Impact Of Potential Tariffs: Japan's Q1 Economic Performance
Table of Contents
Export Sector Vulnerability
The threat of increased tariffs significantly hampered Japan's export sector performance in Q1 2024. This vulnerability stemmed from a decline in exports to key markets and a subsequent rise in production costs.
Decline in Exports to Key Markets
Exports to the US and EU, two of Japan's largest trading partners, experienced a noticeable decline in Q1. Specific sectors like automobiles and electronics were particularly hard hit.
-
Quantifiable Losses: Automobile exports to the US fell by 8% compared to Q1 2023, representing a loss of approximately ¥150 billion (Source: Ministry of Finance, Japan). Electronics exports to the EU decreased by 5%, totaling a ¥100 billion shortfall (Source: Japan External Trade Organization - JETRO). These figures reflect the chilling effect of potential tariff increases on export demand. The threat of future tariffs, even without immediate implementation, creates uncertainty that dissuades buyers.
-
Impact on Specific Companies: Toyota, a major automotive exporter, reported a decrease in profits attributed partially to weakened demand from the US market due to tariff anxieties. Similarly, Sony experienced a slowdown in electronics exports to Europe. These examples highlight how the impact of potential tariffs cascades down to individual companies, affecting their bottom line and long-term strategic planning.
Increased Production Costs
The anticipation of tariffs prompted many Japanese businesses to increase their production costs. This was a preemptive measure to maintain profitability if tariffs were ultimately imposed.
-
Pricing Strategies and Competitiveness: Increased production costs forced many companies to adjust their pricing strategies, reducing profit margins or risking a loss of market share in the face of increased global competition. This makes Japanese goods less competitive internationally.
-
Ripple Effect: The impact extended beyond large corporations. Smaller businesses within the supply chain also experienced increased costs, potentially leading to job losses and business closures in some cases. Many adopted cost-cutting measures impacting employees and overall business prospects.
-
Hedging Strategies: Some Japanese firms employed hedging strategies, such as diversifying their export markets or investing in automation to reduce labor costs and mitigate potential tariff risks. However, these strategies are often expensive and do not fully offset the negative impacts of tariff uncertainty.
Impact on Investment and Consumer Confidence
The uncertainty surrounding potential tariffs significantly dampened both business investment and consumer confidence during Q1 2024.
Reduced Business Investment
The looming threat of tariffs created a climate of uncertainty, leading many businesses to postpone or cancel investment projects.
-
Postponed Projects: Data from the Bank of Japan indicates a significant slowdown in capital expenditure in Q1, partly attributable to the hesitation among businesses to commit to large-scale investments under the threat of increased tariffs. Several large infrastructure projects were delayed, impacting both economic activity and employment.
-
Impact on Job Creation and Future Growth: The reduction in business investment directly impacted job creation and future economic growth. Reduced spending on expansion and innovation limited opportunities for employment and hindered long-term economic prospects.
Weakening Consumer Sentiment
The threat of higher prices due to potential tariff increases negatively impacted consumer confidence and spending.
-
Consumer Surveys and Retail Sales: Consumer confidence surveys conducted during Q1 showed a significant decline, with consumers expressing concerns about rising prices for imported goods. This apprehension translated into reduced retail sales figures, particularly in non-essential goods categories.
-
Impact on Household Budgets: The potential for higher prices on imported goods, even if tariffs are not immediately imposed, created anxiety among consumers. This impacted household budgets and spending habits, leading to a decrease in overall consumer expenditure.
Government Response and Mitigation Strategies
The Japanese government responded to the economic slowdown caused by the potential tariffs through fiscal and monetary policy adjustments, as well as active trade negotiations.
Fiscal and Monetary Policy Adjustments
The government implemented several measures aimed at mitigating the negative effects of potential tariffs.
-
Government Interventions: These interventions included a supplementary budget focused on supporting businesses and consumers. This comprised direct financial aid to affected industries, tax breaks, and infrastructure investment to stimulate economic growth.
-
Effectiveness of Measures: The effectiveness of these measures is still being assessed. While some sectors showed signs of recovery, the overall impact remains uncertain, particularly concerning the long-term effects on investment and consumer confidence.
Trade Negotiation Efforts
Japan actively engaged in trade negotiations to reduce or avoid potential tariffs.
-
Trade Agreements and Negotiations: Japan intensified efforts to strengthen existing trade agreements and negotiate new bilateral deals with key trading partners. These negotiations focused on reducing trade barriers and promoting free trade.
-
Strategic Alliances and Collaborative Efforts: Japan also actively collaborated with other countries facing similar protectionist pressures, seeking to form strategic alliances to counter protectionist measures on a global scale. This collaborative approach aims to strengthen the influence of free-trade proponents in international forums.
