Pilbara Iron Ore Mining: Rio Tinto Responds To Forrest's Criticism

Table of Contents
Rio Tinto's Defence of its Pilbara Operations
Rio Tinto has vigorously defended its operations in the Pilbara, highlighting its commitment to sustainable practices and community engagement. Their response centers on three key areas: environmental stewardship, respect for Indigenous land rights, and significant economic contributions to the region.
Environmental Stewardship
Rio Tinto emphasizes its substantial investments in environmental protection within the Pilbara. Their initiatives aim to minimize the environmental footprint of their iron ore mining activities. Key strategies include:
- Aggressive Carbon Emission Reduction Targets: Rio Tinto has publicly committed to ambitious goals for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, aiming for net-zero emissions by a specific date. This involves transitioning to renewable energy sources and improving operational efficiency.
- Innovative Water Management Strategies: Facing a challenging arid climate, Rio Tinto has implemented advanced water recycling and conservation techniques to minimize water consumption in their mining processes. They utilize technologies like desalination and water reuse systems.
- Biodiversity Conservation Programs: Recognizing the importance of biodiversity, Rio Tinto supports various programs aimed at protecting native flora and fauna in the Pilbara. This includes habitat restoration projects and partnerships with conservation organizations.
These initiatives directly counter Forrest's criticisms concerning the environmental damage caused by Pilbara iron ore mining, showcasing Rio Tinto's commitment to sustainable mining and water conservation. While acknowledging the environmental challenges, Rio Tinto provides data demonstrating significant progress in reducing carbon emissions and protecting biodiversity.
Addressing Indigenous Land Rights Concerns
A crucial aspect of the debate revolves around Indigenous land rights and the consultation processes employed by Rio Tinto. Forrest's criticisms focus on the potential impacts on traditional owners and the adequacy of engagement with Indigenous communities.
Collaboration with Traditional Owners
Rio Tinto maintains that it is actively engaged in collaborative partnerships with Traditional Owners in the Pilbara. These efforts include:
- Joint Ventures and Agreements: Rio Tinto has established numerous joint ventures and benefit-sharing agreements with Indigenous groups, providing economic opportunities and ensuring their involvement in decision-making processes.
- Employment Opportunities: A significant number of Indigenous people are employed by Rio Tinto and its contractors, contributing to economic empowerment within the communities.
- Cultural Heritage Protection: Rio Tinto invests in the preservation of significant cultural heritage sites within its operational areas, working closely with Traditional Owners to protect ancestral lands.
These actions aim to directly counter the accusations of insufficient consultation and disregard for Indigenous land rights. Rio Tinto emphasizes its commitment to community engagement and the importance of benefit-sharing agreements in fostering mutually beneficial relationships with traditional owners.
Economic Contributions and Regional Development
The economic contributions of Pilbara iron ore mining are substantial, with Rio Tinto playing a major role in driving regional growth and job creation.
Job Creation and Infrastructure Investment
Rio Tinto's operations directly and indirectly create thousands of jobs in the Pilbara, supporting a significant population and driving economic activity. This impact includes:
- Direct Employment: A large workforce is directly employed by Rio Tinto in its mining operations, processing facilities, and related services.
- Indirect Employment: The industry supports a vast network of contractors and businesses, generating numerous indirect employment opportunities.
- Tax Revenue Generation: Rio Tinto contributes significantly to government revenue through taxes and royalties, funding essential public services and infrastructure development.
- Infrastructure Investments: Rio Tinto has invested heavily in infrastructure projects in the Pilbara, improving transport networks, utilities, and community facilities.
This substantial economic contribution refutes claims of economic exploitation, emphasizing the positive economic impact and significant job creation resulting from Rio Tinto's infrastructure investment in regional development.
Future of Pilbara Iron Ore Mining: A Path Forward
The long-term sustainability of Pilbara iron ore mining depends on adapting to evolving environmental and social expectations.
Sustainable Mining Practices and Community Relations
Rio Tinto outlines its vision for the future, focusing on:
- Sustainable Development Goals: Alignment with global sustainable development goals, prioritizing environmental protection and social responsibility.
- Technological Advancements: Investing in research and development to implement innovative, environmentally friendly technologies to minimize impacts.
