Pilbara Future: Rio Tinto's Response To Environmental Concerns
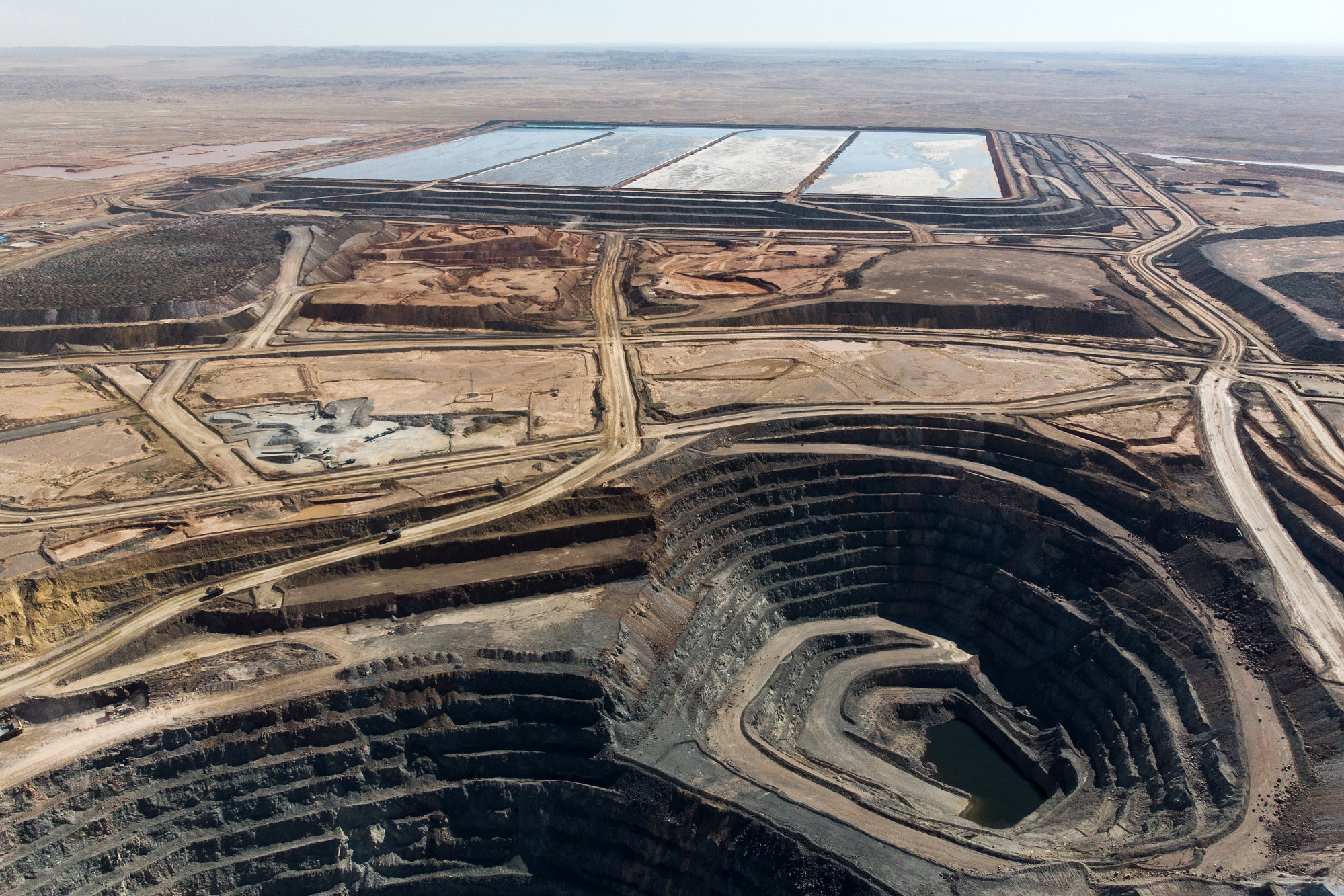

Table of Contents
Rio Tinto's Commitment to Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Rio Tinto recognizes the urgent need to reduce its carbon footprint and is actively investing in a range of initiatives to achieve this goal. Their commitment extends across various operational aspects, prioritizing renewable energy transition and operational emission reduction strategies.
