Financial Sustainability Of US Universities: The Role Of International Student Enrollment, Focusing On China
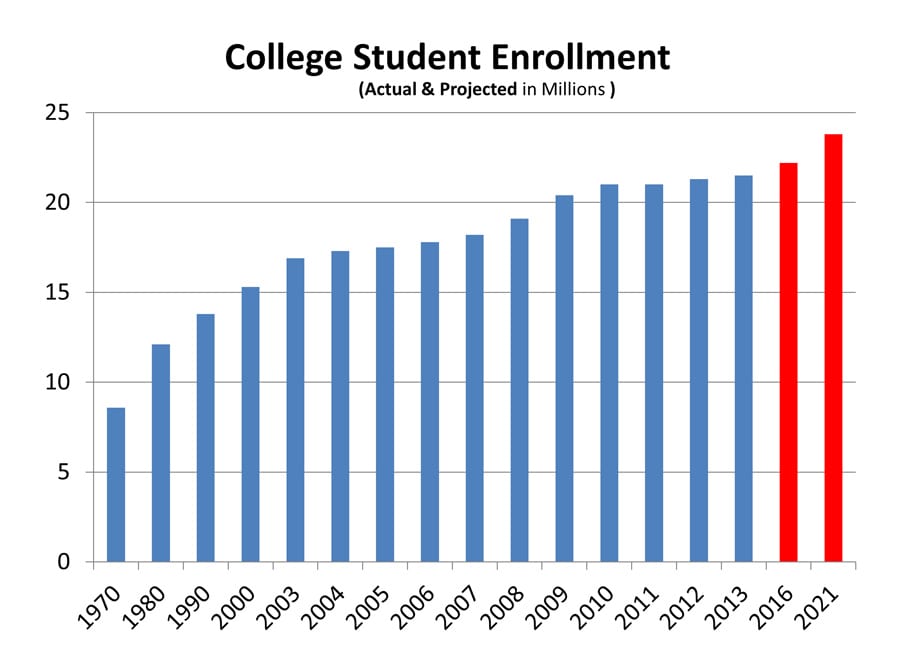
Table of Contents
2. The Economic Impact of Chinese Students on US Universities
H2: Tuition Revenue and its Significance:
Chinese students represent a substantial source of tuition revenue for US universities. The tuition fees paid by international students, including those from China, often exceed those paid by domestic students, creating a significant financial buffer for institutions. For example, a study by [insert reputable source and data here] showed that Chinese students contributed [insert specific dollar amount] in tuition revenue to US universities in [insert year]. This differential significantly impacts university budgets; a reduction in Chinese enrollment directly translates to a considerable loss of revenue.
- Tuition Differential: International students typically pay significantly higher tuition than their domestic counterparts, often covering a larger portion of the cost of their education.
- Budgetary Impact of Reduced Enrollment: A decline in Chinese student enrollment, due to various factors, can create substantial budget deficits, potentially leading to program cuts, faculty layoffs, and a reduction in academic services.
- Financial Planning and Forecasting: Universities increasingly rely on projections of international student enrollment, including Chinese students, for accurate budget forecasting and long-term financial planning.
H2: Research Funding and Grants:
Chinese students actively contribute to research funding and grant acquisition. Their participation in research projects, often alongside faculty, enhances grant applications' competitiveness and increases the likelihood of securing funding from various sources, including government agencies and private foundations. This collaborative research strengthens academic partnerships and fosters innovation.
- Successful Collaboration Examples: [Insert examples of successful research collaborations involving Chinese students and faculty].
- Loss of Research Funding: A decrease in Chinese student participation can directly impact research funding opportunities, hindering the progress of crucial research initiatives and potentially affecting a university's reputation for academic excellence.
- Intellectual Capital: Chinese students bring diverse perspectives and skills which enrich the academic environment and enhance research outcomes.
H2: Indirect Economic Benefits:
Beyond tuition and research funding, Chinese students contribute significantly to the local economies surrounding universities. Their spending on housing, food, transportation, and entertainment generates substantial revenue for local businesses, creating a multiplier effect that boosts the overall economic vitality of the community.
- Spending Power: Chinese students often have considerable disposable income, which they spend within the university's community, supporting local businesses and creating jobs.
- Multiplier Effect: The economic activity generated by Chinese students extends beyond their direct spending, stimulating further economic growth in the surrounding area.
- Community Development: The economic contribution of international students fosters community development and enhances the overall quality of life in university towns and cities.
