Inflation's Persistence: ECB Links It To Continued Pandemic Fiscal Support

Table of Contents
The ECB's Stance on Inflation and Fiscal Policy
The ECB's primary mandate is price stability, defined as maintaining inflation at 2% over the medium term. However, current inflation levels in the Eurozone significantly exceed this target, prompting considerable concern within the ECB. The Bank views the relationship between fiscal stimulus and inflation as complex, acknowledging the beneficial role of government spending in supporting economic recovery during crises. However, prolonged and excessive fiscal support can overheat the economy, leading to demand-pull inflation, where strong demand outpaces supply.
The ECB's analysis emphasizes that while fiscal support played a vital role in mitigating the immediate economic impact of the pandemic, its continued presence contributes to inflationary pressures. This is particularly true when considering the supply chain disruptions that have also fueled inflation.
- ECB Statements and Policy Decisions:
- In several press releases and statements, the ECB has emphasized the need for a gradual reduction in fiscal support to avoid further fueling inflation.
- The ECB closely monitors inflation expectations, recognizing that persistently high inflation can become self-fulfilling if individuals and businesses expect prices to continue rising.
- The ECB has responded to rising inflation with a series of interest rate hikes, aiming to cool down the economy and curb inflation. These decisions reflect a shift towards a more restrictive monetary policy stance.
The Impact of Pandemic Fiscal Support on Inflation
The surge in government spending during the pandemic significantly boosted aggregate demand. Wage subsidies, grants to businesses, and direct payments to households all increased disposable income, leading to higher consumer spending. This surge in demand, coupled with supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic, exacerbated inflationary pressures.
Supply chain bottlenecks, resulting from factory closures, logistical challenges, and labor shortages, restricted the supply of goods and services. This supply-side constraint contributed to cost-push inflation, where increased production costs are passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
The current inflationary environment is a complex interplay of both demand-pull and cost-push factors. While pandemic fiscal support fueled demand, supply-side constraints amplified the inflationary impact.
- Effects of Specific Fiscal Support Measures:
- Government support measures led to a noticeable increase in consumer spending across various sectors, contributing to demand-pull inflation.
- Interventions aimed at supporting businesses also influenced input costs. For example, measures intended to mitigate energy price increases for businesses inadvertently increased their production costs, further fueling cost-push inflation.
- Analysis of various fiscal programs reveals varying degrees of effectiveness, with some contributing more significantly to inflationary pressures than others.
Potential Future Monetary Policy Responses
To combat persistent inflation, the ECB has several monetary policy tools at its disposal. These include further interest rate hikes, quantitative tightening (reducing the size of its balance sheet), and adjustments to its forward guidance (communication about future policy intentions). The ECB faces a delicate balancing act: controlling inflation while simultaneously supporting economic growth and avoiding a sharp economic downturn.
Raising interest rates increases borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially dampening economic activity. Quantitative tightening reduces the amount of liquidity in the financial system, similarly aiming to curb inflation. However, these measures could also negatively affect investment and economic growth.
- Possible Future Policy Decisions:
- Further interest rate increases are a strong possibility, depending on the evolution of inflation and economic growth.
- Quantitative tightening is another tool the ECB might employ to reduce liquidity and curb inflation.
- The impact of these policy decisions on different sectors of the economy will vary, with some sectors being more sensitive to interest rate changes than others.
Conclusion
The ECB's assessment clearly links persistent inflation in the Eurozone to the continued impact of pandemic fiscal support. While necessary in the initial stages of the pandemic, prolonged fiscal stimulus, coupled with supply chain disruptions, has fueled both demand-pull and cost-push inflation. The ECB's response, involving interest rate hikes and potential quantitative tightening, aims to regain price stability without triggering a significant economic slowdown.
To stay informed about the evolving inflation landscape and the ECB's policy responses, continue researching topics such as "ECB inflation forecasts," "impact of fiscal policy on inflation," and "managing inflation in the Eurozone." Understanding the complex interplay between fiscal and monetary policies is essential for comprehending and navigating the challenges of inflation management in the Eurozone. Staying informed about the ECB's actions is key to understanding and managing the impact of inflation on your personal finances and business investments.

