Increased Retail Sales: What It Means For Bank Of Canada Interest Rates
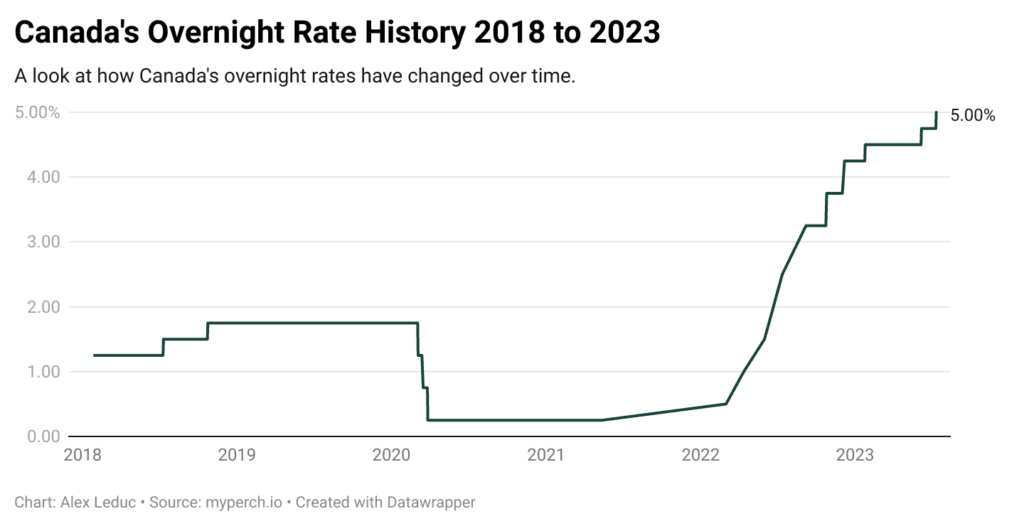
Table of Contents
The Relationship Between Retail Sales and Inflation
How Increased Retail Sales Fuel Inflation
A direct correlation exists between increased retail sales and inflation. Higher sales figures indicate robust consumer demand. When demand significantly outpaces supply, businesses often respond by raising prices, leading to inflation. This upward pressure on prices is a key concern for central banks worldwide, including the Bank of Canada.
- Examples of Sectoral Impact: A surge in automobile sales, for instance, can drive up the price of vehicles and related services. Similarly, strong furniture sales can contribute to increased lumber and manufacturing costs, impacting overall inflation.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): The CPI, a measure of the average change in prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services, directly reflects the impact of increased retail sales. Rising retail sales often translate to a higher CPI.
- Supply Chain Issues: Supply chain disruptions can exacerbate the inflationary effects of increased retail sales. When supply cannot keep pace with heightened demand, prices are likely to increase further.
Inflation's Impact on Bank of Canada Policy
The Bank of Canada closely monitors inflation data, primarily the CPI, to guide its monetary policy decisions. The Bank aims to maintain inflation within a specific target range, typically around 2%. Deviations from this target trigger policy responses.
- Bank of Canada's Mandate: The Bank's primary mandate is to maintain the stability of the Canadian dollar and keep inflation low, predictable, and sustainable.
- High Inflation and Interest Rates: When inflation rises significantly above the target rate, as often indicated by strong retail sales figures, the Bank of Canada typically responds by increasing interest rates. This is a tool to cool down the economy and curb excessive spending.
- Recessionary Risk: Aggressively raising interest rates to combat inflation carries the risk of slowing economic growth too much, potentially leading to a recession. Finding the right balance is a key challenge for the Bank.
How the Bank of Canada Responds to Increased Retail Sales
Interest Rate Hikes as a Cooling Mechanism
Raising interest rates is a primary mechanism the Bank of Canada uses to dampen excessive consumer spending and cool an overheated economy. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive.
- Impact on Borrowing Costs: Increased interest rates directly translate to higher mortgage rates, credit card interest, and business loan rates. This makes it more costly for consumers and businesses to borrow money, thus reducing spending.
- Impact on Consumer Confidence and Investment: Higher interest rates can also negatively impact consumer confidence, leading to reduced spending and investment. This cooling effect helps to moderate inflation.
