Japan's Rising Bond Yields: A Challenge For Economic Stability

Table of Contents
The Causes of Rising JGB Yields
The upward trajectory of JGB yields is a multifaceted problem stemming from both internal and external factors. Understanding these root causes is crucial to addressing the broader economic implications.
Weakening Yen and Inflationary Pressures
The weakening yen, coupled with rising global inflation, is a major driver of increased JGB yields. This combination creates a perfect storm impacting Japan's economy.
- Increased import costs directly impact inflation: A weaker yen makes imported goods more expensive, fueling domestic price increases and eroding purchasing power. This forces the Bank of Japan (BOJ) to reconsider its monetary policy, potentially leading to adjustments in yield curve control.
- A weaker yen makes foreign investments in JGBs less attractive: Reduced demand from foreign investors contributes to upward pressure on yields as the relative return on JGBs diminishes compared to investments in other currencies.
- Global inflationary pressures increase investor expectations for higher yields globally: The global inflationary environment leads investors to seek higher returns, impacting demand for JGBs and pushing yields higher. This global context cannot be ignored when analyzing Japan's specific situation.
Shifting Market Sentiment and Speculation
Growing speculation about the BOJ abandoning its yield curve control (YCC) policy is significantly contributing to the rise in JGB yields. This market sentiment is a powerful force driving investor behavior.
- Increased market volatility increases uncertainty and influences investor behavior towards JGBs: Uncertainty surrounding the future direction of BOJ policy creates volatility, prompting investors to adjust their positions and potentially driving up yields.
- Speculation around policy changes creates a self-fulfilling prophecy, driving up yields: The anticipation of higher interest rates can lead to immediate action by investors, creating a feedback loop that amplifies the upward pressure on JGB yields.
- International investors' changing risk appetite also plays a crucial role in the market sentiment: Global economic conditions and shifts in risk tolerance among international investors influence their demand for JGBs, impacting yields.
Implications of Rising JGB Yields for Japan's Economy
The rise in JGB yields has far-reaching consequences for the Japanese economy, impacting government finances, corporate investment, and consumer spending.
Increased Borrowing Costs for the Government
Higher yields directly translate into increased borrowing costs for the Japanese government, putting pressure on its already substantial public debt.
- Higher interest payments necessitate budget reallocations, potentially impacting social programs: Increased debt servicing costs could force the government to cut spending in other areas, potentially impacting vital social programs and infrastructure development.
- Increased borrowing costs could lead to reduced government spending in other areas: To manage the rising interest burden, the government may be forced to reduce spending on critical areas like education, healthcare, or research and development.
- The potential for a debt crisis is a significant concern if yields continue to rise rapidly: Uncontrolled increases in JGB yields could lead to a debt crisis if the government is unable to manage its interest payments.
Impact on Corporate Investment and Consumer Spending
Rising interest rates ripple through the economy, impacting both businesses and consumers.
- Reduced corporate investment may hinder economic growth and job creation: Higher borrowing costs discourage businesses from investing in expansion, innovation, and job creation, potentially leading to slower economic growth.
- Higher mortgage rates can decrease consumer spending on housing and other durable goods: Increased borrowing costs for mortgages and loans reduce consumer spending, dampening overall economic activity.
- A slowdown in economic activity could negatively impact tax revenues for the government: Reduced economic activity leads to lower tax revenues, creating a vicious cycle that exacerbates the government's fiscal challenges.
Potential Responses and Policy Adjustments
Addressing the challenge of Japan's rising bond yields requires a coordinated response involving both monetary and fiscal policy adjustments.
The Bank of Japan's Policy Dilemma
The BOJ faces a difficult balancing act: maintaining its YCC policy to support economic growth while simultaneously controlling inflation.
- Gradual adjustments to YCC policy might be a more manageable approach: A gradual and controlled adjustment to the YCC policy could help to manage market expectations and minimize disruption.
- Communication with the market is crucial to manage expectations and avoid sudden market reactions: Clear and transparent communication from the BOJ about its policy intentions is essential to maintain market stability.
- Close monitoring of inflation and economic indicators is critical for informed decision-making: The BOJ must carefully monitor economic data to make informed decisions about its policy adjustments.
Fiscal Policy Measures to Mitigate the Impact
The Japanese government can also employ fiscal measures to mitigate the negative impacts of rising JGB yields.
- Strategic investments in infrastructure projects could stimulate economic activity: Investing in infrastructure can boost economic activity, create jobs, and stimulate demand, counteracting the negative effects of higher interest rates.
- Tax incentives for businesses and consumers might encourage spending and investment: Targeted tax cuts or incentives can encourage businesses to invest and consumers to spend, boosting economic growth.
- Careful consideration of the long-term fiscal sustainability is essential: Any fiscal measures must be carefully considered within the context of Japan's long-term fiscal sustainability.
