New Data Points To Respiratory Virus As Sole Cause Of Kawasaki Disease
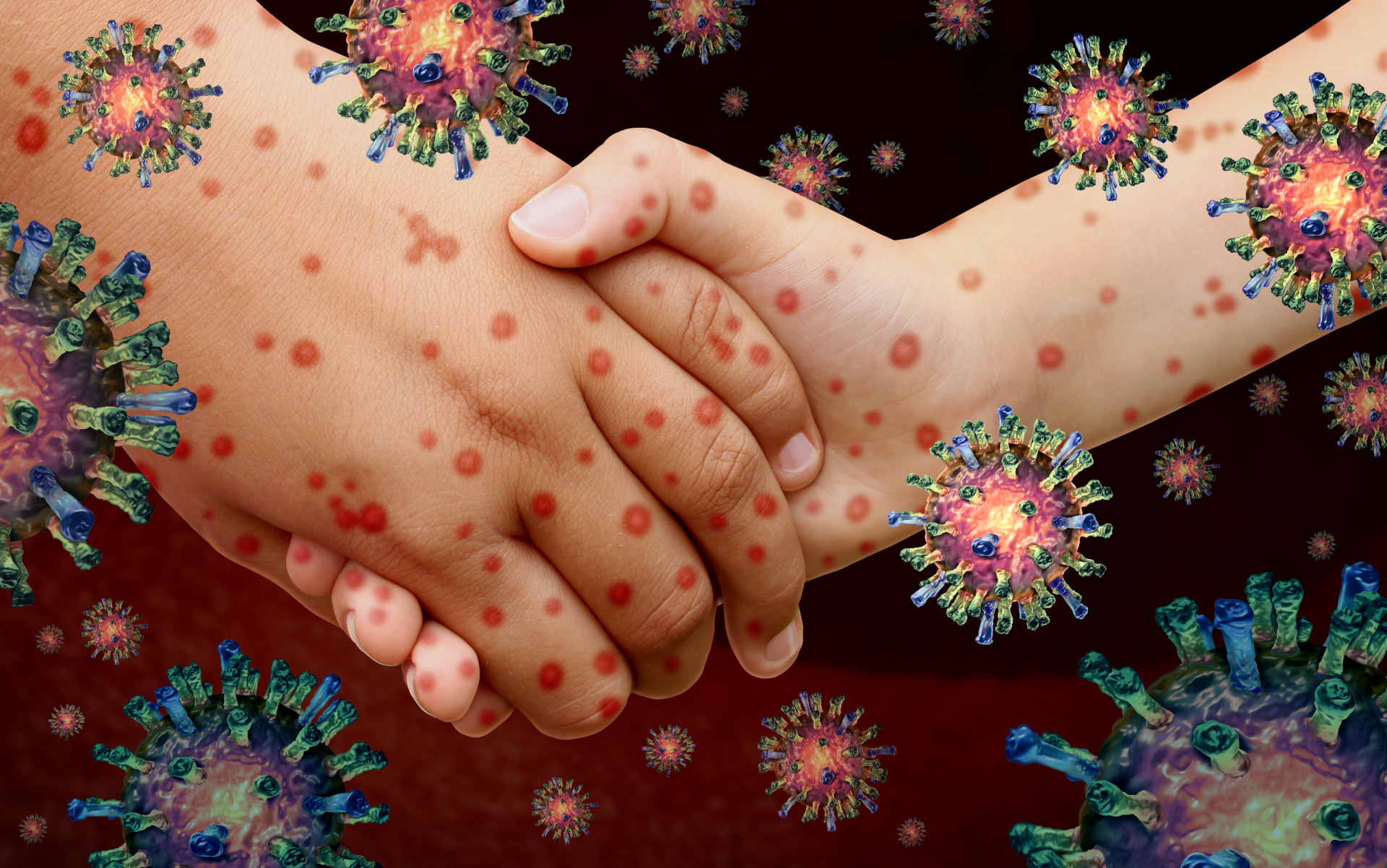
Table of Contents
The Evidence Linking Respiratory Viruses to Kawasaki Disease
Several recent studies have significantly strengthened the link between respiratory viral infections and the development of Kawasaki disease.
Viral Detection in Kawasaki Disease Patients
Numerous studies have demonstrated a high prevalence of specific respiratory viruses in children diagnosed with KD. Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) and adenoviruses have been particularly implicated. These findings are supported by robust methodologies:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing: This highly sensitive technique detects viral DNA or RNA in patient samples, confirming the presence of specific viruses.
- Viral culture: This technique involves growing viruses in a laboratory setting from patient samples, allowing for viral identification and characterization.
The statistical significance of these findings, often showing a much higher prevalence of these viruses in KD patients compared to control groups, strongly suggests a causal relationship.
