Fewer Excessive Heat Warnings: The Science Behind The Shift
Table of Contents
Improved Meteorological Forecasting and Technology
Advancements in weather forecasting technology are significantly impacting the frequency and accuracy of heat warnings. More precise predictions mean fewer unnecessary warnings, leading to a better allocation of resources and reducing public fatigue.
Enhanced Predictive Models
The accuracy of heat warnings has dramatically improved thanks to advancements in weather modeling and prediction capabilities.
- Increased computational power: Modern supercomputers can process vast amounts of data, leading to more sophisticated models.
- Higher-resolution satellite imagery: Improved satellite technology provides more detailed atmospheric data, allowing for more precise temperature predictions at a hyperlocal level.
- Improved atmospheric data collection: A denser network of weather stations and advanced sensors provides a more comprehensive understanding of atmospheric conditions.
- Incorporation of real-time ground observations: Real-time data from ground-based sensors, including temperature and humidity readings, are integrated into models for real-time updates.
These improvements translate to more precise forecasts, effectively targeting high-risk areas and minimizing the need for overly broad warnings. This targeted approach ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that warnings are only issued when absolutely necessary, leading to fewer instances of excessive heat warnings.
Early Warning Systems and Dissemination
Rapid dissemination of critical information is paramount in heat wave preparedness. Advanced early warning systems play a crucial role.
- Use of mobile alerts: Targeted SMS and app-based alerts can reach individuals directly, providing timely warnings and instructions.
- Social media campaigns: Social media platforms offer a powerful tool for rapid dissemination of information and community engagement.
- Targeted messaging based on vulnerability: Tailoring messages to specific demographics (elderly, individuals with pre-existing conditions) ensures that the most vulnerable populations receive timely alerts.
- Integration with community outreach programs: Collaboration with community organizations helps ensure that information reaches those who may not have access to technology.
Faster dissemination significantly reduces the lag time between prediction and public awareness. This preparedness, driven by advanced early warning systems, contributes to fewer excessive warnings.
Changing Communication Strategies and Public Awareness
Improved communication strategies are crucial in making heat warnings more effective and reducing the need for excessive alerts. This involves both targeted messaging and increased public awareness campaigns.
Targeted Messaging and Risk Communication
Tailoring heat warnings based on individual vulnerability significantly improves their impact.
- Age-specific messaging: Messages are adapted to resonate with different age groups, conveying the specific risks and necessary actions.
- Location-based alerts: Warnings are hyperlocal, focusing on areas most at risk, thus avoiding unnecessary alerts in less affected regions.
- Messaging that considers pre-existing health conditions: Alerts take into account underlying health conditions, providing specific guidance for individuals with increased vulnerability.
- Highlighting protective behaviors: Warnings emphasize practical steps to mitigate heat risk, such as staying hydrated, seeking shade, and avoiding strenuous activity.
By focusing on those most at risk, resources are better utilized, and the overall impact of warnings is magnified.
Public Education and Heat Preparedness
Proactive public education is essential for improving community resilience to extreme heat.
- Increased awareness of heat-related illnesses: Educational campaigns raise awareness about heatstroke, heat exhaustion, and other heat-related health problems.
- Promotion of preventative measures (hydration, seeking shade): Public health initiatives encourage proactive measures to mitigate heat-related risks.
- Community-based support networks: Establishing support networks ensures that vulnerable populations receive assistance during heat waves.
Increased preparedness and awareness empower individuals to take preventative action, lessening the reliance on extensive warnings.
The Complex Role of Climate Change
Climate change presents a complex challenge. While the frequency of extreme heat events is increasing, advancements in forecasting technology often lead to more precise warnings.
Increased Frequency vs. Improved Prediction
There's a potential paradox: climate change increases extreme heat events, but improved forecasting leads to fewer excessive warnings.
- Correlation between rising temperatures and improved forecasting accuracy: Better technology allows for more accurate predictions even with increasing heat wave frequency.
- The importance of distinguishing between frequency of events and frequency of warnings: It's crucial to differentiate between the actual number of heat events and the number of warnings issued.
This nuanced relationship requires careful consideration, avoiding oversimplified conclusions. Improved prediction doesn't negate the reality of climate change, but it does offer a more effective response.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
Long-term solutions, including adaptation and mitigation, are crucial in shaping the future of heat warnings.
- Infrastructure changes to improve the urban heat island effect: Urban planning initiatives can mitigate the impact of heat in cities.
- Implementation of heat action plans: Proactive community strategies can significantly reduce heat-related risks.