Renewable Energy Transition
Rio Tinto is heavily investing in renewable energy sources to power its Pilbara operations, transitioning away from fossil fuels. This includes significant investment in both solar and wind power projects.
- Solar Power: The company is developing large-scale solar farms to provide clean energy for its processing facilities. For example, the company is actively pursuing solar projects with the capacity to generate hundreds of megawatts, significantly reducing reliance on traditional energy sources.
- Wind Power: Wind farms are another key element of Rio Tinto's renewable energy strategy, supplementing solar power and providing a reliable baseload power source. Specific projects are underway, with targets set for a substantial percentage of their energy needs to be met by wind power within a defined timeframe.
- Target Reduction: Rio Tinto has set ambitious targets for reducing its greenhouse gas emissions, aiming for net-zero emissions by a specific year. These targets are regularly reviewed and updated to reflect advancements in technology and evolving climate science. These efforts contribute to their overall goal of minimizing their carbon footprint and promoting a sustainable Pilbara future.
- Keywords: Renewable energy, solar power, wind power, carbon emissions, net-zero emissions, Pilbara operations, decarbonization.
Reducing Operational Emissions
Beyond renewable energy, Rio Tinto is focused on minimizing emissions directly from its mining processes. This multifaceted approach encompasses technological innovation and operational improvements.
- Technological Advancements: The company is actively exploring and implementing cutting-edge technologies to improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions during mining and processing. This includes advancements in automation, improved equipment design and the adoption of more efficient processes.
- Efficiency Improvements: Rio Tinto is continuously optimizing its operations to minimize energy consumption and emissions. This involves streamlining processes, improving logistics and optimizing the use of resources.
- Waste Reduction Initiatives: Reducing waste generation is crucial for emission reduction. Rio Tinto is implementing various waste management programs to minimize waste sent to landfills and to recover valuable materials.
- Keywords: Operational efficiency, emissions reduction, process optimization, waste management, sustainable mining practices, greenhouse gas reduction.
Water Management and Conservation in the Pilbara
Water is a precious resource in the Pilbara, and Rio Tinto is implementing comprehensive water management strategies to minimize its environmental footprint and ensure responsible water usage.
Water Recycling and Reuse
Rio Tinto is significantly investing in water recycling and reuse technologies to reduce its reliance on freshwater sources.
- Recycling Percentage: A substantial percentage of the water used in Rio Tinto's operations is now recycled and reused, reducing the overall water withdrawal from local sources.
- Innovative Water Treatment: The company employs advanced water treatment technologies to ensure the recycled water meets the required quality standards for reuse in various processes.
- Impact on Local Water Resources: These initiatives have a positive impact on local water resources, reducing pressure on aquifers and ensuring the sustainability of water supplies for both industrial and ecological uses.
- Keywords: Water recycling, water reuse, water conservation, water management, sustainable water practices, Pilbara water resources, water footprint.
Water-Efficient Technologies
Rio Tinto is actively adopting and developing water-efficient technologies to minimize water consumption in its mining and processing operations.
- Dry Stacking: This technique significantly reduces water usage in tailings management by eliminating the need for traditional tailings dams.
- Dust Suppression: Innovative dust suppression techniques minimize water usage while effectively controlling dust emissions.
- Minimising Water Footprint: Through continuous improvements, Rio Tinto strives to constantly reduce its water footprint and improve the overall water sustainability of its operations.
- Keywords: Water-efficient technologies, dry stacking, dust suppression, minimizing water footprint, environmental impact assessment, water stewardship.
Biodiversity Conservation and Rehabilitation Efforts
Rio Tinto is committed to protecting and enhancing biodiversity in the Pilbara region, integrating conservation into its operational practices and long-term planning.
Protecting Native Flora and Fauna
Rio Tinto actively supports various initiatives aimed at protecting the unique flora and fauna of the Pilbara.
- Habitat Restoration Programs: These programs focus on restoring degraded habitats and creating corridors to connect fragmented ecosystems.
- Species Protection Strategies: Specific strategies are implemented to protect endangered and threatened species, often involving partnerships with local experts and conservation organizations.
- Partnerships with Communities: Collaboration with local Aboriginal communities is crucial in ensuring culturally appropriate and ecologically effective conservation measures.
- Keywords: Biodiversity conservation, habitat restoration, species protection, ecological impact, environmental rehabilitation, Pilbara ecosystem, native flora and fauna.
