Is A New COVID-19 Variant Behind The Rising Case Numbers?
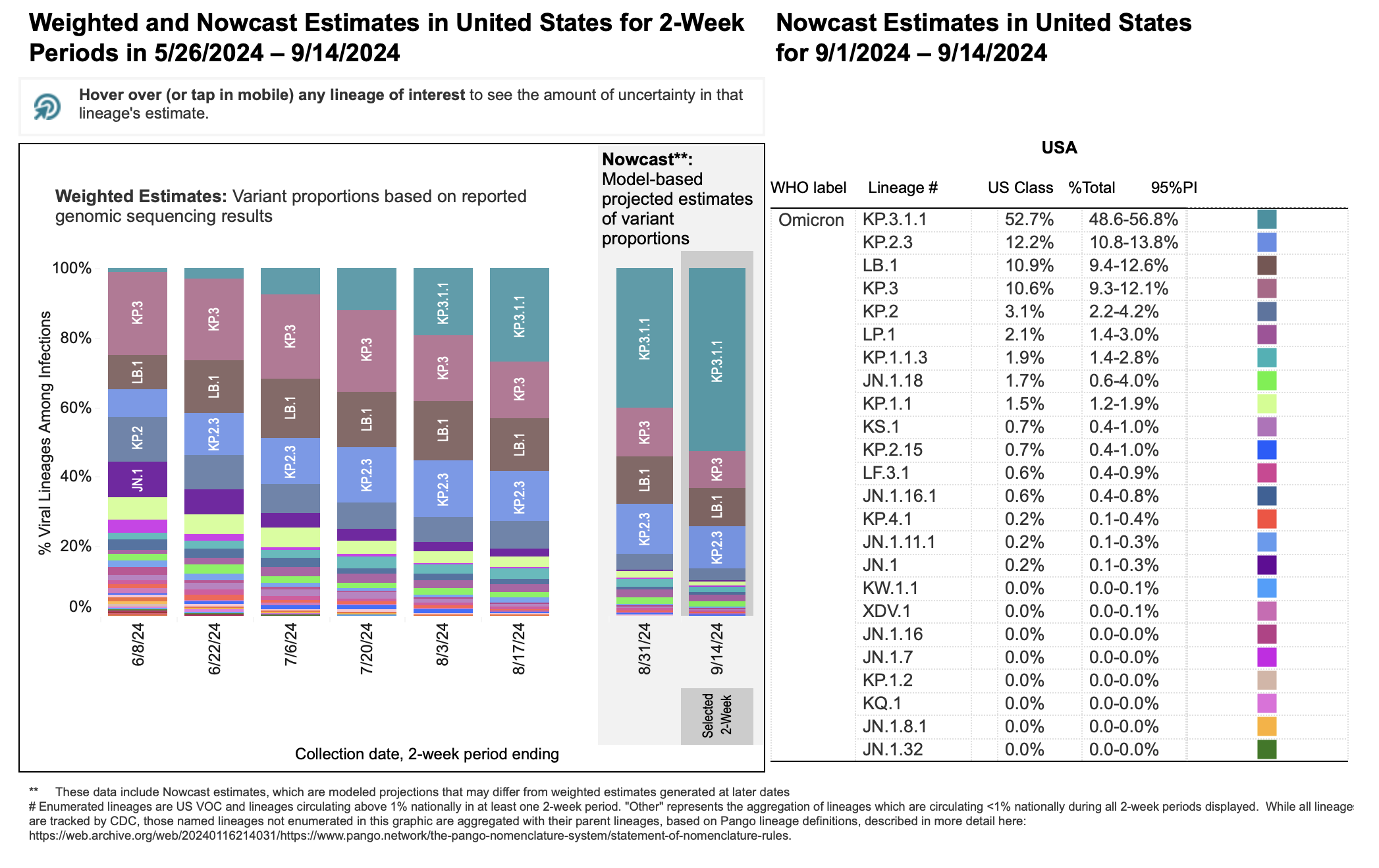
Table of Contents
The Current COVID-19 Landscape: Understanding the Increase
Global Case Numbers and Trends
Recent reports from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicate a noticeable increase in COVID-19 infections across various regions. This isn't a uniform global surge; certain areas are experiencing more significant increases than others.
- Percentage Increase: Some regions report a 20-30% increase in cases within the past month. (Source: [Insert Link to WHO or CDC data]).
- Regions Most Affected: [List specific regions with the most substantial increases, citing sources]. For example, [Region A] is experiencing a sharp rise in hospitalizations, while [Region B] is seeing a more gradual increase but with a concerning rise in severe cases.
