Over-the-Counter Birth Control: Implications For Reproductive Freedom After Roe V. Wade
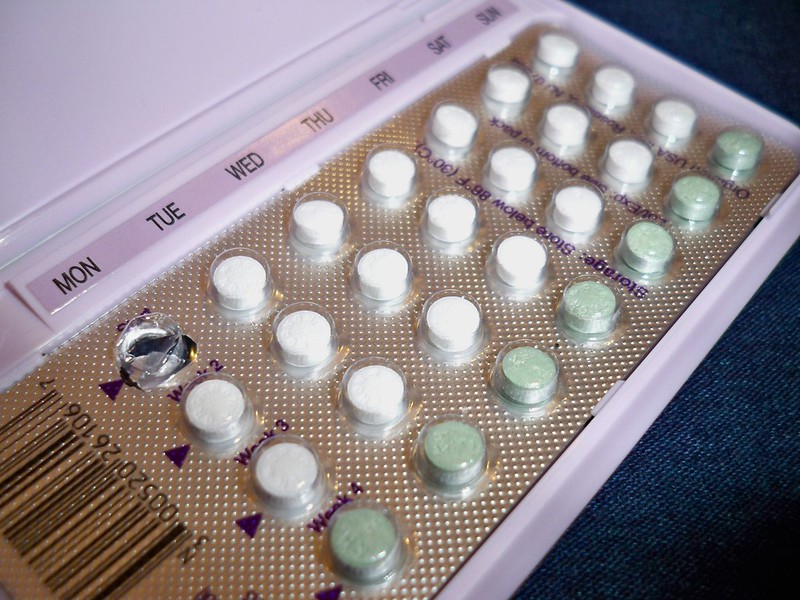
Table of Contents
Increased Accessibility and its Impact on Reproductive Health
Increased accessibility to over-the-counter birth control methods holds significant implications for reproductive health outcomes. Making birth control readily available without a prescription can dramatically alter the landscape of family planning.
Reduced Barriers to Access
Over-the-counter availability eliminates several key barriers to accessing birth control:
- Lower cost: Removing the need for doctor's visits and insurance copays significantly reduces the financial burden, making birth control accessible to low-income individuals and those without health insurance. This is especially crucial for affordable birth control options.
- Convenience: Easy access to pharmacies and drugstores means individuals can obtain birth control discreetly and conveniently, without scheduling appointments or navigating complex healthcare systems.
- Increased privacy: Purchasing over-the-counter birth control offers a greater sense of privacy compared to seeking care from a healthcare provider, potentially encouraging individuals who might otherwise feel stigmatized or uncomfortable to use contraception.
- Improved adherence: Convenient access can lead to better adherence to birth control regimens, increasing effectiveness and reducing unintended pregnancies.
The demographic impact is potentially huge. Underserved populations, including low-income individuals, those living in rural communities, and minority groups, often face significant barriers to accessing reproductive healthcare. Over-the-counter birth control can help bridge this gap, improving health equity.
Improved Birth Control Use and Reduced Unintended Pregnancies
Increased access to over-the-counter birth control is strongly correlated with higher rates of consistent contraceptive use. This directly translates to fewer unintended pregnancies and subsequent abortions.
- Data supports this correlation: Numerous studies have demonstrated a link between increased contraceptive access and decreased unintended pregnancy rates.
- Specific methods: This includes various contraceptive methods, from emergency contraception ("morning-after" pill) to long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) like IUDs and implants, though the latter may still require a medical provider's intervention for insertion.
- Addressing counterarguments: Concerns exist regarding potential misuse and self-medication risks. However, robust public health campaigns focusing on responsible use and providing clear instructions can mitigate these risks. Proper labeling and readily available information are vital.
The Role of Affordable Over-the-Counter Birth Control in Reducing Health Disparities
Over-the-counter birth control plays a significant role in mitigating existing health disparities.
Addressing Systemic Inequalities
The current healthcare system disproportionately affects marginalized communities. Over-the-counter birth control can:
- Improve access in underserved areas: Rural communities and low-income neighborhoods often have limited access to healthcare providers. Over-the-counter options can drastically increase access to vital reproductive healthcare in these areas.
- Reduce racial disparities: Minority groups often face higher rates of unintended pregnancies and abortions. Increased access to affordable birth control can help reduce these disparities.
- Improve health outcomes: By increasing access to contraception, we can expect to see a decrease in unintended pregnancies, STIs, and other reproductive health issues within these communities. Comprehensive data on unintended pregnancies and abortions within these communities supports this argument.