Mine Site Rehabilitation
Rio Tinto is committed to rehabilitating mine sites after operations cease, aiming to restore the land to a productive and ecologically valuable state.
- Rehabilitation Techniques: A range of advanced techniques are employed, focusing on restoring soil health, re-establishing vegetation, and creating sustainable landscapes.
- Timelines for Completion: Detailed rehabilitation plans are developed with clear timelines for the completion of various phases, ensuring accountability and effective land management.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Long-term monitoring programs are implemented to assess the success of rehabilitation efforts and ensure the long-term health of the restored ecosystems.
- Keywords: Mine site rehabilitation, land reclamation, ecological restoration, post-mining landscape, sustainable land management, mine closure planning.
Engaging with Local Communities and Stakeholders
Rio Tinto recognizes the importance of strong relationships with local communities and stakeholders, actively engaging in meaningful dialogue and collaboration.
Community Consultation and Partnerships
Rio Tinto prioritizes open communication and collaboration with local Aboriginal communities and other stakeholders.
- Consultation Processes: Formal consultation processes are established to ensure the voices of local communities are heard and considered in decision-making processes.
- Collaborative Projects: Various collaborative projects are undertaken to maximize the positive social and economic benefits for local communities.
- Shared Benefits Agreements: These agreements formalize the commitment to sharing the benefits of mining operations with local communities.
- Community Development Initiatives: Rio Tinto invests in a range of community development initiatives to support education, healthcare and other essential services.
- Keywords: Community engagement, stakeholder consultation, Indigenous engagement, social responsibility, community partnerships, Pilbara communities, corporate social responsibility.
Conclusion
Rio Tinto's commitment to building a sustainable Pilbara future is evident in its multifaceted approach to addressing environmental concerns. From significant investments in renewable energy and water conservation to robust biodiversity protection and community engagement initiatives, the company is demonstrably working towards minimizing its environmental impact and contributing to the long-term prosperity of the region. Their ongoing commitment to transparency and collaboration underscores their dedication to responsible mining practices. To learn more about Rio Tinto's sustainability initiatives and the future of the Pilbara, visit their website and explore their comprehensive sustainability reports. Understanding Rio Tinto's Pilbara future is key to understanding the future of sustainable mining.

Featured Posts
-
 Bolidul De Milioane De Euro Al Fratilor Tate Defilare Prin Centrul Bucurestiului
May 22, 2025
Bolidul De Milioane De Euro Al Fratilor Tate Defilare Prin Centrul Bucurestiului
May 22, 2025 -
 Original Sins Finale How It Makes Dexters Debra Morgan Mistake Worse
May 22, 2025
Original Sins Finale How It Makes Dexters Debra Morgan Mistake Worse
May 22, 2025 -
 The World Trading Tournament Wtt Aimscaps Success Story
May 22, 2025
The World Trading Tournament Wtt Aimscaps Success Story
May 22, 2025 -
 Gospodin Savrseni Vanja I Sime Fotografije Koje Govore Vise Od Rijeci
May 22, 2025
Gospodin Savrseni Vanja I Sime Fotografije Koje Govore Vise Od Rijeci
May 22, 2025 -
 How To Survive A Screen Free Week With Kids A Practical Guide
May 22, 2025
How To Survive A Screen Free Week With Kids A Practical Guide
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Gray Wolf Mortality Second Colorado Wolf Dies In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
Gray Wolf Mortality Second Colorado Wolf Dies In Wyoming
May 22, 2025 -
 Shifting Strategies Otter Conservation In Wyoming Reaches A Turning Point
May 22, 2025
Shifting Strategies Otter Conservation In Wyoming Reaches A Turning Point
May 22, 2025 -
 Colorado Gray Wolfs Death In Wyoming A Setback For Reintroduction Efforts
May 22, 2025
Colorado Gray Wolfs Death In Wyoming A Setback For Reintroduction Efforts
May 22, 2025 -
 Wyoming Otter Management A Pivotal Moment
May 22, 2025
Wyoming Otter Management A Pivotal Moment
May 22, 2025 -
 Thousands Of Zebra Mussels Discovered On Boat Lift In Casper
May 22, 2025
Thousands Of Zebra Mussels Discovered On Boat Lift In Casper
May 22, 2025
