Increased ADHD Diagnosis Rates Among Adults With Autism And Intellectual Disability: Study Findings
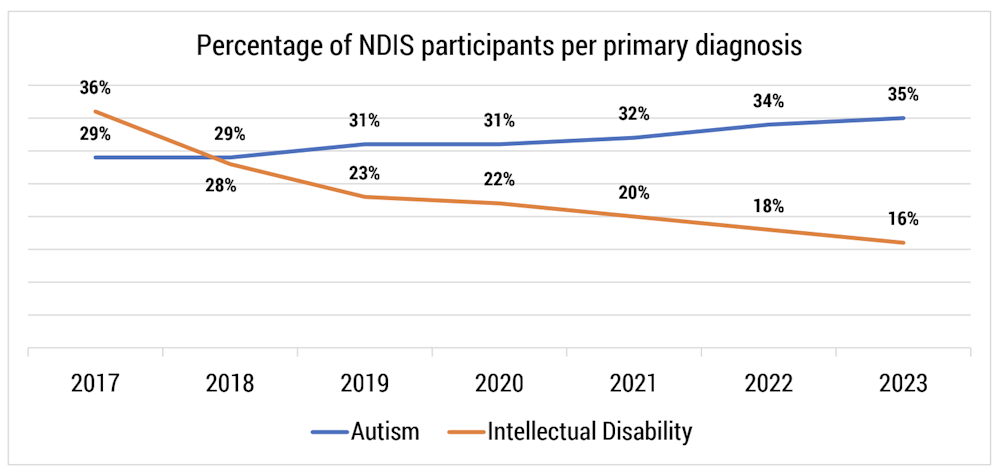
Table of Contents
The Complex Relationship Between ADHD, Autism, and Intellectual Disability
ADHD, autism, and intellectual disability often share overlapping symptoms, making accurate diagnosis challenging when multiple conditions are present. This comorbidity creates a complex interplay of behavioral manifestations, leading to potential misdiagnosis or significant delays in receiving appropriate support. Understanding the intricate connections between these conditions is vital for effective clinical practice.
- Difficulty Distinguishing Inattentive ADHD from Autism: The inattentive subtype of ADHD presents with symptoms like difficulty focusing, poor organization, and forgetfulness – traits also commonly associated with autism. Differentiating between the two can be challenging and requires careful assessment.
- Intellectual Disability Masking ADHD Symptoms: Individuals with intellectual disability may have difficulty communicating or demonstrating ADHD symptoms in typical ways. Their cognitive limitations can mask the underlying ADHD, leading to an underdiagnosis.
- Impact of Comorbidity on Symptom Severity and Functional Outcomes: The presence of multiple conditions often exacerbates symptom severity and negatively impacts daily functioning. Individuals with comorbid ADHD, autism, and ID may experience greater challenges in areas like academics, social interaction, and independent living. Effective interventions require a tailored approach that addresses all co-occurring conditions.
Findings from Recent Studies on ADHD Diagnosis Rates
Epidemiological studies are increasingly revealing higher prevalence rates of ADHD in adults with autism and intellectual disability compared to the general population. These research findings underscore the need for increased awareness and improved diagnostic practices within the clinical community. However, methodological limitations in some studies, such as variations in diagnostic criteria and challenges in data collection, need to be considered.
- Increased Prevalence: Several studies have reported significantly higher rates of ADHD diagnoses among adults with autism and/or intellectual disability. For example, [cite specific study 1] found that X% of adults with autism also met criteria for ADHD, while [cite specific study 2] reported a Y% prevalence rate of ADHD in adults with intellectual disability.
- Delayed Diagnosis: Many individuals with these co-occurring conditions receive their ADHD diagnosis significantly later in life, often in adulthood. This delay highlights the need for greater screening and awareness among healthcare professionals.
- Impact of Diagnostic Criteria: Variations in the diagnostic criteria used across different studies can impact the observed prevalence rates. Further research employing consistent diagnostic methodologies is crucial for accurate comparisons and a clearer understanding of the true prevalence.
Challenges in Diagnosing ADHD in Adults with Autism and Intellectual Disability
Assessing for ADHD in individuals with co-occurring autism and intellectual disability presents unique challenges. Traditional diagnostic tools often fall short, requiring specialized assessment approaches and expertise in comorbid conditions. Relying solely on standardized questionnaires may be insufficient due to communication and cognitive limitations.
- Limitations of Self-Report Measures: Self-report questionnaires, commonly used in ADHD assessments, may be unreliable for individuals with autism or intellectual disability who struggle with self-awareness or expressive language skills.
- Importance of Multiple Assessment Methods: A comprehensive approach necessitates multiple assessment methods, including informant reports from family members or caregivers, direct behavioral observation, and cognitive testing tailored to the individual's capabilities.
- Need for Specialized Assessment Tools: Specialized assessment tools are crucial to account for the complex interplay of symptoms and potential confounds in individuals with co-occurring conditions. These tools must be sensitive to the specific challenges posed by autism and intellectual disability.
The Importance of Comprehensive Assessments
A comprehensive evaluation conducted by a multidisciplinary team is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective interventions. This team should include professionals with expertise in ADHD, autism, and intellectual disability, allowing for a thorough differential diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Such a multidisciplinary approach ensures a more nuanced understanding of the individual's needs and challenges.
