Global Forest Loss Reaches Record High: Wildfires Fuel The Destruction

Table of Contents
The Alarming Extent of Global Forest Loss
The scale of global deforestation is staggering. Recent data from the Global Forest Watch indicates a significant increase in forest loss in recent years, exceeding previous records. Visual representations, such as interactive maps and charts, clearly illustrate the alarming rate of deforestation across the globe. Regions like the Amazon rainforest, the Congo Basin, and Southeast Asia are particularly hard hit.
- Quantifiable Loss: Millions of hectares of forest are lost annually, representing a substantial loss of vital ecosystems.
- Accelerated Rate: The rate of forest loss has increased dramatically in the last decade, surpassing previous years' figures.
- Countries Most Affected: Brazil, Indonesia, and the Democratic Republic of Congo are among the countries experiencing the most significant losses. [Insert chart or infographic here showing forest loss data by country and year].
Wildfires as a Major Driver of Forest Destruction
The increased frequency and intensity of wildfires globally are directly linked to climate change. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and more frequent heatwaves create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly, consuming vast tracts of forest. Human activities, including deforestation and improper land management, further exacerbate the risk.
- Major Wildfire Events: The devastating wildfires in Australia (2019-2020), California (2020, 2021), and Siberia (2021) exemplify the scale of destruction and the impact on forest ecosystems. [Insert images or data on these events].
- Wildfire-Related Forest Loss Statistics: A significant percentage of annual global forest loss is directly attributable to wildfires. [Insert statistical data on wildfire impact on forest loss].
- Changing Climate Patterns: Shifting climate patterns, including changes in rainfall and wind patterns, are influencing wildfire behavior, making them more unpredictable and destructive.
Other Contributing Factors to Deforestation Beyond Wildfires
While wildfires are a major driver, other factors contribute significantly to deforestation. These include:
- Logging: Unsustainable logging practices deplete forests for timber, often illegally.
- Agriculture: Conversion of forests for agricultural land, particularly for large-scale monoculture farming, is a leading cause of deforestation.
- Mining: Mining operations often involve clearing vast areas of forest for access to resources.
- Urbanization: Expanding cities and infrastructure encroach on forested areas.
These activities are often driven by economic pressures and a lack of sustainable alternatives. The unsustainable practices employed often lead to soil erosion, biodiversity loss, and further environmental damage.
- Detailed Explanation of Drivers: Each driver requires a detailed explanation of its mechanisms and impacts on forest ecosystems. [Elaborate on each bullet point with specific examples and data].
- Statistics on Contribution to Loss: Quantify the contribution of each driver to the overall percentage of global forest loss. [Insert relevant statistics].
- Sustainable Alternatives: Highlight sustainable alternatives such as sustainable forestry, agroforestry, and responsible mining practices.
The Devastating Consequences of Global Forest Loss
The consequences of global forest loss are far-reaching and devastating.
-
Environmental Impacts: Biodiversity loss, habitat destruction, increased greenhouse gas emissions, and disruptions to hydrological cycles are major concerns.
-
Social and Economic Repercussions: Deforestation leads to the displacement of indigenous communities, loss of livelihoods dependent on forests, and reduced ecosystem services.
-
Climate Change Implications: Forests play a crucial role in carbon sequestration. Deforestation releases significant amounts of stored carbon, exacerbating climate change.
-
Endangered Species: Mention specific examples of endangered species directly impacted by deforestation. [Provide examples and data].
-
Economic Costs: Quantify the economic losses associated with reduced timber production, tourism decline, and decreased ecosystem services. [Insert economic data].
-
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Highlight the contribution of deforestation to overall greenhouse gas emissions and its impact on global warming. [Use data from credible sources].
Conclusion: Addressing the Crisis of Global Forest Loss
Record-high global forest loss, fueled significantly by devastating wildfires, poses a grave threat to the environment, society, and the global climate. The consequences— biodiversity loss, climate change exacerbation, and economic instability—demand immediate action. Combating global forest loss requires immediate and concerted action. We must all work together to protect our forests and mitigate the devastating effects of wildfires and unsustainable practices. Let's act now to prevent further record-high global forest loss. For more information and to get involved, visit [link to relevant organizations like Greenpeace, WWF, etc.].