The Importance of Education and Comprehensive Sexual Health Education
Alongside increased access, comprehensive sexual health education is vital:
- Responsible use: Education campaigns should focus on responsible use of over-the-counter birth control, including proper usage, potential side effects, and when to seek medical advice.
- Method selection: Education should also empower individuals to make informed decisions about which method best suits their needs and health conditions.
- Sex education in schools and communities: Comprehensive sex education, starting at a young age, is crucial in fostering responsible reproductive health practices.
Potential Challenges and Concerns Regarding Over-the-Counter Birth Control
Despite the potential benefits, challenges and concerns remain.
Misinformation and Misuse
The potential for incorrect use of over-the-counter birth control is a valid concern:
- Reduced effectiveness: Misuse can lead to reduced effectiveness, increasing the risk of unintended pregnancy.
- Health risks: Incorrect use might also pose certain health risks.
- Clear labeling and patient education: Addressing this requires clear and concise labeling on products, coupled with easily accessible patient education materials.
Regulatory and Policy Considerations
The FDA and other regulatory bodies play a crucial role:
- Safety and efficacy: Rigorous regulatory approval processes are essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of over-the-counter birth control options.
- Political obstacles: Political opposition to wider access can create significant hurdles in implementing policies that support the availability of over-the-counter birth control.
Access to Comprehensive Reproductive Healthcare
Increased access to over-the-counter birth control shouldn't replace comprehensive reproductive healthcare:
- Prenatal care: Access to prenatal care remains crucial for healthy pregnancies and childbirth.
- Gynecological check-ups: Regular check-ups are important for overall reproductive health.
- Other reproductive health services: A range of other reproductive health services, such as STI testing and treatment, should remain accessible to all.
Conclusion
The debate surrounding over-the-counter birth control is complex, but its potential to significantly impact reproductive freedom in the post-Roe era is undeniable. Increased accessibility to over-the-counter birth control offers a crucial pathway to reducing unintended pregnancies, improving reproductive health outcomes, and addressing existing health disparities. While challenges related to misuse and regulatory hurdles remain, the benefits of expanded access to affordable and convenient over-the-counter birth control options are substantial. Continued advocacy for policies that ensure safe and equitable access to this essential form of reproductive healthcare is crucial. Let's work together to ensure that everyone has access to the over-the-counter birth control they need to make informed choices about their reproductive health.

Featured Posts
-
 Assista Ao Vivo Corinthians X Guarani Paulistao 2025 Ultima Rodada
May 05, 2025
Assista Ao Vivo Corinthians X Guarani Paulistao 2025 Ultima Rodada
May 05, 2025 -
 Westbrooks 25 Point Performance A Look At The Nbas Reaction
May 05, 2025
Westbrooks 25 Point Performance A Look At The Nbas Reaction
May 05, 2025 -
 Malone Loue Westbrook Son Triple Double Un Atout Majeur Pour Denver
May 05, 2025
Malone Loue Westbrook Son Triple Double Un Atout Majeur Pour Denver
May 05, 2025 -
 Kentucky Derby 151 What You Need To Know Before Race Day
May 05, 2025
Kentucky Derby 151 What You Need To Know Before Race Day
May 05, 2025 -
 Eurovision 2025 Germanys Selection Process Following Eurovision 2024
May 05, 2025
Eurovision 2025 Germanys Selection Process Following Eurovision 2024
May 05, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Arnold Schwarzenegger Bueszke Lehet Joseph Baenara
May 06, 2025
Arnold Schwarzenegger Bueszke Lehet Joseph Baenara
May 06, 2025 -
 Arnold Schwarzenegger On Patrick Schwarzeneggers Nude Photography
May 06, 2025
Arnold Schwarzenegger On Patrick Schwarzeneggers Nude Photography
May 06, 2025 -
 Fotosessiya Patrika Shvartseneggera I Ebbi Chempion Dlya Kim Kardashyan
May 06, 2025
Fotosessiya Patrika Shvartseneggera I Ebbi Chempion Dlya Kim Kardashyan
May 06, 2025 -
 Joseph Baena Arnold Schwarzenegger Oeroekoese
May 06, 2025
Joseph Baena Arnold Schwarzenegger Oeroekoese
May 06, 2025 -
 Arnold Schwarzenegger Es Fia Joseph Baena Kapcsolata
May 06, 2025
Arnold Schwarzenegger Es Fia Joseph Baena Kapcsolata
May 06, 2025
