Planning A Reactor Power Uprate? Navigating The NRC Process
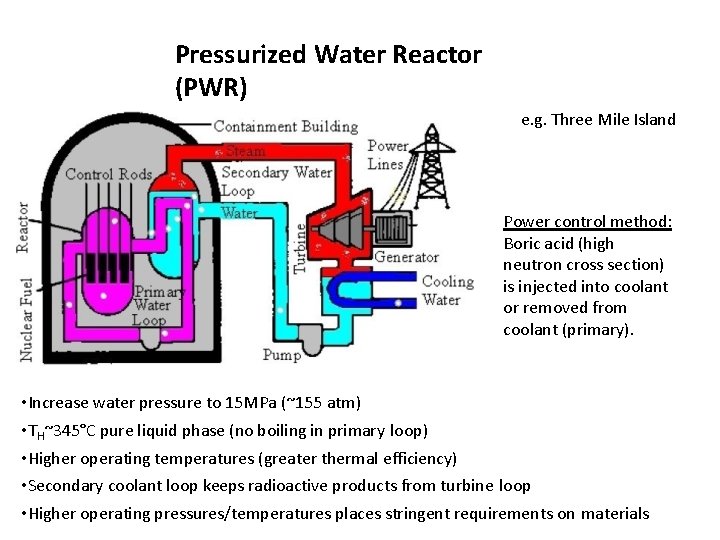
Table of Contents
Understanding the NRC's Regulatory Framework for Reactor Power Uprates
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) holds the ultimate authority in approving reactor power uprates in the United States. Their role is to ensure the safety and security of nuclear power plants while also overseeing the efficiency and effectiveness of the industry. Understanding the NRC's regulatory framework is paramount for a successful power uprate. This framework is primarily defined in Title 10, Code of Federal Regulations, Part 50 (10 CFR Part 50), which outlines the licensing requirements for nuclear power plants. This part details the specific regulations and standards related to the design, construction, operation, and modification of nuclear reactors.
The NRC differentiates between minor and major power uprates. Minor modifications may allow for streamlined approvals, whereas major power uprates necessitate a far more extensive review process, involving significant documentation and safety analyses. The specific classification depends on the extent of the proposed changes and their potential impact on plant safety.
- Review of existing plant operating licenses: A thorough review of the current operating license is essential to identify any limitations or conditions that could affect the power uprate.
- Detailed safety analysis reports: Comprehensive reports are required to demonstrate that the uprate will not compromise the safety of the plant or the surrounding environment.
- Compliance with applicable NRC regulations: Strict adherence to all applicable NRC regulations and industry standards is mandatory throughout the entire process.
- Public notification and comment periods: The NRC mandates public notification and allows for comment periods, ensuring transparency and public participation in the decision-making process.
Preparing the Preliminary Safety Analysis Report (PSAR)
The Preliminary Safety Analysis Report (PSAR) serves as the cornerstone of the NRC review process for a reactor power uprate. This comprehensive document meticulously details all aspects of the proposed uprate, justifying its safety and compliance with regulatory requirements. A well-prepared PSAR is crucial for a successful application.
The key elements of a PSAR include a detailed description of the proposed modifications, a thorough evaluation of potential safety impacts, and justifications for design changes. It needs to demonstrate how the proposed power uprate will maintain or improve the plant's overall safety margins. This often includes detailed safety analyses such as:
- Thermal-hydraulic analyses: Evaluating the effects of increased power on the plant's thermal performance and cooling systems.
- Structural analyses: Assessing the integrity of plant structures under increased operating conditions.
- Probabilistic risk assessments (PRA): Quantifying the risks associated with the power uprate and demonstrating that these risks remain acceptably low.
Key components of a robust PSAR also include:
- Identification of potential safety impacts: Proactively identifying and addressing potential negative consequences.
- Justification for design modifications: Clearly explaining the rationale behind any proposed design changes.
- Demonstration of compliance with safety limits: Providing concrete evidence that all safety limits and operating parameters will be met.
- Mitigation strategies for identified risks: Outlining plans to mitigate any potential risks associated with the power uprate.
Navigating the NRC Review and Approval Process
The NRC review process for a reactor power uprate is a multi-stage process that can take considerable time. Effective communication and proactive engagement with the NRC are crucial throughout this process. The process generally follows these stages:
- Pre-application consultations with the NRC staff: Early engagement with the NRC staff allows for early identification and resolution of potential issues. This helps streamline the application review process.