Featured Posts
-
 Cao Toc Bien Vung Tau Chuan Bi Thong Xe 2 9
May 22, 2025
Cao Toc Bien Vung Tau Chuan Bi Thong Xe 2 9
May 22, 2025 -
 The Swiss Governments Reaction To Chinas Military Exercises
May 22, 2025
The Swiss Governments Reaction To Chinas Military Exercises
May 22, 2025 -
 Air Travel Summer Outlook Airlines Anticipate High Demand And Operational Difficulties
May 22, 2025
Air Travel Summer Outlook Airlines Anticipate High Demand And Operational Difficulties
May 22, 2025 -
 Thach Thuc Va Co Hoi Tu Cac Du An Ha Tang Tp Hcm Binh Duong
May 22, 2025
Thach Thuc Va Co Hoi Tu Cac Du An Ha Tang Tp Hcm Binh Duong
May 22, 2025 -
 2024 25 Premier League Champions Photo Feature
May 22, 2025
2024 25 Premier League Champions Photo Feature
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Significant Route 581 Traffic Disruption Due To Box Truck Crash
May 22, 2025
Significant Route 581 Traffic Disruption Due To Box Truck Crash
May 22, 2025 -
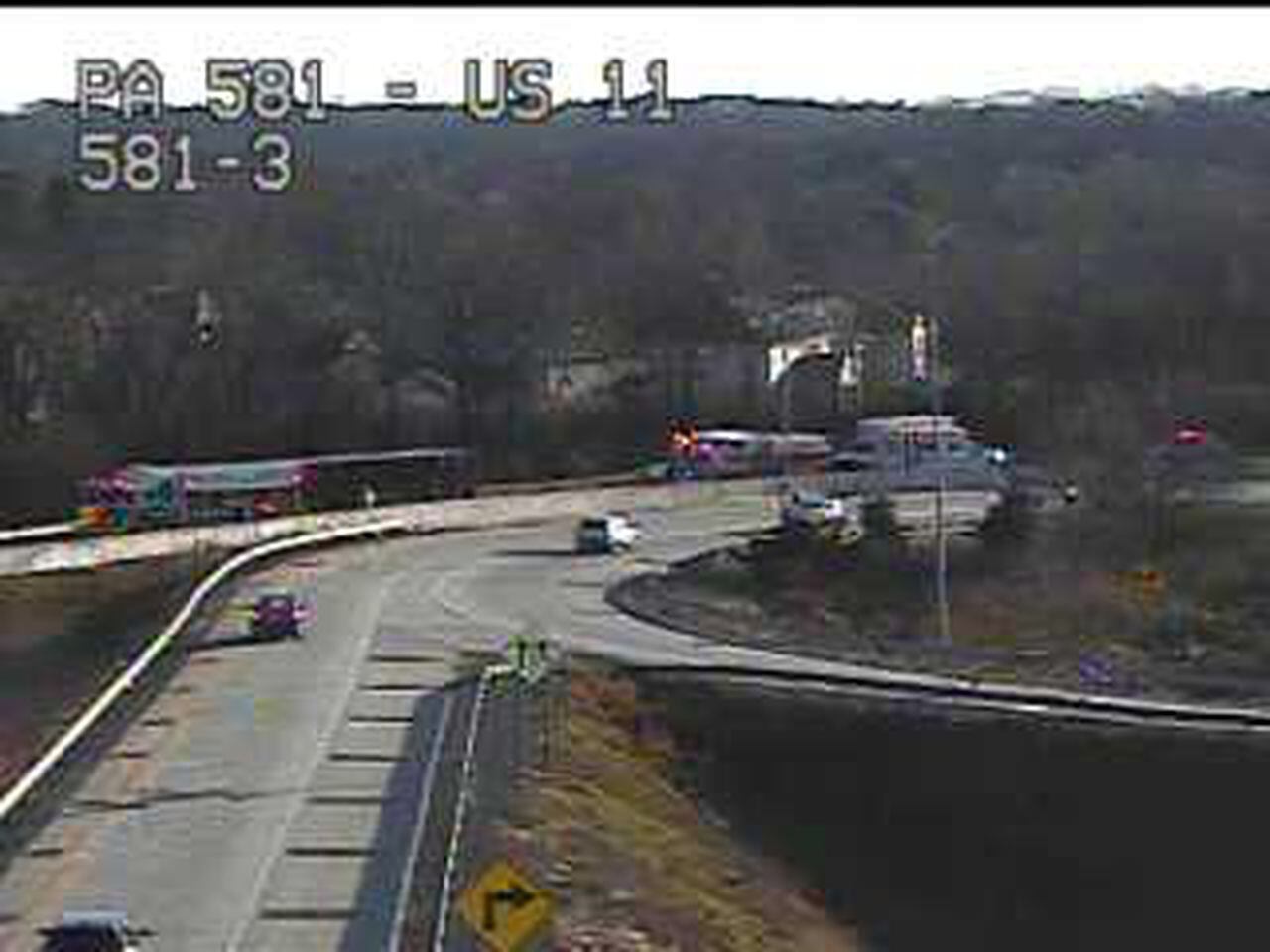 Route 581 Traffic Stopped After Box Truck Collision
May 22, 2025