- [Insert graph or chart visualizing global case number trends, clearly labeled and sourced].
Severity of Current Infections
While case numbers are rising, the severity of the current infections is crucial to understand. Are we seeing a return to the high hospitalization and death rates of previous waves, or is the current situation less severe?
- Hospitalization Rates: [Compare current hospitalization rates with previous waves, citing specific data and sources]. Are these rates significantly higher, lower, or comparable?
- ICU Admissions: Similar to hospitalization rates, a comparison of current ICU admissions with past waves is vital to understanding the severity. [Insert data and sources].
- Death Rates: The mortality rate provides a critical indicator of disease severity. [Compare current death rates with those of previous waves, providing sources].
- Symptom Variations: Anecdotal reports suggest [mention any reported variations in symptoms compared to previous waves, acknowledging the limitations of anecdotal evidence]. Further research is needed to confirm these observations.
Identifying Potential New Variants
Variant Tracking and Surveillance
Scientists constantly monitor for new COVID-19 variants through genomic sequencing. This process involves analyzing the genetic material of the virus to identify mutations and track the emergence of new variants.
- Genomic Sequencing Process: Genomic sequencing involves isolating the virus's RNA, converting it to DNA, and then sequencing the DNA to determine its genetic code. This process allows scientists to identify mutations and track the spread of different variants.
- Key Organizations: The WHO, CDC, and numerous national public health agencies worldwide actively participate in variant tracking and surveillance, sharing data globally through collaborative networks.
Characteristics of Emerging Variants (if any)
[If specific new variants are suspected to be contributing to the rise in cases, include this section. Otherwise, remove or adjust this section to reflect the current scientific understanding.]
- Variant Name (e.g., XBB.1.16): [Describe the variant's key mutations and their potential impact on transmissibility, severity, and vaccine efficacy. Cite reputable scientific publications or pre-print studies supporting your claims].
- Transmissibility: [Discuss the variant's potential to spread more easily than previous variants].
- Severity: [Explain whether the variant is associated with more severe illness or different clinical presentations].
- Vaccine Resistance: [Assess whether the variant exhibits resistance to currently available vaccines].
Other Factors Contributing to Rising Cases
Seasonality and Immunity Waning
Several factors beyond new variants might contribute to the increase in cases.
- Seasonality: Respiratory viruses, including coronaviruses, often show seasonal patterns. The colder months may favor viral transmission.
- Waning Immunity: Immunity from previous infections or vaccinations can wane over time, making individuals more susceptible to reinfection. This waning immunity is a significant factor to consider in understanding rising case numbers.
Reduced Public Health Measures
The relaxation or discontinuation of public health measures can also influence the spread of COVID-19.
- Reduced Testing: Decreased testing rates might lead to underreporting of actual case numbers.
- Reduced Masking and Social Distancing: The reduced adherence to these preventative measures can contribute to increased transmission.
- Reasons for Reduced Measures: The reasons for reduced public health measures are complex and vary across regions, often related to the perceived lower risk due to lower severity and the desire to return to normalcy.
Conclusion
While the possibility of a new COVID-19 variant driving the current increase in cases cannot be ruled out, it's crucial to consider other factors like waning immunity, seasonal effects, and reduced public health measures. The current situation underscores the need for continued monitoring of emerging variants and vigilant public health surveillance. The identification and characterization of any new COVID-19 variant are essential for informed public health responses and the development of effective countermeasures. Stay informed about potential new COVID-19 variants and protect yourself and your community by consulting reliable sources such as the WHO and CDC websites for the latest updates and guidance.

Featured Posts
-
 Animal Pornography Case Kelvedon Resident Matthew Sexton
May 31, 2025
Animal Pornography Case Kelvedon Resident Matthew Sexton
May 31, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Thursday April 10th Clues And Answers
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Thursday April 10th Clues And Answers
May 31, 2025 -
 Are Tech Companies Responsible When Algorithms Radicalize Mass Shooters
May 31, 2025
Are Tech Companies Responsible When Algorithms Radicalize Mass Shooters
May 31, 2025 -
 Learn Skywarn Spotter Skills From Meteorologist Tom Atkins
May 31, 2025
Learn Skywarn Spotter Skills From Meteorologist Tom Atkins
May 31, 2025 -
 Alexander Zverev Loses To Tallon Griekspoor At Indian Wells
May 31, 2025
Alexander Zverev Loses To Tallon Griekspoor At Indian Wells
May 31, 2025