Mechanism of Viral Infection in Kawasaki Disease Development
While the precise mechanism remains under investigation, researchers propose that respiratory viral infection triggers a cascade of events leading to KD. This likely involves:
- Initial viral infection: The virus infects cells in the respiratory tract.
- Immune system activation: The body's immune system mounts a response to the infection, leading to inflammation.
- Cytokine storm: The release of excessive pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) contributes to widespread inflammation affecting blood vessels.
- Endothelial cell damage: This inflammation damages the endothelial cells lining blood vessels, resulting in the characteristic vasculitis of KD.
Understanding these pathways is crucial for developing targeted therapies.
Comparison with Previous Theories on Kawasaki Disease Etiology
Previous theories regarding KD etiology included genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. While genetic factors may play a role in susceptibility, the compelling evidence of viral detection in virtually all KD cases challenges these earlier hypotheses. Comparative studies directly comparing viral detection rates in KD patients versus control groups consistently demonstrate a much higher prevalence of specific respiratory viruses in KD patients, providing stronger evidence for a viral etiology.
Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment of Kawasaki Disease
The identification of a respiratory virus as the likely cause of Kawasaki disease has profound implications for diagnosis and treatment.
Improved Diagnostic Approaches
A viral etiology suggests more accurate and timely diagnostic strategies:
- Viral testing: Routine viral PCR testing could become a key component of KD diagnosis, leading to earlier intervention.
- Early detection: Faster diagnosis translates into earlier initiation of treatment, potentially minimizing the risk of coronary artery aneurysms.
The advantages of viral-based diagnostic strategies are significant, offering earlier intervention and potentially better patient outcomes.
Targeted Treatment Strategies
The possibility of antiviral therapies offers a paradigm shift in KD treatment:
- Antiviral medications: Specific antiviral agents targeting implicated viruses like HHV-6 and adenoviruses could be explored.
- Personalized medicine: Treatment tailored to the specific virus identified in each patient could enhance efficacy.
- Immunomodulation: Therapies aimed at controlling the excessive inflammatory response could be beneficial.
Further research is crucial to determine the efficacy and safety of these approaches.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions in Kawasaki Disease Research
While the evidence is compelling, further research is essential to solidify the understanding of the role of respiratory viruses in KD.
Further Studies Needed to Confirm the Findings
- Larger, more diverse studies: Larger studies with diverse populations are needed to validate the findings across different geographical regions and demographics.
- Longitudinal studies: Longitudinal studies tracking patients over time are essential to understand the long-term effects of viral infection and the potential for long-term complications.
- Geographical variations: Investigating geographical variations in viral prevalence and KD incidence is crucial to refine our understanding of the disease.
These studies will solidify the link between respiratory viruses and KD and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the disease's pathogenesis.
Potential for Prevention Strategies
The identification of specific viruses opens up the possibility of preventive measures:
- Vaccination: Development of vaccines against implicated viruses could significantly reduce KD incidence.
- Improved hygiene: Public health initiatives promoting better hygiene practices could help reduce the spread of these viruses.
This research holds the potential to significantly impact public health strategies.
The Role of Respiratory Viruses in Understanding and Treating Kawasaki Disease
In conclusion, the mounting evidence strongly suggests a respiratory virus as the primary cause of Kawasaki disease. This groundbreaking discovery holds tremendous implications for improved diagnostic approaches and treatment strategies, potentially leading to earlier interventions and better patient outcomes. Ongoing research is crucial to confirm these findings, unravel the intricate mechanisms involved, and develop effective preventative measures. Stay updated on the latest advancements in Kawasaki disease research to better understand and manage this important condition. For more information, consult resources such as the American Heart Association and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Featured Posts
-
 Greve Sncf Le Ministre Annonce T Il L Inevitable
May 30, 2025
Greve Sncf Le Ministre Annonce T Il L Inevitable
May 30, 2025 -
 Real Madrid Eyeing Record 90m Transfer For Manchester United Player
May 30, 2025
Real Madrid Eyeing Record 90m Transfer For Manchester United Player
May 30, 2025 -
 Andrej Kramarics Penalty Hoffenheim Hold In Form Augsburg
May 30, 2025
Andrej Kramarics Penalty Hoffenheim Hold In Form Augsburg
May 30, 2025 -
 Setlist Fm Ticketmaster Experiencia Unificada Para Fans De Conciertos
May 30, 2025
Setlist Fm Ticketmaster Experiencia Unificada Para Fans De Conciertos
May 30, 2025 -
 Seminar Russkoy Inzhenernoy Shkoly Tolyatti
May 30, 2025
Seminar Russkoy Inzhenernoy Shkoly Tolyatti
May 30, 2025
