Mitigating The Risks Of The Great Decoupling: Strategies For Businesses And Governments

Table of Contents
Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions in the Era of Decoupling
The Great Decoupling significantly impacts global supply chains, creating both challenges and opportunities. Businesses must adapt to ensure continued operational efficiency and stability.
Diversifying Supply Chains
Geographically diversifying sourcing and manufacturing is paramount. Over-reliance on single suppliers or regions leaves businesses vulnerable to disruptions. Strategies for identifying and vetting alternative suppliers should include rigorous due diligence, assessing factors such as political stability, infrastructure, and regulatory environments. Technology plays a crucial role; blockchain technology, for example, enhances supply chain visibility and traceability, facilitating better risk management.
- Examples of successful supply chain diversification strategies:
- Moving production from a single country to multiple regions.
- Developing relationships with multiple suppliers for key components.
- Implementing robust risk assessment and mitigation plans.
- Utilizing advanced analytics to predict and respond to potential disruptions.
Building Resilience through Nearshoring and Reshoring
Bringing manufacturing closer to home, through nearshoring (relocating to nearby countries) or reshoring (returning production to the domestic market), offers significant advantages in terms of reduced transit times, improved control over production, and enhanced responsiveness to market demands. However, this approach may involve higher labor costs and potentially reduced access to specialized resources. Governments can play a critical role by offering incentives and support programs to encourage companies to adopt these strategies.
- Case studies of companies successfully implementing nearshoring/reshoring:
- Companies relocating production facilities to Mexico or Canada from Asia to reduce transit times and logistics costs.
- Manufacturing firms returning production to their home countries to gain greater control over quality and production processes.
Enhancing Inventory Management and Buffer Stock Strategies
Robust inventory management systems are crucial for mitigating supply chain shocks. While optimizing inventory levels minimizes storage costs, maintaining adequate buffer stock is essential to absorb unexpected disruptions. Forecasting and predictive analytics play a vital role, enabling businesses to anticipate demand fluctuations and adjust inventory levels proactively.
- Best practices in inventory management during periods of uncertainty:
- Implementing real-time inventory tracking and management systems.
- Developing robust forecasting models to anticipate demand variations.
- Maintaining strategic buffer stocks of critical components and finished goods.
- Utilizing advanced analytics to optimize inventory levels and minimize storage costs.
Adapting to Geopolitical Shifts and Trade Tensions
The Great Decoupling is inextricably linked to geopolitical shifts and trade tensions. Businesses must develop sophisticated strategies to navigate this complex landscape.
Understanding Geopolitical Risks and Their Impact
Geopolitical factors, such as trade wars, sanctions, and political instability, significantly influence business operations and supply chains. Conducting thorough geopolitical risk assessments and developing comprehensive mitigation strategies are essential. This includes building robust risk management frameworks that identify, assess, and respond to potential threats.
- Examples of geopolitical events impacting businesses and their responses:
- The impact of US-China trade tensions on supply chains and manufacturing.
- The effect of sanctions on businesses operating in certain regions.
- The disruption caused by political instability in key sourcing regions.
Navigating Trade Barriers and Regulations
Tariffs, quotas, and other trade restrictions create significant challenges for businesses engaged in international trade. Staying informed about evolving trade regulations and standards is critical. Investing in legal and regulatory expertise is essential to ensure compliance and minimize potential penalties.
- Examples of successful strategies for navigating trade barriers:
- Diversifying markets to reduce reliance on countries with high tariffs.
- Seeking exemptions or waivers from trade restrictions.
- Utilizing free trade agreements to reduce or eliminate tariffs.
Strategic Partnerships and Alliances
Forming strategic partnerships and alliances with local and international businesses is crucial for sharing risk, leveraging resources, and navigating complex regulatory environments. Government-to-business partnerships can facilitate collaboration and foster a more resilient economic ecosystem.
- Examples of successful strategic partnerships and alliances:
- Collaborations between businesses to secure reliable supplies of critical components.
- Joint ventures to establish manufacturing facilities in new regions.
- Partnerships with local businesses to access specific resources or expertise.
Government Strategies for Mitigating the Risks of Decoupling
Governments play a pivotal role in mitigating the risks of the Great Decoupling. Proactive policies are essential to foster economic resilience and sustainable growth.
Investing in Domestic Industries and Infrastructure
Government investment in key sectors, such as technology, manufacturing, and infrastructure, enhances national resilience. Supporting innovation, research, and development fosters technological advancement and competitiveness. Investing in infrastructure – transportation networks, communication systems, and energy grids – is crucial for efficient production and distribution.
