Is Age Just A Number? A Look At Ageism And Its Impact
Table of Contents
Ageism is defined as prejudice or discrimination based on a person's age. It manifests in stereotypes, biased attitudes, and discriminatory actions against individuals simply because of their age, most often targeting older adults. This article will delve into the various forms ageism takes, its devastating effects, and what we can do to create a more equitable and age-inclusive society.
The Reality of Age Discrimination in Employment
Age discrimination in employment is a pervasive issue impacting the lives and livelihoods of millions of older workers. It often manifests subtly, through biased hiring practices, overlooking experienced candidates for younger ones, or denying promotions based on perceived age-related limitations. Workplace ageism can also create a hostile environment where older employees feel undervalued and marginalized.
- Hiring Practices: Recruiters may unconsciously favor younger applicants, assuming they are more technologically savvy or adaptable.
- Promotions & Advancement: Older employees may be passed over for promotions, even if they possess superior skills and experience.
- Forced Retirement: While mandatory retirement is illegal in many countries, subtle pressures to retire early can be pervasive.
Statistics highlight the severity of the problem. Studies consistently show higher unemployment rates among older adults compared to younger workers. Furthermore, the number of age discrimination lawsuits remains substantial, demonstrating the continued prevalence of unfair treatment.
Combating Ageism in the Workplace
Combating workplace ageism requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Highlight Transferable Skills: Older workers should emphasize their adaptability and transferable skills, demonstrating their ability to learn new technologies and adapt to changing workplace dynamics.
- Continuous Learning: Staying current with industry trends and acquiring new skills demonstrates commitment and adaptability, countering age-related stereotypes.
- Networking: Building and maintaining strong professional networks can open doors to new opportunities and help older workers navigate age-related biases.
- Legal Protections: Understanding and utilizing legal protections against age bias in hiring (such as the Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA) in the US) is crucial.
Companies benefit immensely from age diversity. Older workers bring a wealth of experience, institutional knowledge, and a strong work ethic. Embracing age diversity fosters a more inclusive and productive work environment.
Ageism in Healthcare: Access, Treatment, and Bias
Ageism in healthcare is a serious concern, affecting access to quality care, treatment decisions, and overall well-being. Older adults often face age-related stereotypes that influence medical professionals' perceptions and actions. This can result in underdiagnosis, undertreatment, and even premature dismissal of their concerns.
- Access to Care: Older adults may face barriers to accessing specialized care or essential services due to financial constraints, transportation challenges, or ageist assumptions about their needs.
- Treatment Decisions: Age may be used as a factor to justify withholding potentially life-saving treatments or procedures.
- Stereotypical Assumptions: Assumptions about frailty, cognitive decline, or lack of resilience can lead to biased assessments and treatment plans.
Improving Healthcare for Older Adults
Addressing age bias in healthcare requires systemic change:
- Patient-Centered Care: Prioritizing individual patient needs and preferences, recognizing that chronological age doesn't dictate health status or capacity.
- Education & Training: Providing medical professionals with comprehensive training on age-related issues, addressing ageist biases, and promoting culturally competent care.
- Addressing Health Disparities: Tackling age-related health disparities requires proactive efforts to ensure equitable access to healthcare resources for all age groups.
The Social and Psychological Impact of Ageism
The psychological impact of ageism is profound. Ageist stereotypes can lead to feelings of isolation, low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety among older adults. These feelings can significantly impact their overall quality of life and well-being. Social isolation becomes a serious concern as ageist attitudes can lead to exclusion from social circles and diminished opportunities for meaningful interactions.
- Negative Self-Perception: Internalizing ageist stereotypes can negatively affect self-image and lead to reduced self-efficacy.
- Social Exclusion: Ageist attitudes can lead to exclusion from social activities, employment opportunities, and even family interactions.
- Reduced Life Satisfaction: The cumulative effects of ageism can contribute to lower life satisfaction and increased feelings of helplessness.
Challenging Ageist Stereotypes
Combating ageist stereotypes necessitates a societal shift:
- Positive Media Representation: Promoting positive and diverse representations of older adults in media and popular culture can help challenge negative stereotypes.
- Intergenerational Interactions: Encouraging intergenerational programs and activities can foster understanding and break down age-related barriers.
- Challenging Ageist Language: Actively challenging ageist language and attitudes in everyday conversations promotes a more inclusive environment.
Reframing the Narrative – Age is Not Just a Number
This article has highlighted the pervasive and damaging effects of ageism across employment, healthcare, and social well-being. The significant psychological impact and widespread age discrimination demand immediate attention. We must challenge ageist attitudes and behaviors at both individual and systemic levels. Creating a truly age-inclusive society requires conscious effort from individuals, organizations, and policymakers.
Let's work together to challenge the pervasive idea that "age is just a number" and instead embrace age as a source of wisdom, experience, and valuable contributions. Learn more about ageism and how you can make a difference! [Link to relevant resource 1] [Link to relevant resource 2]
Featured Posts
-
 Kamala Harris Criticized For Rambling Speech At Broadway Musical
Apr 30, 2025
Kamala Harris Criticized For Rambling Speech At Broadway Musical
Apr 30, 2025 -
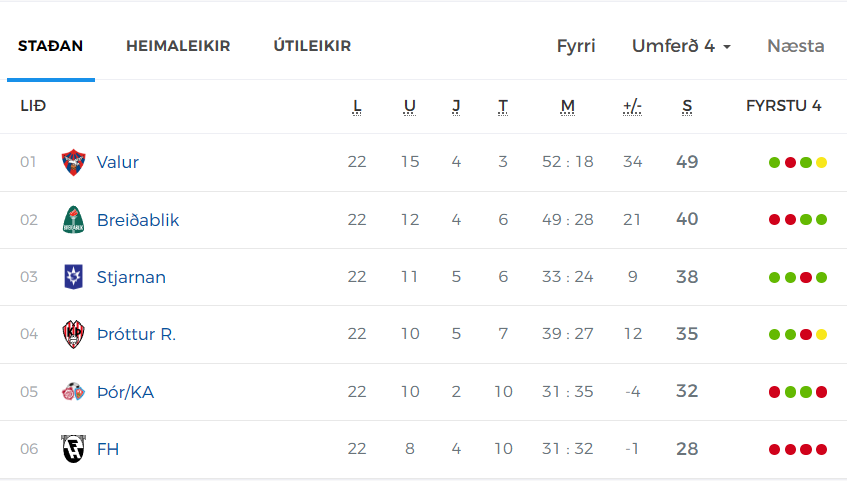 Dagskrain I Dag T Hrir Leikir I Bestu Deildinni
Apr 30, 2025
Dagskrain I Dag T Hrir Leikir I Bestu Deildinni
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Rodon Leads Yankees To Victory In Series Finale Against Cleveland
Apr 30, 2025
Rodon Leads Yankees To Victory In Series Finale Against Cleveland
Apr 30, 2025 -
 20 Nfl Players Who Should Demand A Trade This Offseason
Apr 30, 2025
20 Nfl Players Who Should Demand A Trade This Offseason
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Independent Office For Police Conduct Iopc Challenges Chris Kaba Panorama
Apr 30, 2025
Independent Office For Police Conduct Iopc Challenges Chris Kaba Panorama
Apr 30, 2025