Featured Posts
-
 Harvard University And The Trump Administration A Legal Battle Over Federal Funding
Apr 29, 2025
Harvard University And The Trump Administration A Legal Battle Over Federal Funding
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Voice Assistant Creation Revolutionized Open Ais 2024 Developer Event
Apr 29, 2025
Voice Assistant Creation Revolutionized Open Ais 2024 Developer Event
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Tornado And Flooding Emergency Louisville Under State Of Emergency
Apr 29, 2025
Tornado And Flooding Emergency Louisville Under State Of Emergency
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Trump To Pardon Pete Rose A Look At The Potential Presidential Pardon
Apr 29, 2025
Trump To Pardon Pete Rose A Look At The Potential Presidential Pardon
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Russian Militarys Moves Why Europe Is Concerned
Apr 29, 2025
The Russian Militarys Moves Why Europe Is Concerned
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Legendas F1 Technologia Hogyan Forradalmasitja Ezt A Porsche T
Apr 29, 2025
Legendas F1 Technologia Hogyan Forradalmasitja Ezt A Porsche T
Apr 29, 2025 -
 2024 M Porsche Automobiliu Pardavimu Statistika Lietuvoje
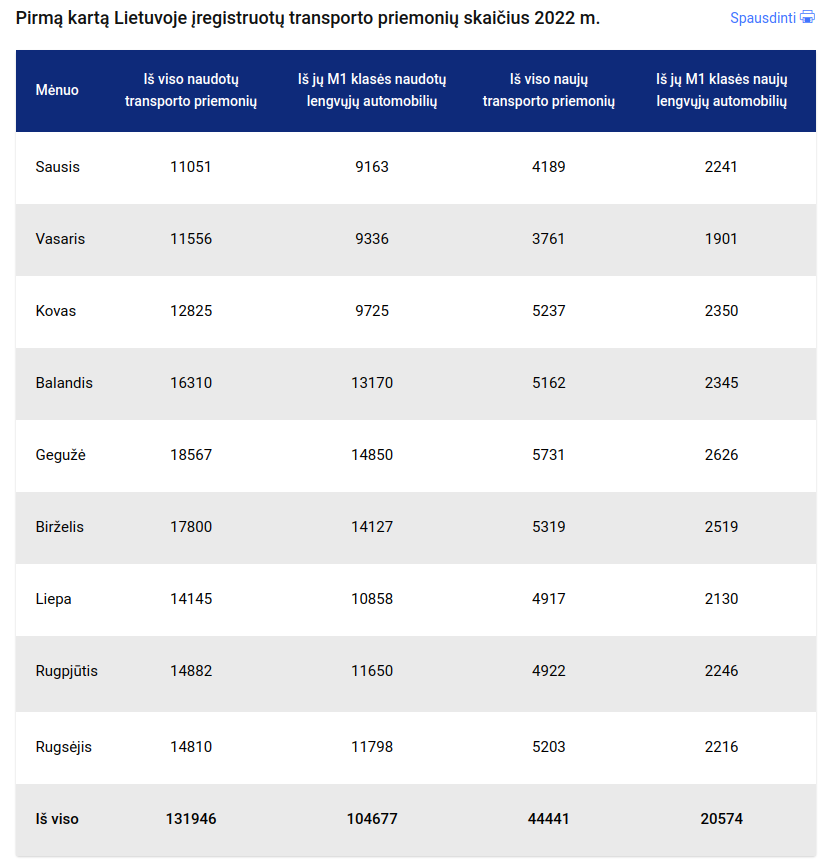
Apr 29, 2025
2024 M Porsche Automobiliu Pardavimu Statistika Lietuvoje
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Porsche Koezuti Autot F1 Motor Haja Muszaki Adatok Es Teljesitmeny
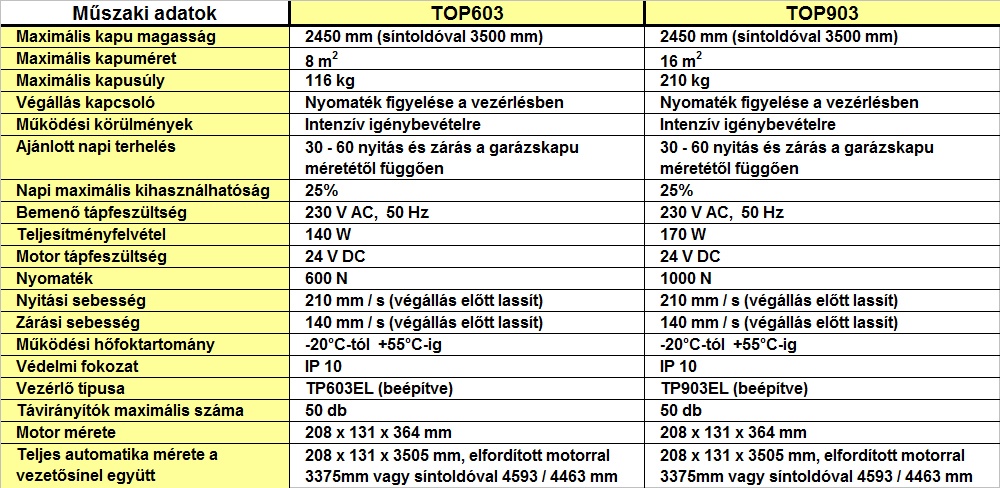
Apr 29, 2025
Porsche Koezuti Autot F1 Motor Haja Muszaki Adatok Es Teljesitmeny
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Hit Sprzedazy Porsche 911 Za 1 33 Mln Zl Podbija Polske
Apr 29, 2025
Hit Sprzedazy Porsche 911 Za 1 33 Mln Zl Podbija Polske
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Lietuvos Porsche Rinkos Augimas 2024 Metais Analize Ir Prognozes
Apr 29, 2025
Lietuvos Porsche Rinkos Augimas 2024 Metais Analize Ir Prognozes
Apr 29, 2025
