Grocery Inflation: Three Months Of Above-Average Increases
Table of Contents
Understanding the Surge in Grocery Inflation
Supply Chain Disruptions
The ongoing impact of supply chain issues significantly contributes to grocery inflation. These disruptions affect food production and distribution at every stage.
- Increased transportation costs: Fuel prices and driver shortages have dramatically increased the cost of moving goods from farms to processing plants and ultimately to supermarkets.
- Labor shortages: A lack of workers across the agricultural and transportation sectors has hampered production and delivery, reducing the available supply of many food items.
- Port congestion: Delays in unloading goods at ports have created bottlenecks, leading to further increases in transportation costs and reduced availability of imported food products.
- Weather events impacting crops: Unpredictable weather patterns, including droughts and floods, have negatively affected agricultural output, leading to shortages and price increases for certain fruits, vegetables, and grains.
These supply chain bottlenecks, coupled with increased freight costs, have squeezed producers and retailers, resulting in higher prices for consumers. Reduced agricultural output further exacerbates the issue, driving up prices for essential staples.
Rising Energy Costs
Increased energy costs are a major driver of grocery inflation, impacting every stage of the food supply chain.
- Increased fertilizer costs: The production of fertilizers is energy-intensive, and soaring fuel prices have translated into higher fertilizer costs for farmers.
- Higher energy usage in food production: From powering farm equipment to operating processing plants, the energy required to produce food has become significantly more expensive.
- Fuel surcharges on transportation: Increased fuel costs are passed on to consumers through fuel surcharges on transportation, impacting the price of almost every grocery item.
The ripple effect of energy price increases is substantial. Higher energy costs translate to higher production costs, impacting everything from the farm to the supermarket shelf, thus directly contributing to grocery inflation.
Increased Demand and Consumer Behavior
Shifting consumer habits and increased demand for certain goods also play a role in driving up grocery prices.
- Changes in eating habits during and post-pandemic: Changes in food consumption patterns, such as increased reliance on home-cooked meals and a shift towards certain convenience foods, have created increased demand in specific sectors.
- Increased demand for specific products: Demand for certain products, often driven by trends and marketing, can outstrip supply, resulting in price increases.
- Impact of marketing and consumer trends: Marketing strategies and consumer trends can influence demand and create artificial scarcity, which can lead to higher prices.
Understanding consumer spending, demand elasticity, and evolving food consumption patterns is crucial to analyzing the complex interplay of factors driving grocery inflation.
Impact on Consumers and the Economy
Budget Strain and Affordability
The surge in grocery inflation puts a significant strain on household budgets, particularly for low-income families.
- Decreased disposable income: Higher grocery bills leave less money for other essential expenses, reducing disposable income.
- Increased food insecurity: Rising food prices contribute to food insecurity, particularly among vulnerable populations.
- Impact on lower-income families: Lower-income families are disproportionately affected, as food represents a larger percentage of their overall spending.
The cost of living crisis, exacerbated by grocery inflation, has real consequences, potentially leading to increased poverty and a reduced quality of life for many households. This economic inequality necessitates attention and effective policy responses.
Changes in Purchasing Habits
Consumers are adapting their shopping behaviors to cope with the rising cost of groceries.
- Switching to cheaper brands: Consumers are increasingly opting for store brands and cheaper alternatives to reduce their grocery bills.
- Buying less meat: Meat is a relatively expensive protein source, leading many to reduce their meat consumption.
- Utilizing coupons and discounts: Consumers are actively seeking ways to save money through coupons, discounts, and loyalty programs.
- Shopping at budget supermarkets: More consumers are turning to discount supermarkets and grocery outlets to find lower prices.
These changes reflect a significant shift in consumer behavior, driven by economic necessity and a determination to manage their grocery budgets amidst rising prices.
Strategies for Managing Grocery Inflation
Budgeting and Meal Planning
Effective budgeting and meal planning are crucial for managing grocery inflation.
- Tracking expenses: Carefully monitoring grocery spending helps identify areas where savings can be made.
- Creating shopping lists: Sticking to a shopping list helps avoid impulse purchases and reduces overall spending.
- Utilizing meal-planning apps: Many apps provide tools for creating weekly meal plans based on available ingredients and budget.
- Cooking at home more often: Cooking at home is generally cheaper than eating out, offering significant savings over time.
By implementing these strategies, you can gain control over your grocery spending and make informed choices to reduce expenses.
Smart Shopping Techniques
Smart shopping techniques can further reduce your grocery bill.
- Comparing prices: Comparing prices across different stores and brands helps ensure you get the best value for your money.
- Using loyalty programs: Loyalty programs often offer discounts, coupons, and other benefits that can add up to significant savings.
- Buying in bulk (when appropriate): Buying in bulk can be cost-effective for non-perishable items with long shelf lives.
- Taking advantage of sales and discounts: Paying attention to weekly flyers and sales can help you snag significant deals on groceries.
By adopting these smart shopping techniques, you can maximize your savings and effectively manage the impact of rising grocery prices.