- Enhanced Community Relations: Strengthening relationships with Indigenous communities through continuous dialogue and collaboration.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Implementing comprehensive strategies to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change on the Pilbara ecosystem.
This approach demonstrates Rio Tinto's commitment to sustainable development, acknowledging the importance of community relations in navigating the challenges of climate change and ensuring responsible mining practices.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Debate Surrounding Pilbara Iron Ore Mining
The debate surrounding Pilbara iron ore mining and its impacts continues. Rio Tinto's response to Andrew Forrest's criticisms highlights its efforts to mitigate environmental damage, respect Indigenous land rights, and contribute significantly to regional economic development. While acknowledging the challenges, Rio Tinto emphasizes its commitment to sustainable practices and responsible community engagement. The ongoing dialogue and collaboration between stakeholders are crucial for ensuring a future where the economic benefits of Pilbara iron ore mining are balanced with environmental protection and social equity. To learn more about the complexities of Pilbara iron ore mining, the environmental and social challenges, and Rio Tinto's detailed responses, we encourage you to explore Rio Tinto's sustainability reports and further research on this vital industry.

Featured Posts
-
 Former Man Utd Players Downfall Personal Problems Cited
May 23, 2025
Former Man Utd Players Downfall Personal Problems Cited
May 23, 2025 -
 Emlyt Washntn Wtsryhat Rwdryghyz Mwjt Jdydt Mn Almtalbat Balhryt Lflstyn
May 23, 2025
Emlyt Washntn Wtsryhat Rwdryghyz Mwjt Jdydt Mn Almtalbat Balhryt Lflstyn
May 23, 2025 -
 Compre Ingressos Para A Atlantida Celebration Com Nando Reis Armandinho E Di Ferrero
May 23, 2025
Compre Ingressos Para A Atlantida Celebration Com Nando Reis Armandinho E Di Ferrero
May 23, 2025 -
 London To Host Grand Ole Oprys 100th Anniversary Show
May 23, 2025
London To Host Grand Ole Oprys 100th Anniversary Show
May 23, 2025 -
 Englands Test Future Assessing Dan Lawrences Potential As An Opener
May 23, 2025
Englands Test Future Assessing Dan Lawrences Potential As An Opener
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Memorial Day Weekend Gas Prices To Hit Decade Lows
May 23, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend Gas Prices To Hit Decade Lows
May 23, 2025 -
 Lowest Gas Prices In Decades Predicted For Memorial Day Weekend
May 23, 2025
Lowest Gas Prices In Decades Predicted For Memorial Day Weekend
May 23, 2025 -
 Memorial Day Weekend Gas Prices Decades Low Expectations
May 23, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend Gas Prices Decades Low Expectations
May 23, 2025 -
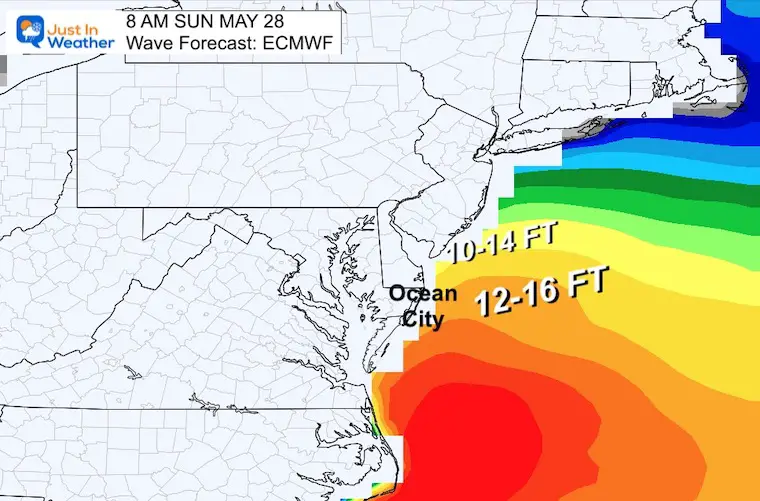 2025 Memorial Day Weekend Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 23, 2025
2025 Memorial Day Weekend Beach Forecast Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point
May 23, 2025 -
 Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point Beach Weather Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Forecast
May 23, 2025
Ocean City Rehoboth Sandy Point Beach Weather Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Forecast
May 23, 2025