- Formal submittal of the application and supporting documentation: A complete and accurate application submission is essential to avoid delays.
- Response to NRC requests for additional information: The NRC may request further clarification or information during the review process. Prompt and thorough responses are crucial.
- Addressing any safety concerns raised by the NRC: Addressing any safety concerns raised by the NRC in a timely and satisfactory manner is vital.
- NRC inspection and audits of the facility: The NRC may conduct inspections and audits to verify the accuracy of information provided and the overall safety of the plant.
Post-Approval Implementation and Ongoing Compliance
After receiving NRC approval, the post-approval implementation phase requires careful monitoring and adherence to regulations. Ongoing compliance is not just a short-term commitment; it is a continuous effort.
- Verification of design modifications: Ensuring that all design modifications are implemented correctly and verified.
- Operational testing and validation: Conducting thorough operational testing to validate the plant's performance at the higher power level.
- Ongoing monitoring of plant performance: Continuous monitoring of plant performance to identify and address any issues promptly.
- Regular reporting to the NRC: Adhering to the regular reporting requirements stipulated by the NRC. Effective training for plant personnel is critical to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the upgraded plant.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the NRC process for a reactor power uprate requires careful planning, thorough preparation, and proactive communication with the NRC. By understanding the regulatory framework, meticulously preparing the necessary documentation, and maintaining open communication throughout the process, you can significantly increase your chances of a smooth and efficient power uprate. Remember to consult with experienced nuclear engineers and regulatory experts to ensure compliance and optimize your project timeline. Don't delay – start planning your reactor power uprate today and ensure you understand the intricacies of the NRC process. Contact us for expert guidance on your reactor power uprate project.

Featured Posts
-
 High Profile Office365 Accounts Breached Resulting In Significant Financial Loss
May 01, 2025
High Profile Office365 Accounts Breached Resulting In Significant Financial Loss
May 01, 2025 -
 Nrc Update Assam Cm Targets Aadhaar Cardholders Not Included
May 01, 2025
Nrc Update Assam Cm Targets Aadhaar Cardholders Not Included
May 01, 2025 -
 Navigating The Dragons Den Tips For Investors And Entrepreneurs
May 01, 2025
Navigating The Dragons Den Tips For Investors And Entrepreneurs
May 01, 2025 -
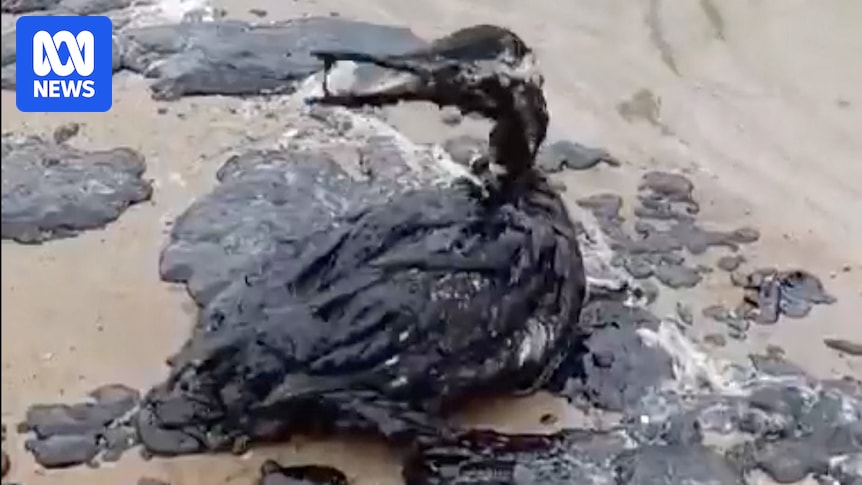 Major Oil Spill Forces Closure Of 62 Miles Of Russian Black Sea Beaches
May 01, 2025
Major Oil Spill Forces Closure Of 62 Miles Of Russian Black Sea Beaches
May 01, 2025 -
 Afterschool Tragedy Car Crashes Into Program Killing Four Children
May 01, 2025
Afterschool Tragedy Car Crashes Into Program Killing Four Children
May 01, 2025