Other Monetary Policy Tools
While interest rate adjustments are the most prominent tool, the Bank of Canada may also employ other monetary policy tools.
- Quantitative Tightening (QT): This involves the Bank selling government bonds, reducing the money supply and thus curbing inflation. This is the opposite of quantitative easing (QE), where the Bank buys bonds to increase the money supply.
- Other Factors: The Bank considers numerous factors beyond retail sales when making decisions, including employment rates, housing market conditions, and global economic developments.
Predicting Future Interest Rate Movements Based on Retail Sales
Analyzing Retail Sales Data for Trends
Analyzing retail sales data over time is crucial for identifying trends and predicting future economic activity, including potential interest rate movements.
- Reliable Data Sources: Statistics Canada provides reliable retail sales data. Analyzing this data, along with other economic indicators, offers valuable insights.
- Seasonal Adjustments: It’s essential to consider seasonal adjustments in retail sales data, as certain sectors experience naturally higher sales during specific times of the year.
- Leading and Lagging Indicators: Retail sales data can serve as a leading indicator of future inflation, providing valuable information for predicting interest rate changes.
The Importance of Context
While retail sales data is vital, it's crucial to consider other economic factors when predicting interest rate movements.
- Other Key Indicators: Employment rates, housing market data (housing starts, prices), and global economic conditions significantly influence the Bank of Canada's decisions.
- Complexity of Forecasting: Predicting interest rate movements is complex. No single indicator, including retail sales, provides a complete picture. A holistic approach, considering multiple economic factors, is necessary for accurate forecasting.
Conclusion
Increased retail sales often signal robust consumer demand, which can lead to inflationary pressures. This, in turn, may prompt the Bank of Canada to raise interest rates to curb spending and maintain price stability. The relationship is complex, requiring careful consideration of various economic indicators beyond just increased retail sales. Understanding the interplay between increased retail sales and Bank of Canada interest rates is crucial for informed financial decision-making.
Call to Action: Stay informed about increased retail sales data and its impact on Bank of Canada interest rates to make informed financial decisions. Regularly monitor economic news and reports to understand the current economic landscape and plan accordingly. Understanding the impact of increased retail sales on interest rates is key to successful financial planning.

Featured Posts
-
 Le Parti Socialiste Divise Bouamrane Face A Faure Au Congres
May 27, 2025
Le Parti Socialiste Divise Bouamrane Face A Faure Au Congres
May 27, 2025 -
 Mission Impossible Dead Reckoning Part One Cast And Character Guide
May 27, 2025
Mission Impossible Dead Reckoning Part One Cast And Character Guide
May 27, 2025 -
 No Relief For Port Of Spain Commuters State Of Emergency Assessment
May 27, 2025
No Relief For Port Of Spain Commuters State Of Emergency Assessment
May 27, 2025 -
 Stavot Na Rubio Tramp Nema Da Pregovara Beskonechno So Putin
May 27, 2025
Stavot Na Rubio Tramp Nema Da Pregovara Beskonechno So Putin
May 27, 2025 -
 Major Bandit Kingpin Eliminated In Zamfara Police Operation
May 27, 2025
Major Bandit Kingpin Eliminated In Zamfara Police Operation
May 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Unsolved Mystery Banksy Paintings Origin And Tagger
May 31, 2025
Unsolved Mystery Banksy Paintings Origin And Tagger
May 31, 2025 -
 Is Banksy Female Exploring The Evidence Surrounding The Anonymous Street Artist
May 31, 2025
Is Banksy Female Exploring The Evidence Surrounding The Anonymous Street Artist
May 31, 2025 -
 Auction Preview Banksys Broken Heart Wall
May 31, 2025
Auction Preview Banksys Broken Heart Wall
May 31, 2025 -
 The Banksy Gender Debate Examining The Clues And Contradictions
May 31, 2025
The Banksy Gender Debate Examining The Clues And Contradictions
May 31, 2025 -
 Banksy Broken Heart Artwork To Be Auctioned
May 31, 2025
Banksy Broken Heart Artwork To Be Auctioned
May 31, 2025
