Kawasaki Disease: A Novel Respiratory Virus As The Culprit?
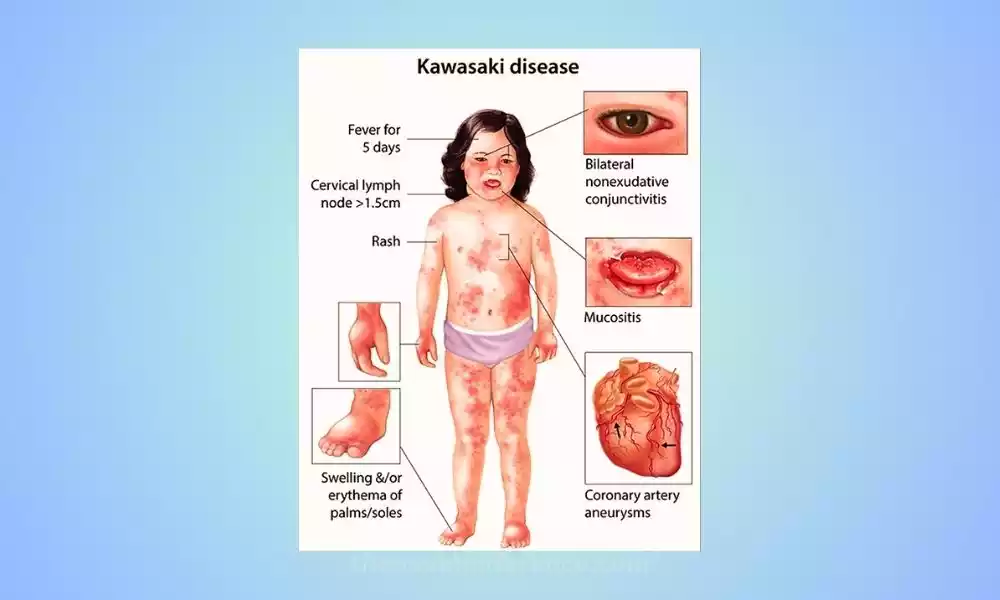
Table of Contents
The Mystery of Kawasaki Disease Etiology
Kawasaki disease presents a clinical picture of systemic vasculitis, impacting various organs. The illness typically begins with high fever lasting several days, followed by the development of a characteristic rash, swelling of the hands and feet, and inflammation of the mucous membranes. Swollen lymph nodes are also common. The most serious complication of KD is the development of coronary artery aneurysms, which can lead to heart damage and long-term cardiovascular problems.
Despite extensive research, the exact cause of Kawasaki disease remains elusive. Current understanding highlights several factors:
- Genetic predisposition: While genetic factors are suspected to play a role in disease susceptibility, they do not fully explain the onset of KD. Certain genetic variations might increase risk, but they are not sufficient on their own.
- Environmental triggers: Environmental factors are also implicated, but their precise nature remains unclear. Exposure to infectious agents or environmental toxins has been speculated, yet no single environmental culprit has been definitively identified.
- Infectious agents: The involvement of infectious agents has been widely investigated, but no single pathogen has been consistently linked to KD. Multiple viral and bacterial agents have been proposed, yet none has met the criteria for establishing causality.
Emerging Evidence Linking a Novel Respiratory Virus to Kawasaki Disease
Recent research has focused on the potential role of respiratory viruses in triggering Kawasaki disease. Several studies suggest a correlation between certain respiratory viral infections and an increased risk of developing KD. This is particularly notable during periods of increased respiratory virus circulation.
- Viral Candidates: While no single virus has been conclusively identified as the cause, several respiratory viruses, including some novel or previously under-recognized strains, are under investigation. Specific studies (e.g., [cite relevant studies here]) have reported increased detection of specific viral RNA or DNA in KD patients compared to controls.
- Mechanisms of Inflammation: The inflammatory response characteristic of Kawasaki disease could be triggered by a viral infection through various mechanisms. Viral components might directly activate the immune system, leading to an excessive inflammatory cascade. Alternatively, a viral infection could trigger an autoimmune response, where the body mistakenly attacks its own blood vessels.
