Near Misses And Outages: Investigating The Risks Of Air Traffic Control System Failures

Table of Contents
Causes of Air Traffic Control System Failures
Air Traffic Control System Failures stem from a variety of interconnected sources, encompassing hardware malfunctions, software vulnerabilities, and human error. Addressing each of these contributing factors is essential to enhance the overall resilience and safety of the system.
Hardware Malfunctions
Hardware failures in air traffic control systems can have devastating consequences. These failures can manifest in several forms, significantly impacting the system's ability to effectively manage air traffic.
- Radar system malfunctions: A failure in the primary radar system can lead to a loss of situational awareness, increasing the risk of mid-air collisions. This includes failures in primary radar, secondary surveillance radar (SSR), and weather radar.
- Communication equipment breakdowns: Loss of communication between air traffic controllers and pilots can lead to confusion and potentially dangerous situations. This encompasses voice communication systems, data links, and emergency communication systems.
- Computer server crashes: Critical computer systems are the backbone of modern ATC, and their failure can cripple the entire system, leading to widespread disruption. This includes the failure of central processing units (CPUs), data storage systems, and network infrastructure.
The importance of regular preventative maintenance and the implementation of redundant systems cannot be overstated. Proactive measures such as regular inspections, component replacements, and comprehensive testing protocols are vital for minimizing the risk of ATC system hardware failure.
Software Glitches and Cyberattacks
Software glitches and increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks pose significant threats to the stability and security of air traffic control systems. These threats necessitate a robust and proactive approach to cybersecurity within the ATC domain.
- Software bugs and vulnerabilities: Unforeseen software errors can lead to system crashes, incorrect data processing, and flawed flight path calculations, potentially leading to near misses or worse.
- Cybersecurity threats to air traffic control: Malicious actors may attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in ATC software to disrupt operations, potentially compromising flight safety. This can range from data manipulation to complete system shutdowns.
Addressing these threats requires robust cybersecurity measures, including regular software updates, penetration testing, and rigorous security audits. Implementing advanced intrusion detection and prevention systems is also crucial to mitigate the risk of ATC software vulnerability exploitation.
Human Error
Human error remains a significant contributing factor to Air Traffic Control System Failures. While technology plays a crucial role, the human element cannot be overlooked.
- Incorrect data entry: Simple mistakes in data entry can have significant consequences, leading to miscalculations and potentially unsafe situations.
- Inadequate training: Insufficient training can leave controllers unprepared for unexpected events or unable to effectively utilize available technology.
- Fatigue and stress: Prolonged working hours and high-pressure situations can lead to errors and reduced performance.
Minimizing human error requires investing in improved training programs, implementing effective workload management strategies, and fostering a safety-conscious culture within the ATC workforce. Enhanced ergonomic design and the integration of decision-support tools can also play a significant role in reducing operator error in air traffic control.
Consequences of Air Traffic Control System Failures
The consequences of Air Traffic Control System Failures are far-reaching and can have severe implications for aviation safety, the economy, and public confidence.
Near Misses and Accidents
The most critical consequence is the potential for near misses and accidents. Even minor system malfunctions can create situations where collisions are narrowly avoided.
- Near-miss incidents due to ATC failure: Statistics indicate a significant number of near-miss incidents are directly or indirectly related to ATC system malfunctions.
- Aviation accidents caused by ATC system malfunction: While less frequent, historical data reveals a number of aviation accidents directly attributable to ATC system failures.
These incidents highlight the critical need for reliable and resilient ATC systems to prevent catastrophic accidents. Detailed investigation of each incident provides crucial insights into improving system safety. Any ATC failure resulting in collision avoidance should be rigorously analyzed to prevent future recurrences.
Flight Delays and Cancellations
ATC system failures lead to widespread flight disruptions, resulting in significant economic and logistical repercussions.
- ATC outage impact on flight schedules: Outages can cause widespread delays and cancellations, impacting airlines, passengers, and the overall efficiency of the air travel system.
- Economic consequences of ATC system failures: The economic costs associated with delays and cancellations are substantial, affecting airlines, airports, and related industries. This includes lost revenue, increased operational costs, and compensation to affected passengers.
The ripple effect of flight delays and cancellations caused by ATC failure extends far beyond the immediate disruption, impacting various sectors of the economy.
Loss of Public Trust
Significant ATC system failures can erode public trust in the safety and reliability of air travel.
- Impact of ATC failures on passenger trust: News of ATC system failures can lead to passenger anxiety and reduced confidence in the safety of air travel.
- Public confidence in air traffic control: Maintaining public trust necessitates transparency and effective communication following significant incidents. Openly acknowledging failures and outlining steps taken to prevent future occurrences are crucial for rebuilding confidence.
Open communication about incidents, along with clear explanations of the steps taken to prevent future occurrences, is essential for maintaining public trust in air traffic control.
Mitigating the Risks of Air Traffic Control System Failures
Mitigating the risks associated with Air Traffic Control System Failures requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses improved redundancy, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and advanced training and simulation.