Route 581 Traffic Stopped After Box Truck Collision
May 22, 2025 -
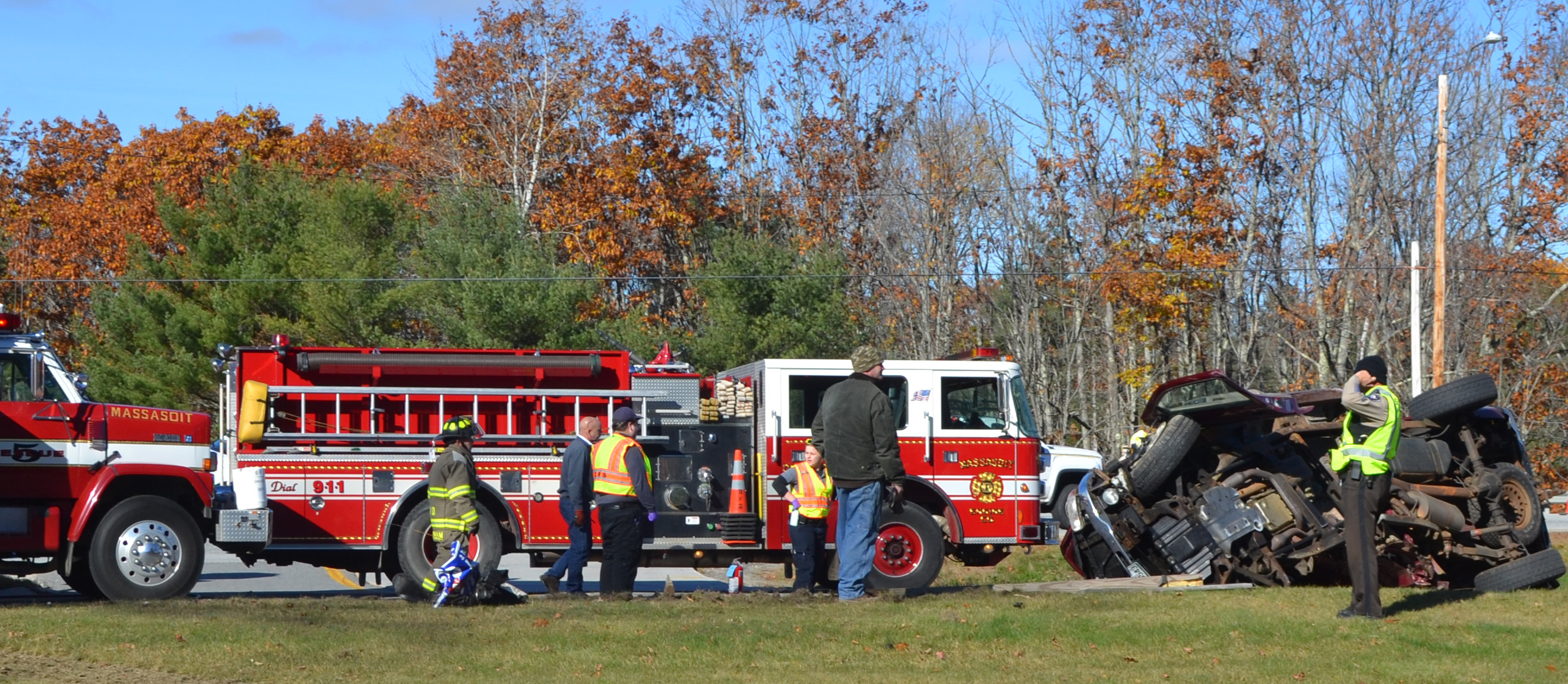 Box Truck Accident Shuts Down Section Of Route 581
May 22, 2025
Box Truck Accident Shuts Down Section Of Route 581
May 22, 2025 -
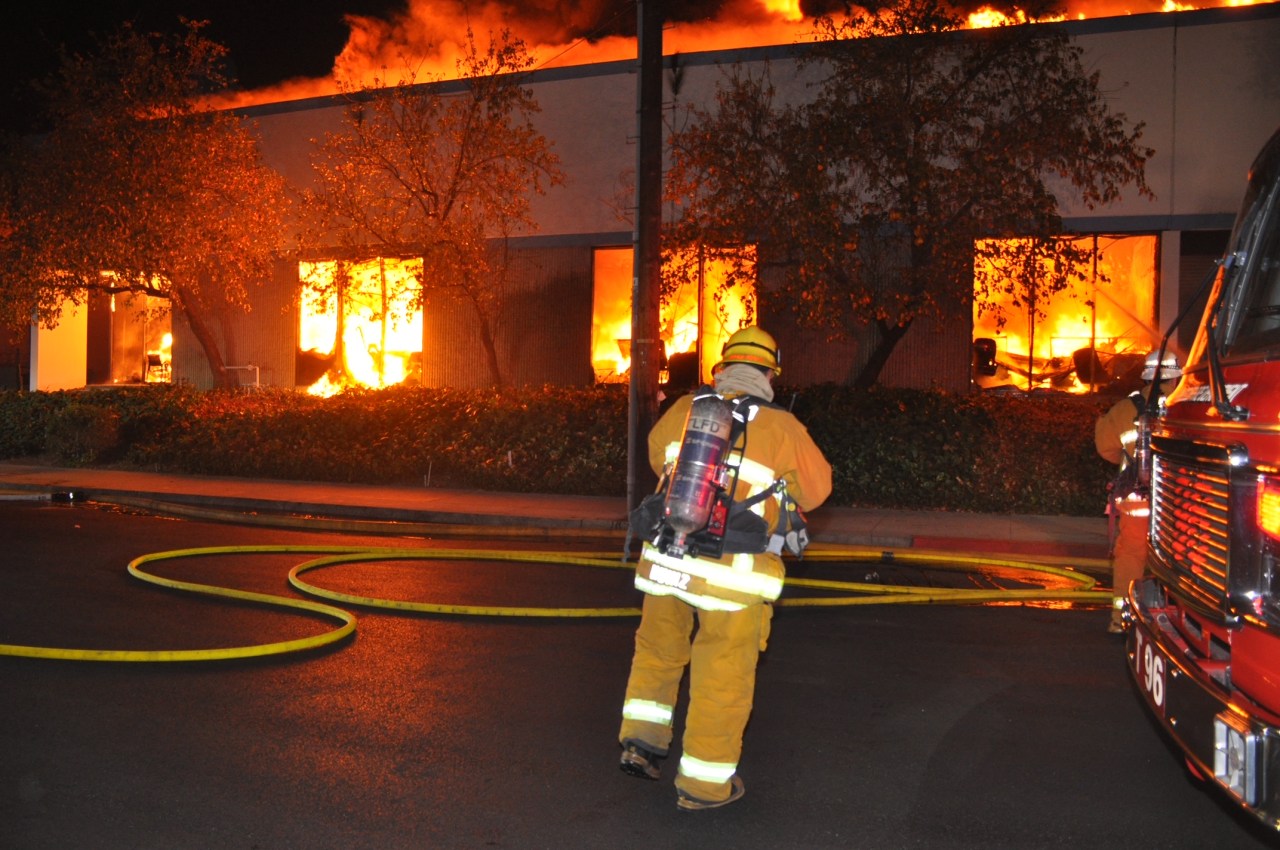 Large Fire Engulfs Used Car Sales Lot Crews On Scene
May 22, 2025
Large Fire Engulfs Used Car Sales Lot Crews On Scene
May 22, 2025 -
 Route 581 Closure Box Truck Crash Causes Major Delays
May 22, 2025
Route 581 Closure Box Truck Crash Causes Major Delays
May 22, 2025