Conclusion
This article highlights the significant increase in ADHD diagnosis rates among adults with autism and intellectual disability, underscoring a pressing clinical need for better diagnostic tools and interventions. The considerable overlap in symptoms between these co-occurring conditions presents substantial diagnostic challenges. Accurate diagnosis hinges on employing comprehensive assessments that incorporate multiple data sources and specialized tools, utilizing a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. Further research is crucial to improve diagnostic accuracy and develop effective treatment strategies for this complex population. If you suspect you or a loved one may have ADHD, autism, intellectual disability, or a combination thereof, seeking a comprehensive diagnosis from a qualified professional is paramount to accessing appropriate support and interventions. Don't hesitate to seek help; early diagnosis and intervention are key to improving quality of life.

Featured Posts
-
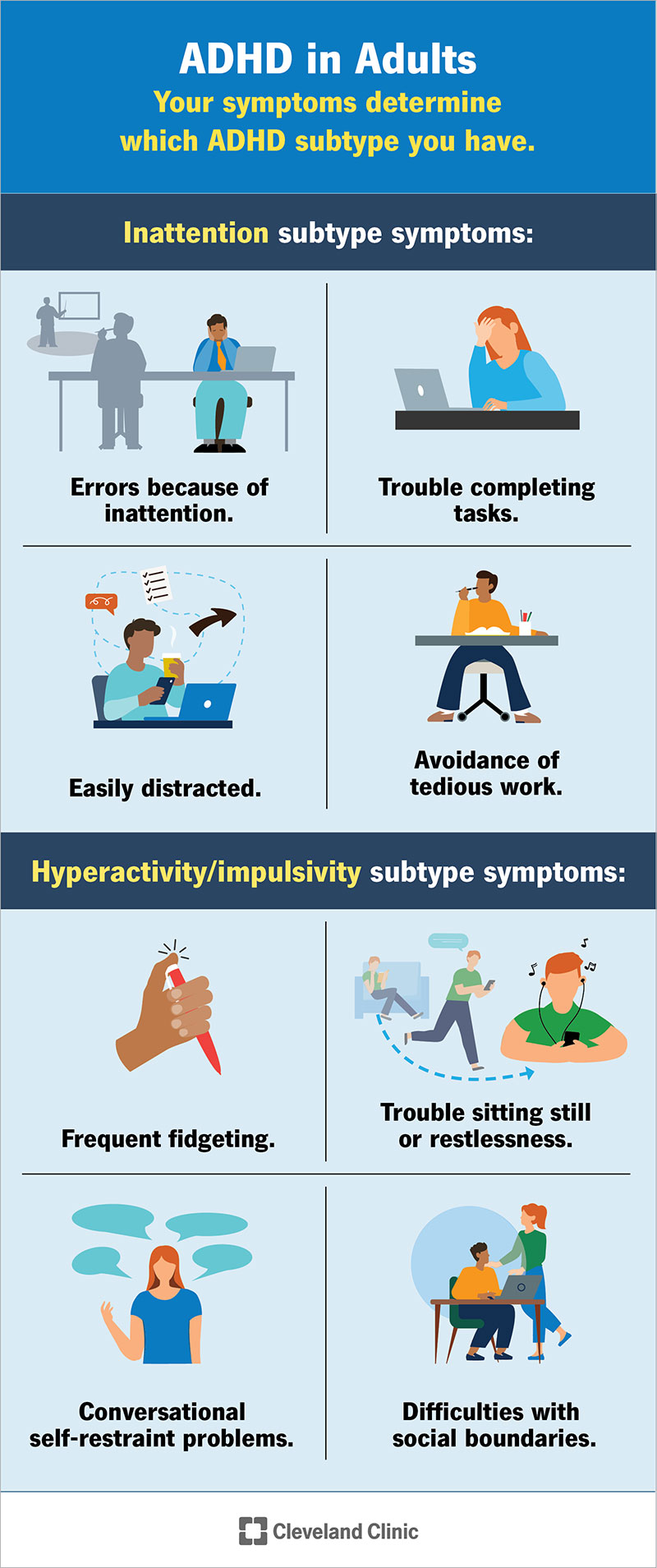 Diagnosed With Adult Adhd Your Action Plan
Apr 29, 2025
Diagnosed With Adult Adhd Your Action Plan
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Willie Nelsons 4th Of July Picnic A Texas Tradition Returns
Apr 29, 2025
Willie Nelsons 4th Of July Picnic A Texas Tradition Returns
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Culture Departments Canoe Awakening Event Highlights And Photos
Apr 29, 2025
The Culture Departments Canoe Awakening Event Highlights And Photos
Apr 29, 2025 -
 How You Tube Caters To Older Viewers A Look At Content And Accessibility
Apr 29, 2025
How You Tube Caters To Older Viewers A Look At Content And Accessibility
Apr 29, 2025 -
 How To Get Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets Tips And Strategies
Apr 29, 2025
How To Get Capital Summertime Ball 2025 Tickets Tips And Strategies
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Remy Cointreau Analyse Du Document Amf Cp 2025 E1029253
Apr 30, 2025
Remy Cointreau Analyse Du Document Amf Cp 2025 E1029253
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Document Amf Valeo Decryptage Du Cp 2025 E1027024 24 03 2025
Apr 30, 2025
Document Amf Valeo Decryptage Du Cp 2025 E1027024 24 03 2025
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Document Amf Arkema Cp 2025 E1027752 Decryptage Et Analyse
Apr 30, 2025
Document Amf Arkema Cp 2025 E1027752 Decryptage Et Analyse
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Rapport Sur Le Document Amf Cp 2025 E1027692 D Ubisoft Entertainment
Apr 30, 2025
Rapport Sur Le Document Amf Cp 2025 E1027692 D Ubisoft Entertainment
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Communique De Presse Valeo Amf Cp 2025 E1027024 24 Mars 2025
Apr 30, 2025
Communique De Presse Valeo Amf Cp 2025 E1027024 24 Mars 2025
Apr 30, 2025