- Examples of successful government initiatives supporting domestic industries:
- Tax incentives and subsidies for companies investing in domestic production.
- Funding for research and development in key technological areas.
- Investment in infrastructure to improve connectivity and logistics.
Promoting Trade Diversification and Regional Integration
Trade agreements and regional economic partnerships play a crucial role in mitigating decoupling risks. Strengthening economic ties with key trading partners through diverse trade agreements reduces dependence on any single market. Fostering collaboration among countries is essential for creating a more stable and interconnected global economy.
- Examples of effective regional economic integration efforts:
- The European Union's single market.
- The Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP).
- Regional trade agreements in Africa and Asia.
Developing Skills and Workforce Training
Adapting the workforce to the changing economic landscape is critical. Governments must invest in workforce development and reskilling programs to ensure that workers possess the skills needed for emerging industries. Education and training in advanced technologies are crucial for maintaining competitiveness in a rapidly evolving global economy.
- Successful examples of government-led workforce development programs:
- Apprenticeship programs in advanced manufacturing.
- Reskilling initiatives for workers displaced by automation.
- Investment in STEM education to develop a skilled workforce in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
Conclusion: Mitigating the Risks of the Great Decoupling – A Proactive Approach
The Great Decoupling presents significant challenges, but also opportunities for businesses and governments to build more resilient and diversified economies. The strategies discussed—diversifying supply chains, building resilience through nearshoring and reshoring, enhancing inventory management, adapting to geopolitical shifts, fostering strategic partnerships, and implementing supportive government policies—are crucial for navigating this evolving global landscape. Proactive planning and adaptation are paramount. We encourage businesses and governments to develop comprehensive strategies for mitigating the risks of the Great Decoupling and to continue researching and exploring innovative solutions to ensure long-term success in this new era of global economic and geopolitical uncertainty. The future of global trade hinges on effectively mitigating the risks of the Great Decoupling.

Featured Posts
-
 Palantir Stock Should You Invest Before May 5th Wall Streets Prediction
May 09, 2025
Palantir Stock Should You Invest Before May 5th Wall Streets Prediction
May 09, 2025 -
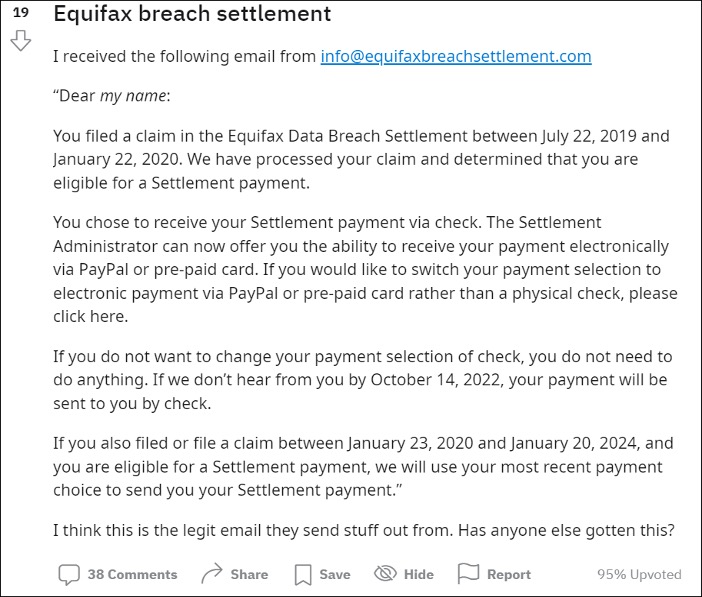 16 Million Fine T Mobiles Data Breach Settlement Explained
May 09, 2025
16 Million Fine T Mobiles Data Breach Settlement Explained
May 09, 2025 -
 Le Ministre Europeen Francais Vante Le Partage Du Bouclier Nucleaire
May 09, 2025
Le Ministre Europeen Francais Vante Le Partage Du Bouclier Nucleaire
May 09, 2025 -
 Understanding Wynne And Joanna All At Sea
May 09, 2025
Understanding Wynne And Joanna All At Sea
May 09, 2025 -
 Frantsiya I Polsha Novoe Oboronnoe Soglashenie Signal Dlya Trampa I Putina
May 09, 2025
Frantsiya I Polsha Novoe Oboronnoe Soglashenie Signal Dlya Trampa I Putina
May 09, 2025
