Measles Cases In US Increase Slightly To 1,046
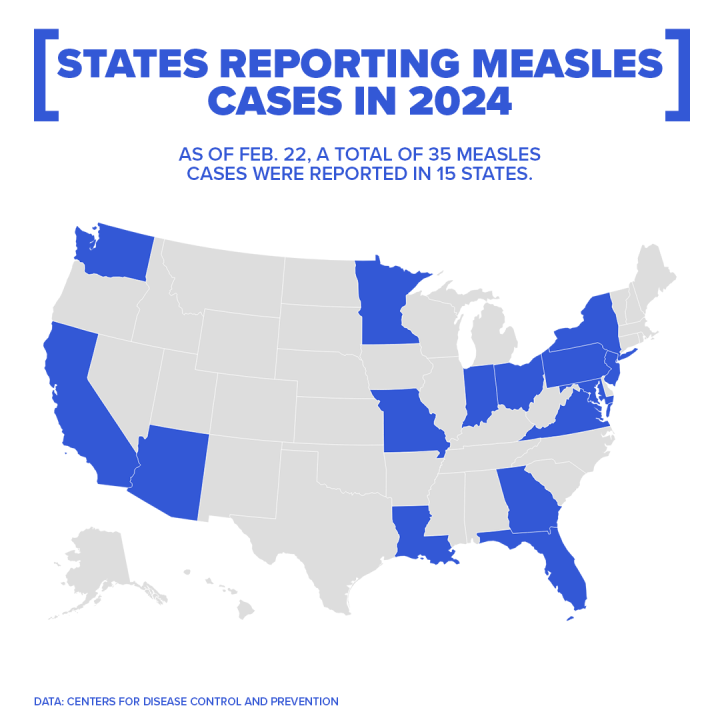
Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to the Rise in Measles Cases (1,046 and beyond)
Several interconnected factors contribute to the resurgence of measles cases, pushing the total to 1,046 and potentially higher. Understanding these factors is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies.
Low Vaccination Rates
A primary driver of measles outbreaks is low vaccination rates. The concept of herd immunity, where a sufficient percentage of the population is vaccinated to protect even those who cannot be vaccinated, is crucial in preventing widespread outbreaks. However, vaccine hesitancy, fueled by misinformation and distrust in vaccines, has led to decreased vaccination rates in certain demographics. This is particularly concerning in some religious communities and among individuals who hold anti-vaccine beliefs.
- Statistics: While national vaccination rates for measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) are generally high, pockets of low vaccination coverage exist across the US, creating vulnerable communities. These variations in vaccination rates across states and regions directly correlate with the incidence of measles outbreaks.
- Consequences: Lower vaccination rates create gaps in herd immunity, allowing measles to spread easily and causing outbreaks even in areas with generally high vaccination levels. This underscores the importance of achieving and maintaining high vaccination coverage across all communities.
- Keywords: measles vaccination, vaccine hesitancy, herd immunity, vaccination rates, MMR vaccine.
International Travel and Importation of Cases
International travel plays a significant role in importing measles cases into the US. Individuals traveling from countries with ongoing measles outbreaks can unknowingly bring the virus back, leading to local transmission if they are unvaccinated or if the virus spreads within communities with low vaccination rates.
- Examples: Several recent outbreaks in the US have been linked to travelers returning from countries experiencing measles epidemics. Effective monitoring and rapid response are crucial in these situations.
- Public Health Surveillance: Robust public health surveillance systems are essential for detecting and containing imported measles cases promptly. This includes identifying potential cases, tracing contacts, and implementing appropriate quarantine measures to prevent further spread.
- Keywords: imported measles cases, international travel, global measles outbreaks, public health surveillance.
Outbreak Clusters and Community Spread
Once measles is introduced into a community, it spreads rapidly due to its highly contagious nature. Outbreak clusters often form in areas with lower vaccination rates or where close contact facilitates transmission.
- Community Spread: Measles is easily transmitted through respiratory droplets produced when an infected individual coughs or sneezes. This means that even a single unvaccinated individual can trigger a significant outbreak in an unvaccinated population.
- Early Detection and Response: Early detection and rapid public health response are critical to limiting the spread of measles outbreaks. This includes identifying cases quickly, isolating infected individuals, and implementing vaccination campaigns to protect those who haven't been immunized.
- Keywords: measles outbreak, community spread, public health response, contact tracing.
The Impact of Increased Measles Cases on Public Health
The increase in measles cases, now at 1,046 and counting, has significant implications for public health.
Health Risks Associated with Measles
Measles is not a benign illness. It can lead to severe complications, especially in vulnerable populations like infants and immunocompromised individuals.
- Severe Complications: Potential complications include pneumonia (a leading cause of measles-related death), encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and even death. These complications can have long-term health consequences, impacting quality of life and imposing substantial medical costs.
- Vulnerable Populations: Infants under six months old are too young to be fully vaccinated and are especially vulnerable to severe complications. Similarly, individuals with weakened immune systems are at greater risk of severe measles outcomes.
- Keywords: measles complications, pneumonia, encephalitis, measles death, immunocompromised.
Strain on Healthcare Resources
Measles outbreaks put a considerable strain on healthcare systems.
- Diagnostic and Treatment Costs: Diagnosing and treating measles cases require resources, including laboratory testing, hospitalization, and supportive care. The cost of managing outbreaks can be substantial, diverting resources from other healthcare priorities.
- Public Health Response: The public health response to measles outbreaks involves contact tracing, vaccination campaigns, and public health education efforts. These activities require significant personnel and financial resources.
- Keywords: healthcare costs, public health burden, resource allocation, public health infrastructure.
Economic Impact of Measles Outbreaks
Measles outbreaks also have a substantial economic impact.
- Lost Productivity: Illness and quarantines lead to lost productivity in schools and workplaces, impacting individuals, businesses, and the overall economy.
- Healthcare Costs: The significant healthcare costs associated with diagnosis, treatment, and prevention efforts contribute to the overall economic burden of measles outbreaks.
- Keywords: economic impact of measles, lost productivity, quarantine, healthcare expenditure.
Conclusion: Understanding the 1,046 Measles Cases and Taking Action
The rise in US measles cases, currently standing at 1,046, underscores the importance of continued vigilance and proactive measures. Low vaccination rates, international travel, and community spread are key factors driving this increase. To prevent further outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations, maintaining high vaccination rates is crucial for achieving herd immunity. We must also strengthen public health surveillance systems to detect and manage imported cases effectively. Consult your healthcare provider to ensure you and your family are up-to-date on your measles vaccination, helping to prevent measles and build strong community immunity. Let's work together to combat measles and protect our communities through informed decisions and proactive measures to boost measles immunity.

Featured Posts
-
 Augsburger Panther Personalrochaden Und Der Abschied Von Stuermer Volek
May 30, 2025
Augsburger Panther Personalrochaden Und Der Abschied Von Stuermer Volek
May 30, 2025 -
 Daniel Cormiers Explosive Revelation What He Told Jon Jones Publicist
May 30, 2025
Daniel Cormiers Explosive Revelation What He Told Jon Jones Publicist
May 30, 2025 -
 Us Visa Restrictions Target Social Media Censorship
May 30, 2025
Us Visa Restrictions Target Social Media Censorship
May 30, 2025 -
 Chronique D Une Banque L Histoire Moderne De La Deutsche Bank
May 30, 2025
Chronique D Une Banque L Histoire Moderne De La Deutsche Bank
May 30, 2025 -
 San Diego County Beaches This Weekend Weather Parking And More
May 30, 2025
San Diego County Beaches This Weekend Weather Parking And More
May 30, 2025