Conclusion
The threat of potential tariffs significantly impacted Japan's Q1 2024 economic performance, creating vulnerabilities in the export sector, dampening investment and consumer confidence. The government responded with fiscal and monetary policy adjustments and engaged in active trade negotiations. However, the long-term effects remain uncertain. Further research and analysis are crucial to fully understand the long-term effects of potential tariffs on Japan’s economic future. Stay updated on the evolving trade landscape and the impact on Japan’s Q1 economic performance and beyond by following reliable economic news sources and government reports. Understanding the ongoing impact of potential tariffs on Japan’s economy is vital for businesses and investors alike. The ongoing monitoring of Japan's Q1 economic performance, coupled with an analysis of potential tariff impacts, is essential for informed decision-making.

Featured Posts
-
 Onibus Universitario Se Envolve Em Acidente Grave Numero De Mortos Confirmados
May 17, 2025
Onibus Universitario Se Envolve Em Acidente Grave Numero De Mortos Confirmados
May 17, 2025 -
 Msum Bestows Honorary Degree On North Dakotas Wealthiest Individual
May 17, 2025
Msum Bestows Honorary Degree On North Dakotas Wealthiest Individual
May 17, 2025 -
 Greenkos Orix Stake Indian Founders Acquisition Plans
May 17, 2025