- Ongoing Debates: It is important to acknowledge that the association between respiratory viruses and Kawasaki disease is still under investigation. Further research is needed to confirm this link definitively and to clarify the precise mechanisms involved. The challenge lies in identifying specific viral strains potentially involved, especially those not readily cultured.
Viral Genetic Analysis and Kawasaki Disease
Advanced molecular techniques, particularly next-generation sequencing, have revolutionized the search for novel viruses in KD patients. Metagenomic sequencing, which analyzes all genetic material in a sample, has proven invaluable in identifying potential viral candidates that might not be detected by traditional methods.
- Challenges in Viral Isolation: One major obstacle is the difficulty in isolating and culturing novel viruses from clinical samples. Many viruses might be difficult to grow in the laboratory, requiring sophisticated molecular approaches for detection.
- Metagenomics' Role: Metagenomic sequencing allows researchers to bypass the need for viral cultivation, enabling the detection of viral RNA or DNA directly from patient samples. This has been crucial in identifying previously unknown viruses or strains associated with KD.
- Evidence from Genetic Analyses: Several studies using metagenomic sequencing have detected unique viral sequences in KD patients, suggesting a potential role for novel respiratory viruses in the disease pathogenesis ([cite relevant studies here]).
Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment of Kawasaki Disease
Identifying a novel respiratory virus as a key factor in Kawasaki disease could revolutionize its diagnosis and treatment.
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests: The development of rapid diagnostic tests based on viral detection would greatly improve the timely diagnosis of KD, enabling earlier intervention and reducing the risk of serious complications.
- Antiviral Therapies: The use of antiviral medications could potentially prevent or treat KD by targeting the implicated virus. Early antiviral treatment might reduce the severity of inflammation and the risk of coronary artery aneurysms.
- Vaccine Development: If a specific virus is definitively linked to KD, the development of a targeted vaccine could offer a powerful preventive strategy. This would be particularly crucial for protecting vulnerable populations, such as infants and young children.
Future Research Directions in Understanding Kawasaki Disease
Further research is critical to solidify the connection between a novel respiratory virus and Kawasaki disease. Several crucial areas warrant attention:
- Large-scale Epidemiological Studies: Large-scale epidemiological studies are needed to confirm the association between specific respiratory viruses and KD incidence, taking into account geographic variations and seasonal patterns.
- Viral Pathogenesis and Immune Response: Detailed investigation into the viral pathogenesis and host immune response is crucial to understand the mechanisms by which a viral infection contributes to the development of KD.
- Animal Models: Developing reliable animal models that mimic KD would allow researchers to study the disease process, test potential therapeutic interventions, and evaluate the efficacy of vaccines.
Conclusion
The emerging evidence strongly suggests that a novel respiratory virus may play a critical role in the etiology of Kawasaki disease. This hypothesis holds significant implications for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Further research, particularly large-scale epidemiological studies, advanced viral genetic analysis, and the development of animal models, are crucial to validate this hypothesis and translate these findings into improved clinical management of Kawasaki disease. Continued investigation into the Kawasaki disease viral etiology is essential for developing effective strategies to combat this debilitating childhood condition.

Featured Posts
-
 Guillermo Del Toro On Frankenstein Horror Or Something Else Entirely
May 30, 2025
Guillermo Del Toro On Frankenstein Horror Or Something Else Entirely
May 30, 2025 -
 Al Hilal In Advanced Talks To Sign Bruno Fernandes
May 30, 2025
Al Hilal In Advanced Talks To Sign Bruno Fernandes
May 30, 2025 -
 Spotkanie Trump Zelenski Fakty I Spekulacje
May 30, 2025
Spotkanie Trump Zelenski Fakty I Spekulacje
May 30, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Taco Trade Deal And Trumps Reaction
May 30, 2025
Analyzing The Taco Trade Deal And Trumps Reaction
May 30, 2025 -
 Exploring The Enduring Legacy Of Anna Neagle In British Cinema
May 30, 2025
Exploring The Enduring Legacy Of Anna Neagle In British Cinema
May 30, 2025
