz Skupe Vile I Milionsko Bogatstvo
May 25, 2025
Ovde Penzioneri Uzivaju Luksuz Skupe Vile I Milionsko Bogatstvo
May 25, 2025 -
 Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend 2025 Ticket Information Full Lineup Confirmed
May 25, 2025
Bbc Radio 1 Big Weekend 2025 Ticket Information Full Lineup Confirmed
May 25, 2025 -
 Avoid Memorial Day Travel Chaos The Busiest Flight Dates In 2025
May 25, 2025
Avoid Memorial Day Travel Chaos The Busiest Flight Dates In 2025
May 25, 2025 -
 Adios A Eddie Jordan Ultima Hora Sobre Su Fallecimiento
May 25, 2025
Adios A Eddie Jordan Ultima Hora Sobre Su Fallecimiento
May 25, 2025 -
 Peaceful Andalusian Farmstay A Day To Day Escape
May 25, 2025
Peaceful Andalusian Farmstay A Day To Day Escape
May 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Feature Film To Detail Wrongful Arrest At Glasgow Airport
May 26, 2025
Feature Film To Detail Wrongful Arrest At Glasgow Airport
May 26, 2025 -
 Alshrtt Alfrnsyt Tkshf Ghmwd Jrymt Qtl Eaylt Tfasyl Sadmt En Dfn Aljthth
May 26, 2025
Alshrtt Alfrnsyt Tkshf Ghmwd Jrymt Qtl Eaylt Tfasyl Sadmt En Dfn Aljthth
May 26, 2025 -
 Glasgow Airport Wrongful Arrest To Become Feature Film
May 26, 2025
Glasgow Airport Wrongful Arrest To Become Feature Film
May 26, 2025 -
 Frnsa Ttwrat Mthyrt Fy Qdyt Qtl Eaylt Wdfn Jththhm Dakhl Almnzl
May 26, 2025
Frnsa Ttwrat Mthyrt Fy Qdyt Qtl Eaylt Wdfn Jththhm Dakhl Almnzl
May 26, 2025 -
 Wrongful Glasgow Airport Arrest Feature Film In Development
May 26, 2025
Wrongful Glasgow Airport Arrest Feature Film In Development
May 26, 2025
