Malaysia Faces US Solar Import Duties: Impact On The Industry
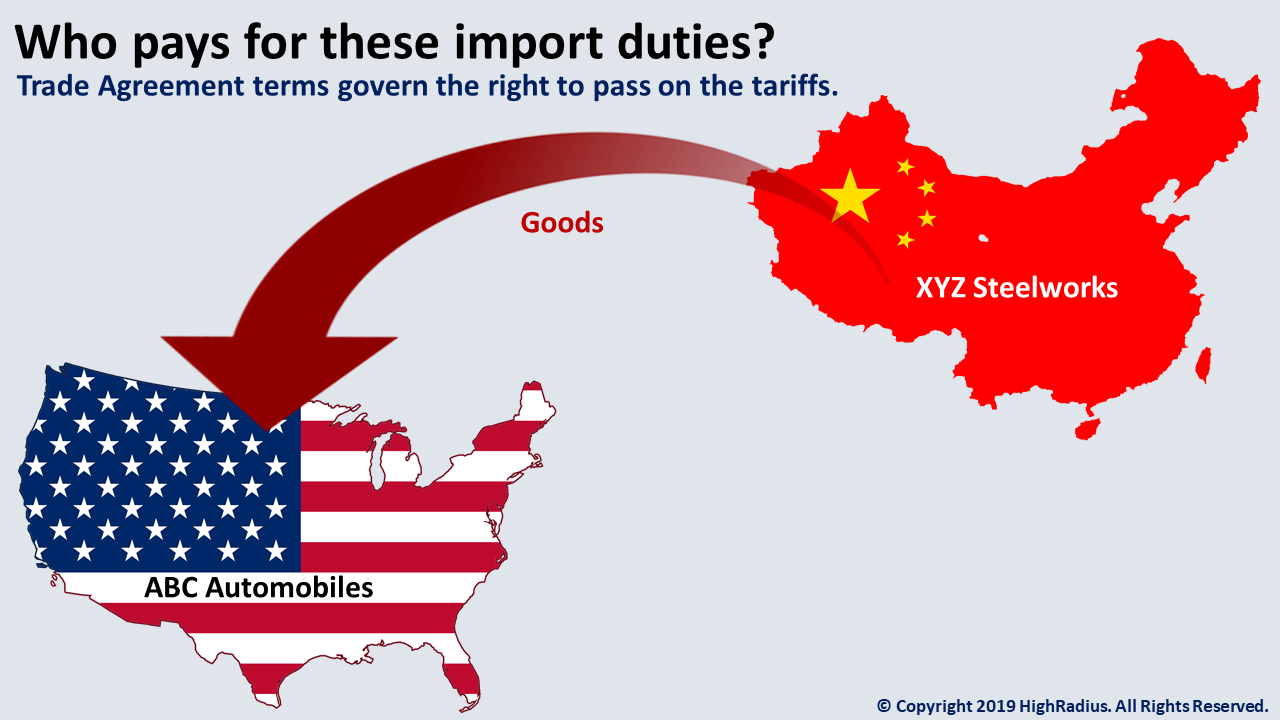
Table of Contents
The recent imposition of US solar import duties has cast a long shadow over the global solar industry, and Malaysia, a nation actively pursuing renewable energy growth, finds itself squarely in the path of this economic storm. The impact of these duties on Malaysia's solar sector is substantial, presenting both immediate challenges and long-term implications for its renewable energy ambitions. This article delves into the multifaceted effects of Malaysia US Solar Import Duties, exploring the difficulties faced and potential strategies for mitigation.
Increased Costs and Reduced Competitiveness
The direct consequence of the US solar import duties is a significant increase in the cost of solar panels imported from affected countries. This surge in prices has wide-ranging repercussions for Malaysia's solar energy landscape.
Higher Solar Panel Prices
The duties directly translate to higher solar panel prices in Malaysia. This increase significantly impacts the financial viability of solar projects across the board.
- Increased project development costs: Developers face higher upfront investments, potentially making projects less attractive.
- Reduced return on investment for investors: The higher costs diminish the profitability of solar projects, deterring investment.
- Potential delays or cancellations of projects: Economic unfeasibility may lead to project delays or outright cancellations, hindering the growth of the solar sector.
Estimates suggest a price increase of approximately 15-20% for solar panels imported from affected regions, impacting various project scales, from residential rooftop installations to large-scale utility projects. This price hike significantly undermines the competitiveness of Malaysian solar energy ventures.
Loss of Market Share to Domestic and Other International Suppliers
Malaysian solar companies, particularly those heavily reliant on exports to the US market, are vulnerable to losing market share. Domestic US producers, now enjoying a competitive advantage, and other international suppliers unaffected by the duties, are poised to capture a larger share of the market.
- Reduced export opportunities for Malaysian solar manufacturers: The price increase reduces the competitiveness of Malaysian exports in the US market.
- Potential job losses in the sector: Reduced export volume and decreased project activity may trigger job losses within the Malaysian solar industry.
