Fiscal Support And Inflation: The ECB's Assessment Of Post-Pandemic Economic Effects
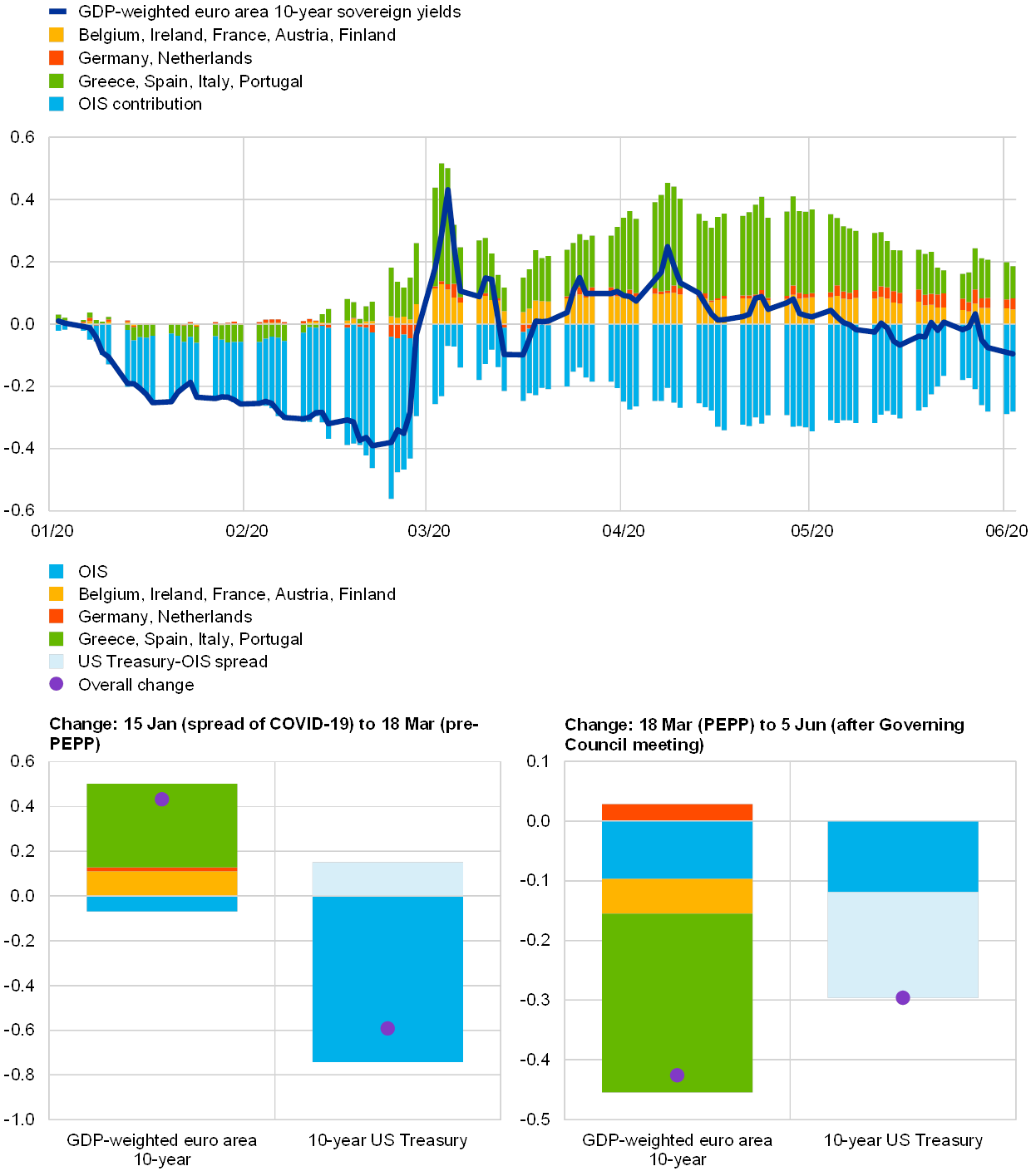
Table of Contents
The Scale and Impact of Fiscal Support Measures
The EU and its member states responded to the pandemic with an unprecedented wave of fiscal stimulus packages designed to mitigate the economic fallout. These measures aimed to support businesses, protect jobs, and stimulate aggregate demand. The scale and scope of these interventions were truly remarkable.
