Germany's Energy Policy: Klingbeil Rejects Russian Gas Imports
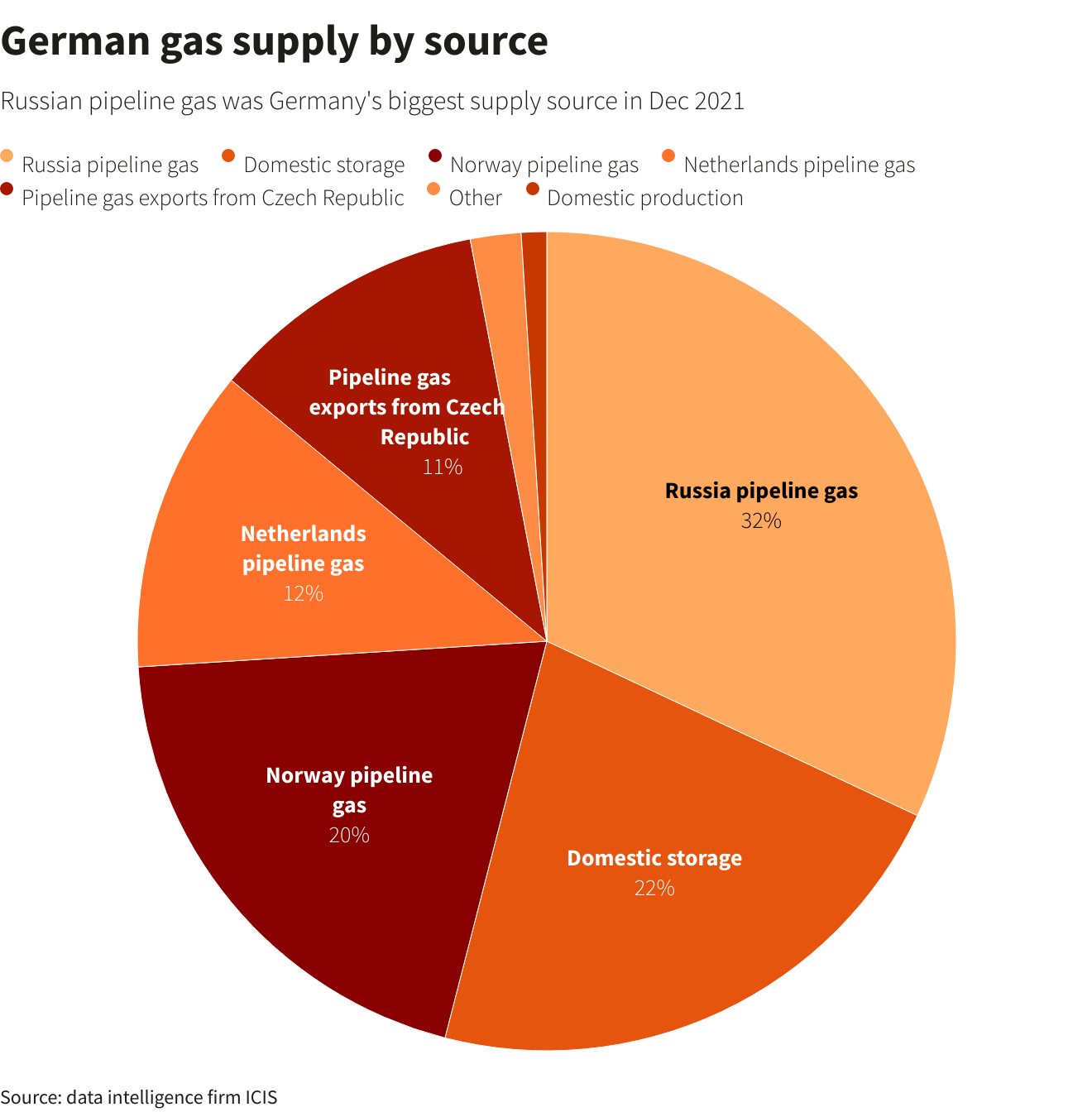
Table of Contents
Lars Klingbeil's recent statement rejecting Russian gas imports marks a significant turning point in Germany's energy policy. This decisive move reflects a growing urgency to secure Germany's energy future and lessen its dependence on volatile global energy markets, particularly those influenced by geopolitical instability. This article will explore the implications of this policy shift and its impact on Germany's energy transition, examining its effects on energy security, economic stability, and the acceleration of renewable energy adoption.
Klingbeil's Statement and its Implications
Klingbeil's public rejection of Russian gas, made in the context of ongoing geopolitical tensions and the war in Ukraine, signaled a profound shift in Germany's approach to energy security. His statement emphasized the need to break free from dependence on a single, unreliable supplier and prioritize ethical considerations alongside economic ones.
Key reasons for rejecting Russian gas include:
- Geopolitical Instability: Reliance on Russian gas leaves Germany vulnerable to political pressure and manipulation, as demonstrated by Russia's weaponization of energy supplies.
- Ethical Concerns: Continued reliance on Russian gas fuels the Russian economy, indirectly supporting the ongoing conflict in Ukraine and undermining international sanctions.
- Energy Security: Diversifying energy sources is paramount for ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply for German households and industries.