Conclusion
The past three months have seen a significant surge in grocery inflation, placing a considerable burden on consumers and the economy. Understanding the factors driving this increase – from supply chain disruptions to rising energy costs – is crucial for navigating this challenging period. By employing effective budgeting techniques, smart shopping strategies, and adapting to changing circumstances, you can mitigate the impact of grocery inflation on your household. Don't let rising grocery prices control your budget; take control of your grocery spending and proactively manage the impact of grocery inflation.

Featured Posts
-
 Why Did Core Weave Inc Crwv Stock Price Increase On Tuesday
May 22, 2025
Why Did Core Weave Inc Crwv Stock Price Increase On Tuesday
May 22, 2025 -
 Groeiende Autobezit Drijft Occasionverkoop Abn Amro Omhoog
May 22, 2025
Groeiende Autobezit Drijft Occasionverkoop Abn Amro Omhoog
May 22, 2025 -
 Where To Dine Outdoors In Manhattan A Selection Of Excellent Restaurants
May 22, 2025
Where To Dine Outdoors In Manhattan A Selection Of Excellent Restaurants
May 22, 2025 -
 Cwd Positive Test At Jackson Hole Elk Feedground Response And Management
May 22, 2025
Cwd Positive Test At Jackson Hole Elk Feedground Response And Management
May 22, 2025 -
 Wednesdays Surge In Core Weave Crwv Stock A Detailed Look
May 22, 2025
Wednesdays Surge In Core Weave Crwv Stock A Detailed Look
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
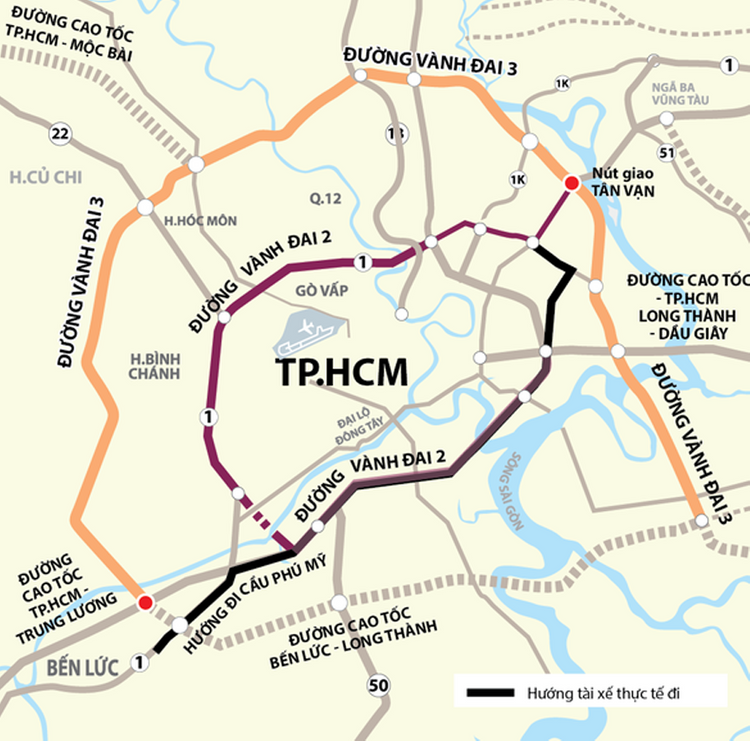 7 Du An Ket Noi Giao Thong Tp Hcm Long An Can Phat Trien
May 22, 2025
7 Du An Ket Noi Giao Thong Tp Hcm Long An Can Phat Trien
May 22, 2025 -
 Dau Tu Co So Ha Tang 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Tp Hcm Long An
May 22, 2025
Dau Tu Co So Ha Tang 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Tp Hcm Long An
May 22, 2025 -
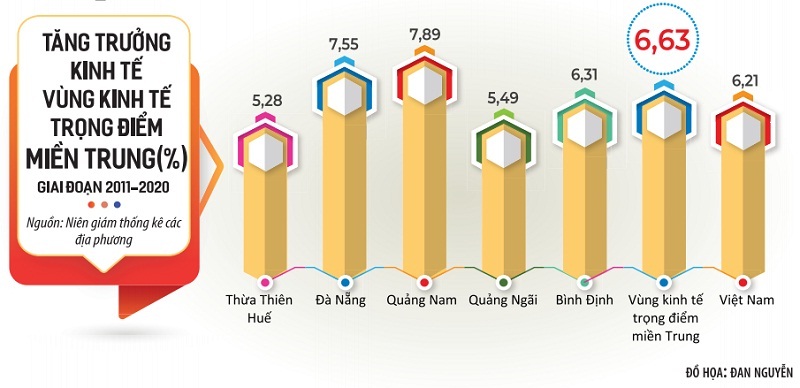 200 Nguoi Chay Bo Hanh Trinh Ket Noi Hai Tinh Mien Trung
May 22, 2025
200 Nguoi Chay Bo Hanh Trinh Ket Noi Hai Tinh Mien Trung
May 22, 2025 -
 Phan Tich 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Tp Hcm Long An Thu Hut Dau Tu
May 22, 2025
Phan Tich 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Tp Hcm Long An Thu Hut Dau Tu
May 22, 2025 -
 Su Kien Chay Bo Hon 200 Nguoi Dak Lak Phu Yen
May 22, 2025
Su Kien Chay Bo Hon 200 Nguoi Dak Lak Phu Yen
May 22, 2025