Greenkos Orix Stake Indian Founders Acquisition Plans
May 17, 2025 -
 The Shrinking Japanese Economy A Q1 2023 Review Before Tariff Implementation
May 17, 2025
The Shrinking Japanese Economy A Q1 2023 Review Before Tariff Implementation
May 17, 2025 -
 Giants Vs Mariners Injury Report April 4 6 Series Preview
May 17, 2025
Giants Vs Mariners Injury Report April 4 6 Series Preview
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Missouri State Board Of Education Welcomes Former Springfield Councilman
May 17, 2025
Missouri State Board Of Education Welcomes Former Springfield Councilman
May 17, 2025 -
 Apartment Building Demolition Approved By Davenport Council
May 17, 2025
Apartment Building Demolition Approved By Davenport Council
May 17, 2025 -
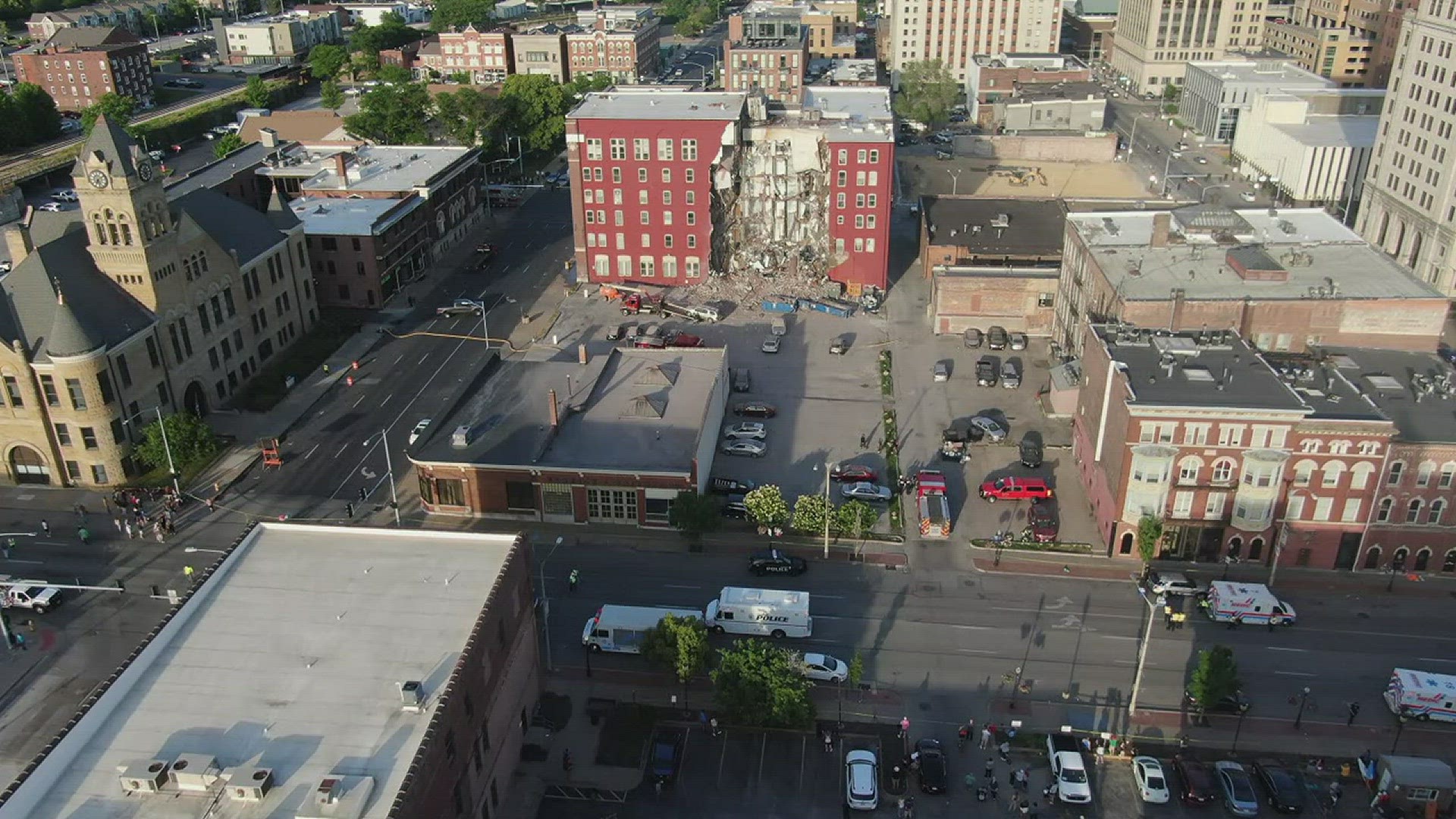 Davenport Greenlights Apartment Building Demolition
May 17, 2025
Davenport Greenlights Apartment Building Demolition
May 17, 2025 -
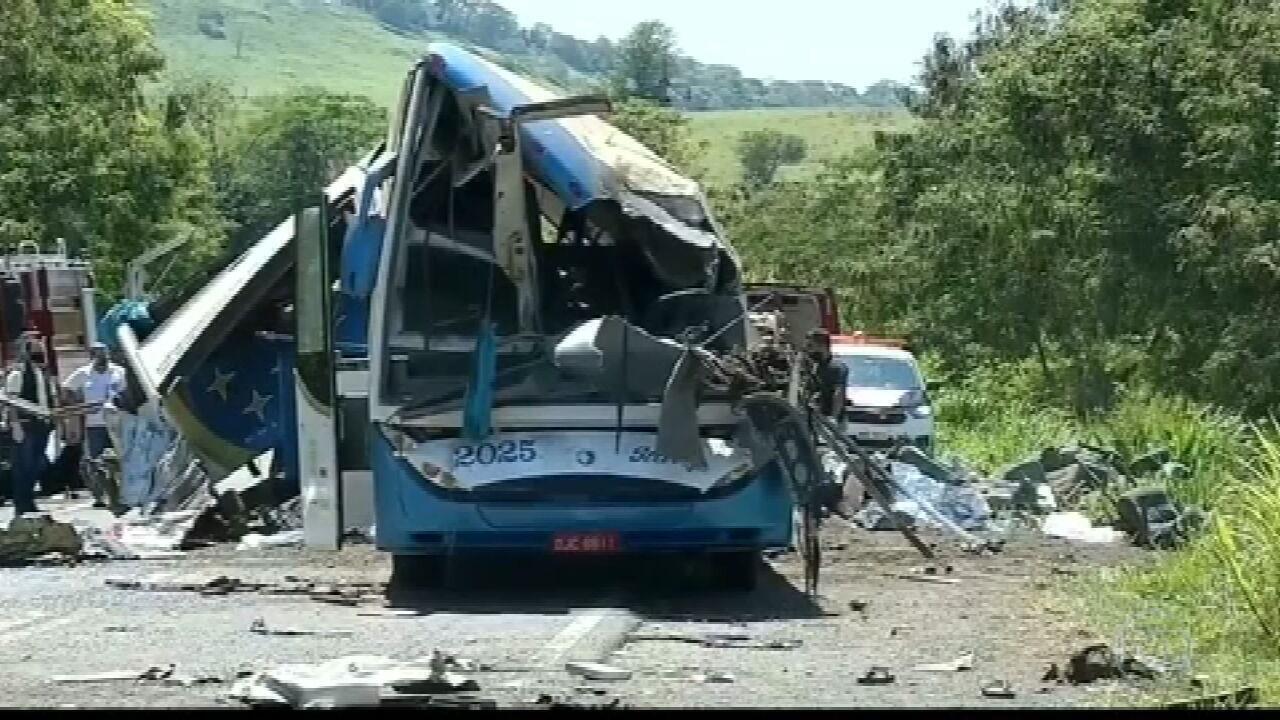 Numero Mortos Em Acidente Com Onibus Universitario Investigacao Em Andamento
May 17, 2025
Numero Mortos Em Acidente Com Onibus Universitario Investigacao Em Andamento
May 17, 2025 -
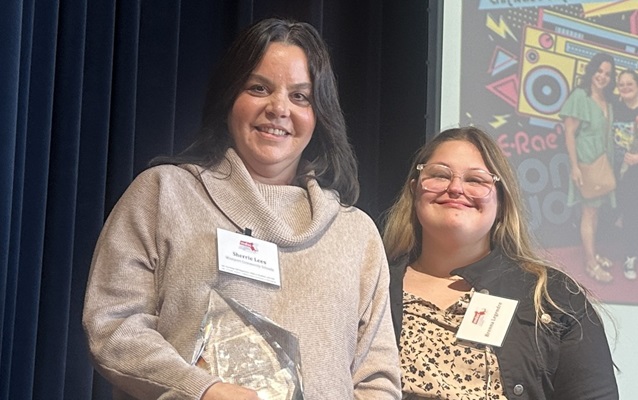 Fargo Educator Recognized For Outstanding Science Teaching Eagleson Honored
May 17, 2025
Fargo Educator Recognized For Outstanding Science Teaching Eagleson Honored
May 17, 2025