Conclusion
The rise in Japan's bond yields presents a complex and significant challenge to its economic stability. The interplay of a weakening yen, global inflation, shifting market sentiment, and the BOJ's monetary policy creates a precarious situation. Addressing this requires a nuanced approach involving careful adjustments to monetary policy, proactive fiscal measures, and transparent communication to manage market expectations. Failure to address Japan's rising bond yields effectively could have significant long-term consequences for the Japanese economy. Understanding the intricacies of Japan's rising bond yields is crucial for navigating the future economic landscape. Stay informed on this critical development and learn more about the implications of Japan's rising bond yields through further research and analysis.

Featured Posts
-
 Securing A Future Local Students Awarded Stem Scholarships
May 17, 2025
Securing A Future Local Students Awarded Stem Scholarships
May 17, 2025 -
 Exclusive Experiences Promised To Donors At Trump Military Events
May 17, 2025
Exclusive Experiences Promised To Donors At Trump Military Events
May 17, 2025 -
 Ray Epps Sues Fox News For Defamation Jan 6th Claims At The Center Of Lawsuit
May 17, 2025
Ray Epps Sues Fox News For Defamation Jan 6th Claims At The Center Of Lawsuit
May 17, 2025 -
 1050 Price Hike At And Ts Concerns Over Broadcoms V Mware Acquisition
May 17, 2025
1050 Price Hike At And Ts Concerns Over Broadcoms V Mware Acquisition
May 17, 2025 -
 Local Students Awarded Stem Scholarships Applications And Resources
May 17, 2025
Local Students Awarded Stem Scholarships Applications And Resources
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Improving Florida School Lockdown Drills Preparing Students And Staff For Active Shooter Situations
May 17, 2025
Improving Florida School Lockdown Drills Preparing Students And Staff For Active Shooter Situations
May 17, 2025 -
 Ralph Laurens Fall 2025 Riser A Comprehensive Overview
May 17, 2025
Ralph Laurens Fall 2025 Riser A Comprehensive Overview
May 17, 2025 -
 Deep Dive Ralph Lauren Fall 2025 Riser Fashion Show
May 17, 2025
Deep Dive Ralph Lauren Fall 2025 Riser Fashion Show
May 17, 2025 -
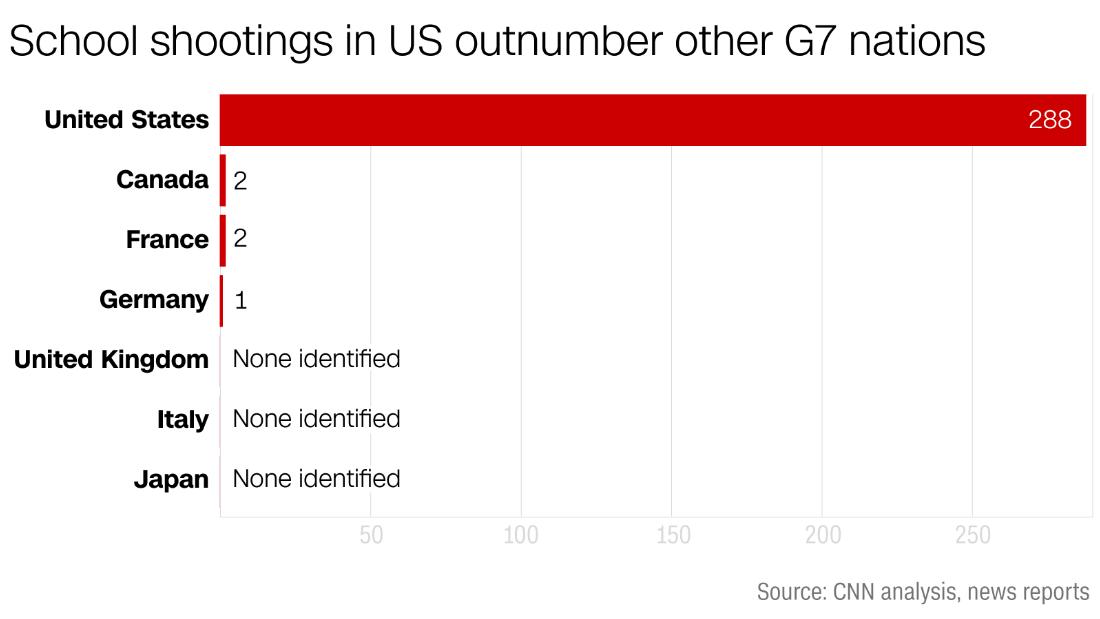 Florida School Shootings Lockdown Procedures And Generational Impact
May 17, 2025
Florida School Shootings Lockdown Procedures And Generational Impact
May 17, 2025 -
 New Orleans Jazz Fest What To Expect And How To Prepare
May 17, 2025
New Orleans Jazz Fest What To Expect And How To Prepare
May 17, 2025