3. Challenges and Risks Associated with Reliance on Chinese Student Enrollment
H2: Geopolitical Factors and Their Influence:
The relationship between the US and China significantly influences student mobility and visa processes. Changes in geopolitical dynamics, trade policies, or diplomatic tensions can directly impact the number of Chinese students choosing to study in the US, creating instability in university finances.
- Visa Policies and Restrictions: Changes in visa application processes or stricter immigration policies can deter prospective Chinese students.
- Political Instability: Political tensions between the US and China can affect students' decisions and willingness to study abroad.
- Risk Mitigation: Universities need to diversify their international student recruitment strategies to mitigate the risk associated with over-reliance on a single country.
H2: Competition for International Students:
The global competition for attracting international students, including Chinese students, is fierce. Many countries are investing heavily in attracting top students, offering scholarships, improved infrastructure, and attractive visa policies.
- Competitive Strategies: Countries like Canada, Australia, and the UK are actively competing with the US for attracting Chinese students.
- Market Share: The US needs to maintain its competitive advantage to retain its share of the international student market.
- Attracting and Retaining Students: Universities must adapt their strategies and offer competitive packages to attract and retain international students.
H2: Maintaining Diversity and Inclusivity:
While Chinese students bring immense value, over-reliance on a single demographic group can compromise diversity and inclusivity on campuses. A diverse student body enriches the educational experience for all students, promoting a broader range of perspectives and fostering global citizenship.
- Campus Climate: A diverse student body contributes to a more vibrant and inclusive campus climate.
- Global Perspective: Exposure to diverse cultures and viewpoints enhances students' understanding of global issues.
- Balanced Representation: Universities must strive for a balanced representation of students from various countries and backgrounds.
4. Strategies for Ensuring Long-Term Financial Sustainability
H2: Diversifying International Student Recruitment:
To mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on Chinese students, universities must diversify their international student recruitment strategies. This involves actively seeking students from various countries, creating a more resilient and financially sustainable student body.
- Global Outreach: Universities should actively promote their programs in various countries, targeting underrepresented regions.
- Targeted Recruitment: Developing specific recruitment strategies for different regions and student groups.
- Scholarships and Financial Aid: Offering competitive financial aid packages to attract students from diverse backgrounds.
H2: Strengthening Domestic Student Enrollment:
Maintaining a strong domestic student base is crucial for long-term financial sustainability. Universities should focus on improving affordability and accessibility of higher education for domestic students.
- Tuition Affordability: Exploring strategies to control tuition costs and increase financial aid for domestic students.
- Student Support Services: Improving student support services to increase student retention rates.
- Recruitment Campaigns: Launching targeted recruitment campaigns to attract more domestic students.
H2: Exploring Alternative Funding Sources:
Universities should actively seek alternative funding sources to reduce reliance on tuition revenue alone. This includes increasing endowments, strengthening alumni relations to boost donations, and exploring private investment opportunities.
- Endowment Management: Efficiently managing endowments to generate sustainable income streams.
- Alumni Engagement: Building stronger relationships with alumni to increase donations and philanthropic support.
- Private Investment: Exploring opportunities for private investment in research and infrastructure projects.
5. Conclusion: Securing the Financial Future of US Universities Through a Strategic Approach to International Student Enrollment
The financial sustainability of US universities is intrinsically linked to international student enrollment, with Chinese students making a significant contribution. However, over-reliance on any single source of funding is inherently risky. A strategic approach to international student enrollment, emphasizing diversification and strengthening domestic student recruitment alongside exploring alternative funding sources, is essential for securing the long-term financial sustainability of US universities. Universities must develop comprehensive strategies that balance the benefits of attracting international students with the need for resilience and stability. Invest in diversification now to ensure a bright financial future.

Featured Posts
-
 The Shifting Global Balance Assessing Us And Chinese Military Strength
May 31, 2025
The Shifting Global Balance Assessing Us And Chinese Military Strength
May 31, 2025 -
 Is Parker Meadows Returning To The Tigers Soon A Notebook Update
May 31, 2025
Is Parker Meadows Returning To The Tigers Soon A Notebook Update
May 31, 2025 -
 Alcaraz Victorious In Rome Passaro Upsets Dimitrov Italian International Highlights
May 31, 2025
Alcaraz Victorious In Rome Passaro Upsets Dimitrov Italian International Highlights
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguia Vs Surace Ii Munguia Takes Points Decision In Riyadh
May 31, 2025
Munguia Vs Surace Ii Munguia Takes Points Decision In Riyadh
May 31, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword March 30 2025 Complete Answers And Clues
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword March 30 2025 Complete Answers And Clues
May 31, 2025