Improved Redundancy and Backup Systems
Implementing redundant systems and backup procedures is crucial for ensuring the continued operation of ATC systems during failures.
- Redundant ATC systems: Employing multiple independent systems that can take over in case of primary system failure is paramount.
- Backup ATC infrastructure: Having a secondary infrastructure ready to handle air traffic in case of primary system failure ensures continued operational capability.
- Fail-safe mechanisms in air traffic control: Building in fail-safe mechanisms and automatic fallback procedures is essential for minimizing disruption in the event of a system failure.
Investing in redundant systems and robust backup procedures is crucial for ensuring continued operational capability and minimizing the impact of system failures.
Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
Robust cybersecurity protocols are essential to protect ATC systems from cyberattacks.
- Cybersecurity in air traffic management: Implementing advanced cybersecurity measures to protect against both external and internal threats is vital for maintaining system integrity.
- Protecting ATC from cyberattacks: Regular security audits, penetration testing, and the implementation of intrusion detection and prevention systems are all crucial components of a strong cybersecurity strategy.
- ATC system security protocols: Establishing and adhering to strict security protocols is essential to mitigate the risk of cyberattacks targeting the air traffic control system.
Advanced Training and Simulation
Advanced training programs and simulation technology are vital for preparing air traffic controllers for diverse scenarios and unexpected events.
- ATC controller training: Enhanced training programs focusing on both theoretical knowledge and practical skills are essential.
- ATC simulation technology: Utilizing advanced simulation technology to replicate real-world scenarios allows controllers to practice their skills in a safe environment.
- Improving ATC operator skills: Investing in continuous training and professional development helps improve the skills and adaptability of air traffic controllers.
Investing in advanced training and simulation technology empowers controllers to better handle unexpected situations and contribute to a safer airspace.
Conclusion
Understanding the risks of Air Traffic Control System Failures is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of air travel. We’ve explored the multifaceted causes of these failures, ranging from hardware and software issues to human error, and analyzed the potentially catastrophic consequences, including near misses, widespread delays, and the erosion of public trust. Mitigating these risks necessitates a comprehensive approach that includes implementing redundant systems, strengthening cybersecurity measures, and investing in advanced training and simulation technologies. Let's work together to prevent future Air Traffic Control System Failures and maintain the highest standards in air traffic management. The safety of millions depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Peppa Pigs Parents Throw Gender Reveal Party A Pink Or Blue Celebration
May 22, 2025
Peppa Pigs Parents Throw Gender Reveal Party A Pink Or Blue Celebration
May 22, 2025 -
 50 000 Accenture Employees Receive Promotions After Six Month Wait
May 22, 2025
50 000 Accenture Employees Receive Promotions After Six Month Wait
May 22, 2025 -
 Trans Australia Run Will A New Record Be Set
May 22, 2025
Trans Australia Run Will A New Record Be Set
May 22, 2025 -
 Vstup Ukrayini Do Nato Riziki Ta Perspektivi Za Otsinkoyu Yevrokomisara
May 22, 2025
Vstup Ukrayini Do Nato Riziki Ta Perspektivi Za Otsinkoyu Yevrokomisara
May 22, 2025 -
 Jackson Elk Hunt Season Changes Fewer Permits Issued
May 22, 2025
Jackson Elk Hunt Season Changes Fewer Permits Issued
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Kien Nghi Xay Dung Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Dong Nai Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
Kien Nghi Xay Dung Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Dong Nai Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
 Duong Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Ngay Thong Xe Chinh Thuc
May 22, 2025
Duong Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Ngay Thong Xe Chinh Thuc
May 22, 2025 -
 Dong Nai Kien Nghi Xay Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Noi Lien Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
Dong Nai Kien Nghi Xay Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Noi Lien Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
 Cao Toc Bien Vung Tau Chuan Bi Thong Xe 2 9
May 22, 2025
Cao Toc Bien Vung Tau Chuan Bi Thong Xe 2 9
May 22, 2025 -
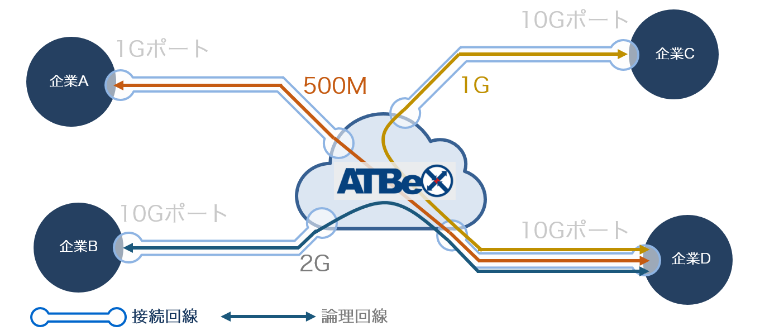 At Be X Ntt Multi Interconnect Ascii Jp
May 22, 2025
At Be X Ntt Multi Interconnect Ascii Jp
May 22, 2025