Companies like [insert example of a Malaysian solar company] could experience a significant downturn in their US operations, highlighting the vulnerability of Malaysian players in the face of these trade barriers. The increased competitiveness of non-affected suppliers such as those from [insert example of a country not affected by duties] further exacerbates the situation.
Impact on Malaysia's Renewable Energy Targets
Malaysia has set ambitious renewable energy targets, aiming to significantly increase its renewable energy capacity in the coming years. The US solar import duties pose a serious threat to achieving these goals.
Delayed Renewable Energy Transition
The elevated cost of solar energy, driven by the import duties, could significantly impede Malaysia's progress towards its renewable energy targets.
- Slowdown in the adoption of solar energy: Higher prices may discourage consumers and businesses from adopting solar energy.
- Reduced capacity additions in the renewable energy sector: The financial burden may lead to a reduction in the number of new solar projects undertaken.
Malaysia aims to reach [insert percentage]% of renewable energy in its energy mix by [insert year]. The current situation risks delaying the attainment of this target, potentially pushing back the timeline for a greener energy future.
Increased Reliance on Fossil Fuels
If the increased cost of solar energy renders it less competitive compared to traditional fossil fuels, Malaysia might find itself relying more heavily on these unsustainable energy sources.
- Increased carbon emissions: A slower transition to renewable energy will hinder Malaysia's efforts to reduce its carbon footprint.
- Negative environmental consequences: Continued reliance on fossil fuels will exacerbate environmental problems, such as air pollution and climate change.
This shift back to fossil fuels would undermine Malaysia's sustainability efforts and its commitment to combating climate change.
Potential Mitigation Strategies
While the challenges posed by the Malaysia US Solar Import Duties are substantial, several mitigation strategies can be employed to minimize the negative impact.
Government Support and Incentives
The Malaysian government can play a crucial role in supporting the solar industry by implementing policies designed to offset the effects of the import duties.
- Subsidies for solar energy projects: Financial assistance can make solar projects more affordable and attractive.
- Tax breaks for solar energy investments: Tax incentives can encourage both private and public investment in the sector.
- Streamlined approval processes for solar projects: Reducing bureaucratic hurdles can speed up project development and deployment.
The government's proactive intervention is crucial in cushioning the blow and ensuring the continued growth of the Malaysian solar industry.
Diversification of Supply Chains
Reducing reliance on specific suppliers is vital. Malaysian companies can mitigate risks by exploring alternative sources of solar panels.
- Sourcing solar panels from countries not affected by the duties: This could involve establishing new partnerships with suppliers in regions such as [insert example of unaffected country/region].
- Negotiating better terms with existing suppliers: Improved negotiations could help alleviate some of the cost burden.
This diversification will make Malaysian companies less susceptible to future trade disputes and disruptions.
Investing in Domestic Solar Manufacturing
Investing in local solar panel manufacturing capacity is a long-term strategy that can significantly reduce dependence on imports.
- Government investment in research and development: This can foster innovation and improve the competitiveness of Malaysian-made panels.
- Incentives for domestic solar manufacturers: Providing support for local production can stimulate growth in this vital sector.
This strategy not only mitigates the impact of import duties but also fosters economic growth and job creation within Malaysia.
Conclusion
The imposition of US solar import duties presents serious challenges to Malaysia's solar energy industry and its broader renewable energy ambitions. The resulting increased costs, reduced competitiveness, and potential delays in the energy transition necessitate immediate action. However, by adopting proactive mitigation strategies – including government support, supply chain diversification, and investment in domestic manufacturing – Malaysia can navigate these difficulties and secure a sustainable energy future. Addressing the complex issues surrounding Malaysia US Solar Import Duties is not merely a matter of economic survival, but a critical step in ensuring a cleaner, greener future for the nation. Further research, strategic policy adjustments, and collaborative efforts are key to effectively mitigating the negative impacts and maximizing the potential of solar energy in Malaysia.

Featured Posts
-
 Elections Assemblee Nationale Le Rn Tente De Contrer Lfi Sur Le Theme Des Frontieres
May 30, 2025
Elections Assemblee Nationale Le Rn Tente De Contrer Lfi Sur Le Theme Des Frontieres
May 30, 2025 -
 Amorim Garante Permanencia De Bruno Fernandes No Manchester United
May 30, 2025
Amorim Garante Permanencia De Bruno Fernandes No Manchester United
May 30, 2025 -
 Red Tide Alert Issued For Cape Cod Urgent Safety Information
May 30, 2025
Red Tide Alert Issued For Cape Cod Urgent Safety Information
May 30, 2025 -
 Gorillazs House Of Kong And Anniversary Concerts Details Revealed
May 30, 2025
Gorillazs House Of Kong And Anniversary Concerts Details Revealed
May 30, 2025 -
 Definitys 3 3 Billion Acquisition Of Travelers Canada A Deal Analysis
May 30, 2025
Definitys 3 3 Billion Acquisition Of Travelers Canada A Deal Analysis
May 30, 2025