-
Examples of Specific Programs: The NextGenerationEU recovery plan, a cornerstone of the EU's response, provided substantial funding for member states' recovery and resilience plans. Simultaneously, individual countries implemented national furlough schemes, such as Germany's Kurzarbeit, to safeguard employment. These programs, along with other national initiatives, represent a massive injection of fiscal stimulus.
-
Quantitative Analysis of Fiscal Spending: The total fiscal spending across the EU amounted to trillions of euros, representing a significant percentage of the bloc's GDP. This massive injection of liquidity aimed to prevent a deeper economic recession. However, such a significant increase in government spending also carried potential risks.
-
Intended Effects and Unintended Consequences: While the intended effects of these measures—supporting businesses, protecting jobs, and stimulating demand—were largely achieved in the short term, the large-scale fiscal injections also resulted in some unintended consequences.
- Overheating the Economy: The substantial increase in liquidity risked overheating the economy, leading to inflationary pressures. Excess demand, fueled by government spending and pent-up consumer demand, put upward pressure on prices.
- Impact on Public Debt Levels: The significant increase in government borrowing to finance these stimulus packages led to a substantial rise in public debt levels across many Eurozone member states. This poses long-term challenges for fiscal sustainability.
The ECB's Monetary Policy Response
The ECB's monetary policy response mirrored the scale and urgency of the fiscal measures. The bank implemented a series of unconventional measures to support the economy and maintain financial stability.
-
Quantitative Easing (QE) Programs: The ECB launched expansive QE programs, purchasing vast quantities of government bonds and other assets to inject liquidity into the financial system and lower long-term interest rates. These programs were significantly larger than those implemented during previous crises.
-
Targeted Longer-Term Refinancing Operations (TLTROs): The ECB offered TLTROs to banks, providing them with cheap and long-term funding to encourage lending to businesses and households. This aimed to stimulate credit creation and support economic activity.
-
Negative Interest Rates: The ECB implemented negative interest rates on commercial banks' deposits held at the central bank. This unconventional policy aimed to encourage banks to lend more readily, but it also raised concerns about its potential impact on bank profitability.
As inflation rose significantly, the ECB shifted its monetary policy stance.
-
Gradual Withdrawal of QE: The ECB gradually phased out its QE programs, reducing the pace of asset purchases as the economic recovery gained momentum.
-
Interest Rate Hikes: The ECB began raising interest rates to combat rising inflation, marking a significant shift from its previous ultra-loose monetary policy.
-
Forward Guidance and Communication Strategies: Clear communication of the ECB's policy intentions became crucial to guide market expectations and ensure a smooth transition to a less accommodative monetary policy.
Inflationary Pressures and Supply Chain Disruptions
The surge in inflation following the pandemic was a complex phenomenon driven by a combination of factors, including the interplay between fiscal support and supply-side constraints.
-
Demand-Pull Inflation: The large-scale fiscal stimulus, coupled with pent-up consumer demand, fueled strong aggregate demand, pulling prices upwards.
-
Cost-Push Inflation: Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the pandemic and geopolitical events, led to significant increases in production costs, contributing to cost-push inflation. Rising energy prices, particularly natural gas, played a significant role in this.
-
Global Factors: Global factors, such as rising commodity prices and heightened geopolitical uncertainty, also contributed to the inflationary pressures experienced in the Eurozone.
The ECB's Assessment and Outlook
The ECB regularly publishes assessments and projections of the Eurozone's economic outlook, including inflation forecasts. These assessments incorporate various economic indicators and models.