- Reduction of carbon footprint: Mitigating climate change is crucial in reducing the frequency and intensity of future heat waves.
These long-term solutions can significantly influence the need for future heat warnings.
Conclusion
The perceived decrease in excessive heat warnings is multifaceted, influenced by improved forecasting, refined communication, and the ongoing challenge of climate change. While better prediction and public awareness are positive, ongoing vigilance and adaptation remain crucial. Understanding this shift allows for better preparation and more resilient communities. Continue to learn about effective heat warning systems and stay informed about local weather forecasts to stay safe during periods of extreme heat. Remember to check for updated excessive heat warnings in your area regularly.

Featured Posts
-
 San Diego Weather 4 Day Sunny And Warm Forecast
May 30, 2025
San Diego Weather 4 Day Sunny And Warm Forecast
May 30, 2025 -
 Lutte D Influence A L Assemblee Nationale Rn Vs Lfi Sur La Question Des Frontieres
May 30, 2025
Lutte D Influence A L Assemblee Nationale Rn Vs Lfi Sur La Question Des Frontieres
May 30, 2025 -
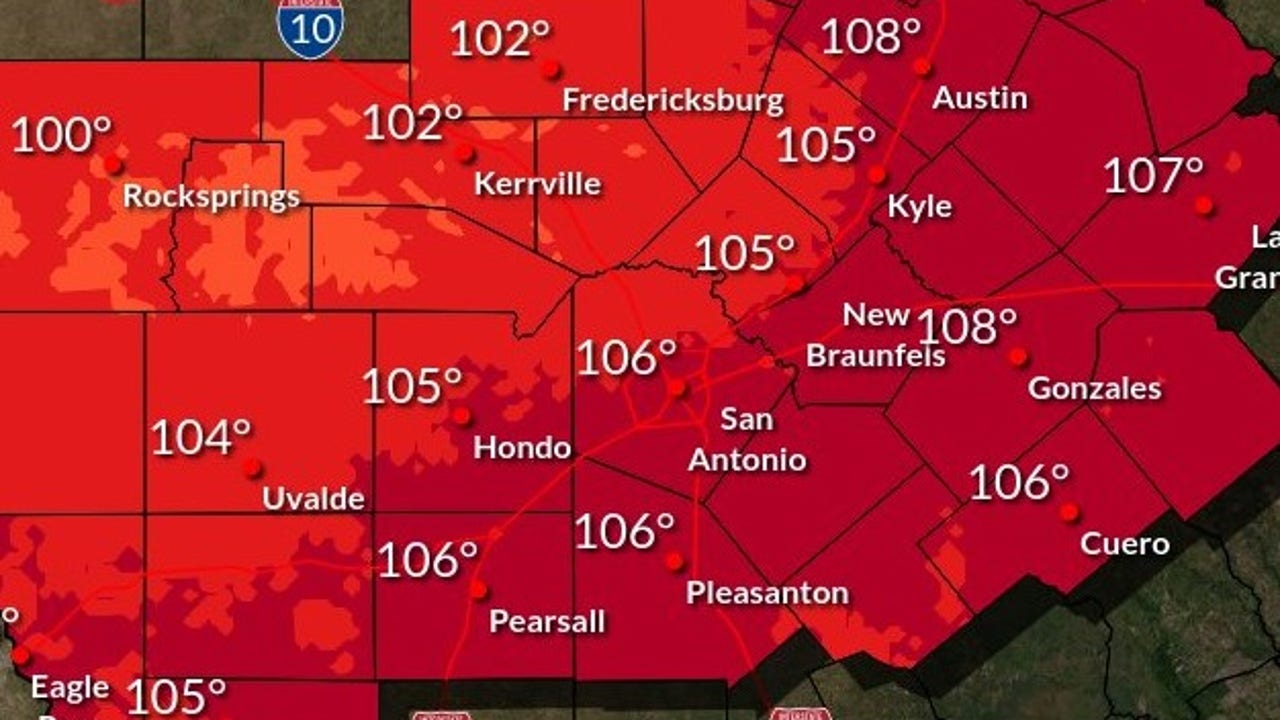 111 Degree Heat Warning Issued For Texas
May 30, 2025
111 Degree Heat Warning Issued For Texas
May 30, 2025 -
 Jacob Alons Unconventional Journey Why He Didnt Become A Dentist
May 30, 2025
Jacob Alons Unconventional Journey Why He Didnt Become A Dentist
May 30, 2025 -
 Programma Tileoptikon Metadoseon Savvatoy 15 3
May 30, 2025
Programma Tileoptikon Metadoseon Savvatoy 15 3
May 30, 2025