This decision has significant political ramifications. It underscores a growing consensus within the German government and among the public regarding the necessity of energy independence and a faster energy transition. However, it also presents challenges, including potential short-term economic disruptions and navigating complex international relations to secure alternative energy sources.
Accelerating the Energy Transition in Germany
Germany's Energiewende, the ambitious energy transition program, aims to shift away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources. Klingbeil's statement accelerates this transition by creating an immediate need to find alternative gas supplies and significantly boosting investment in renewable energy infrastructure.
The rejection of Russian gas accelerates the adoption of renewable energy sources by:
- Increased Investment: The urgency of the situation necessitates expedited investment in solar, wind, and hydro power generation, as well as energy storage solutions.
- Policy Initiatives: The government is likely to introduce further incentives and regulations to support the rapid deployment of renewable energy technologies, including streamlining permitting processes and providing financial support for renewable energy projects. This includes expanding offshore wind farms and accelerating the development of green hydrogen production.
- Technological Advancements: The pressure to replace Russian gas will drive innovation and investment in next-generation renewable energy technologies.
However, challenges remain:
- Infrastructure Limitations: Germany needs significant upgrades to its energy grid to handle the influx of renewable energy from decentralized sources.
- Public Acceptance: Ensuring public acceptance of new energy infrastructure, such as wind turbines and solar farms, is crucial for successful implementation.
- Economic Costs: The transition will require substantial investments, potentially leading to short-term economic adjustments.
Diversifying Gas Supplies for Enhanced Energy Security
Germany is actively pursuing multiple strategies to diversify its gas supply:
- LNG Imports: Increasing imports of liquefied natural gas (LNG) through new terminals is a critical element of the strategy.
- European Pipeline Connections: Strengthening pipeline connections with neighboring European countries enhances gas supply security and allows for better resource sharing across the continent.
- Increased Domestic Gas Production: Exploring and potentially increasing domestic gas production, albeit limited, can contribute to a more resilient energy mix.
International cooperation plays a crucial role:
- EU Energy Policy: Collaboration within the European Union is vital for coordinating gas procurement, infrastructure development, and establishing common energy security goals.
- Global Partnerships: Germany is actively seeking partnerships with diverse gas suppliers to avoid over-reliance on any single country.
Diversification strategies, however, present both advantages and disadvantages:
- Advantages: Improved energy security, reduced geopolitical risks, and greater energy independence.
- Disadvantages: Increased costs, potential logistical challenges, and risks associated with new suppliers.
Economic Impacts of Shifting Away from Russian Gas
The shift away from Russian gas carries both short-term and long-term economic implications:
- Short-term Impacts: Increased energy prices are likely in the short term, impacting industries and consumers. Government support measures like energy subsidies might be necessary to mitigate these effects.
- Long-term Impacts: The transition to renewable energy is expected to create new jobs in the renewable energy sector and related industries, driving economic growth. Furthermore, reduced reliance on fossil fuels will contribute to a more sustainable economy and long-term environmental benefits.
Economic benefits of a successful energy transition include:
- Job Creation: The expansion of renewable energy infrastructure and related industries will create numerous high-skilled jobs.
- Technological Leadership: Germany can become a global leader in renewable energy technologies, generating export opportunities and economic growth.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduced greenhouse gas emissions will contribute to a healthier environment and reduce the long-term costs associated with climate change.
Conclusion
Klingbeil's rejection of Russian gas imports represents a pivotal moment in German energy policy. This decisive action acts as a catalyst for accelerating the energy transition, enhancing energy security, and promoting energy independence. The shift will necessitate significant investments in renewable energy infrastructure and a concerted effort to diversify gas supplies. While short-term economic challenges are anticipated, the long-term benefits of a sustainable and secure energy future are undeniable. Germany’s commitment to renewable energy sources is shaping not only its own energy future but also influencing global efforts towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape. Staying informed about Germany's evolving energy policy is crucial for understanding its future economic and geopolitical landscape. Learn more about Germany’s plans for energy independence and how you can contribute to a sustainable energy future by exploring further resources on German energy policy and renewable energy initiatives.

Featured Posts
-
 Bao Cao Tran Mo Man Vong Chung Ket Giai Bong Da Thanh Nien Sinh Vien
Apr 30, 2025
Bao Cao Tran Mo Man Vong Chung Ket Giai Bong Da Thanh Nien Sinh Vien
Apr 30, 2025 -
 X Files Reboot Gillian Andersons Possible Return As Star
Apr 30, 2025
X Files Reboot Gillian Andersons Possible Return As Star
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Royals Defeat Guardians 4 3 Garcia Homer And Witts Game Winning Hit
Apr 30, 2025
Royals Defeat Guardians 4 3 Garcia Homer And Witts Game Winning Hit
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Panthers At 8 Draft Day Decisions And Potential Impact
Apr 30, 2025
Panthers At 8 Draft Day Decisions And Potential Impact
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Police Watchdog Seeks Ofcom Investigation Into Chris Kaba Panorama
Apr 30, 2025
Police Watchdog Seeks Ofcom Investigation Into Chris Kaba Panorama
Apr 30, 2025