-
Inflation Forecasts: The ECB's inflation forecasts reflect the ongoing challenges in bringing inflation back to its target level of 2%. These forecasts are based on complex models considering various factors, including energy prices, wage growth, and supply-side conditions.
-
Risks and Uncertainties: The economic outlook remains subject to significant risks and uncertainties, including geopolitical instability, energy price volatility, and the potential for further supply chain disruptions.
-
Policy Objectives and Future Monetary Policy: The ECB's primary objective is maintaining price stability, but it also considers other factors, such as economic growth and employment, when making monetary policy decisions. Its future actions will depend on incoming economic data and the evolution of inflationary pressures.
Challenges and Future Considerations
The ECB faces significant challenges in navigating the current economic landscape. It must balance the need to control inflation with the risk of triggering a sharp economic slowdown.
-
Trade-offs Between Inflation Control and Economic Growth: Aggressive monetary tightening could curb inflation but might also lead to a recession. The ECB needs to carefully manage this delicate balance.
-
Risks of Overly Aggressive Monetary Tightening: Raising interest rates too quickly could stifle economic activity, leading to job losses and a deeper recession.
-
Long-Term Strategy for Price Stability and Economic Resilience: The ECB needs a long-term strategy for ensuring price stability and building a more resilient Eurozone economy capable of weathering future shocks. This involves considering structural reforms and fiscal sustainability alongside monetary policy.
Conclusion
The ECB's response to the post-pandemic economic landscape has been a complex interplay between substantial fiscal support and the subsequent management of inflationary pressures. Understanding the dynamics between fiscal policies and the ECB's monetary policy actions is key to comprehending the current economic situation and anticipating future trends. The ECB's ongoing assessment of this relationship, as detailed above, continues to shape its monetary policy decisions and significantly influence the Eurozone's economic trajectory. To stay updated on the latest developments regarding the ECB's Post-Pandemic Economic Assessment, regularly consult the ECB's official publications and follow reputable financial news sources.

Featured Posts
-
 Zuffenhausen Jerman Mengenal Sejarah Produksi Porsche 356
Apr 29, 2025
Zuffenhausen Jerman Mengenal Sejarah Produksi Porsche 356
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nyt Spelling Bee February 28 2025 Find The Spangram And All Answers
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Spelling Bee February 28 2025 Find The Spangram And All Answers
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Treasury Market Insights Key Takeaways From April 8th
Apr 29, 2025
Treasury Market Insights Key Takeaways From April 8th
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Schumer Stays Put No Plans To Pass The Torch Says Senate Majority Leader
Apr 29, 2025
Schumer Stays Put No Plans To Pass The Torch Says Senate Majority Leader
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Inter Miami Cf Where To Watch Lionel Messi Play In Mls Schedule Live Streams And Betting
Apr 29, 2025
Inter Miami Cf Where To Watch Lionel Messi Play In Mls Schedule Live Streams And Betting
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Jancker Wird Neuer Austria Klagenfurt Coach
Apr 29, 2025
Jancker Wird Neuer Austria Klagenfurt Coach
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Austria Klagenfurt Jancker Uebernimmt Traineramt
Apr 29, 2025
Austria Klagenfurt Jancker Uebernimmt Traineramt
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Janckers Zukunft Nach Leoben Wohin Fuehrt Der Weg
Apr 29, 2025
Janckers Zukunft Nach Leoben Wohin Fuehrt Der Weg
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nyr Porsche Macan Allt Um Fyrstu Rafutgafuna
Apr 29, 2025
Nyr Porsche Macan Allt Um Fyrstu Rafutgafuna
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Buy A Pts Riviera Blue Porsche 911 S T Exceptional Condition
Apr 29, 2025
Buy A Pts Riviera Blue Porsche 911 S T Exceptional Condition
Apr 29, 2025
