Preventing Black Screens And Silent Radios: Improving Air Traffic Control Reliability

Table of Contents
Hardware Upgrades and Maintenance for Enhanced Air Traffic Control Reliability
Investing in robust and reliable hardware is fundamental to improving Air Traffic Control reliability. This involves both proactive maintenance and strategic upgrades to modern technologies.
Regular System Inspections and Preventative Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance is not merely a cost; it's an investment in safety and efficiency. Preventative measures are far more cost-effective than emergency repairs triggered by unexpected failures.
- Redundant Systems: Implementing redundant systems ensures that if one component fails, a backup is immediately available, preventing service interruptions.
- Backup Power Generators: Reliable backup power is essential to maintain operations during power outages, avoiding black screens and silent radios.
- Rigorous Testing: Regular and comprehensive testing of all hardware components, including simulated failure scenarios, is crucial to identify potential weaknesses before they cause problems.
- Software Updates: Regular software updates are critical to patching security vulnerabilities and incorporating performance improvements.
Preventative maintenance significantly reduces the likelihood of unexpected downtime, saving money in the long run by avoiding costly emergency repairs and minimizing operational disruptions.
Investing in Modernized Hardware and Technology
Upgrading to modern hardware offers significant advantages in terms of reliability and performance. The transition to newer technologies is an investment in the future of safe and efficient air traffic management.
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs): Replacing traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) with SSDs significantly improves data access speeds and reduces the risk of data loss due to mechanical failure.
- Advanced Network Infrastructure: Modern network architectures offer higher bandwidth, improved stability, and enhanced security features, reducing the risk of communication failures.
- Improved Radar Systems: Upgrading to advanced radar systems with increased range, accuracy, and resolution allows for better surveillance and tracking of aircraft, enhancing situational awareness for controllers.
Modern hardware translates to increased uptime, reduced maintenance requirements, and ultimately, higher Air Traffic Control reliability.
Software Development and Cybersecurity for Robust Air Traffic Control Systems
The software underpinning Air Traffic Control systems is equally critical to its reliability. Robust software development practices and stringent cybersecurity measures are essential to preventing failures and protecting the system from external threats.
Secure Software Development Lifecycle
Secure coding practices are crucial to building reliable and resilient ATC software. This involves careful planning, rigorous testing, and continuous monitoring.
- Penetration Testing: Simulating cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
- Code Reviews: Having multiple developers review each other's code helps catch errors and vulnerabilities early in the development process.
- Regular Security Audits: Periodic audits identify weaknesses and ensure the system remains protected against emerging threats.
Software bugs, if not addressed, can lead to system instability, malfunctions, and even complete system failures.
Cybersecurity Measures to Protect ATC Networks
Protecting ATC networks from cyberattacks is paramount. The consequences of a successful cyberattack can be catastrophic, disrupting air traffic and potentially causing accidents.
- Firewalls: Implementing strong firewalls to filter out malicious traffic and protect the network from unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity and alerting administrators to potential threats.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple forms of authentication to access sensitive systems, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Cybersecurity is not a one-time investment but an ongoing process of vigilance and adaptation to protect the integrity and reliability of Air Traffic Control systems.
Training and Human Factors in Maintaining Air Traffic Control Reliability
Human factors play a significant role in the overall reliability of Air Traffic Control. Well-trained controllers and ergonomically designed workspaces are vital for efficient and safe operations.
Comprehensive Training Programs for Air Traffic Controllers
Ongoing training is crucial to maintaining the skills and knowledge of air traffic controllers, ensuring they can effectively manage complex situations and utilize the technology efficiently.
- Simulator Training: Realistic simulations allow controllers to practice handling various scenarios, including emergencies and system failures, enhancing their response capabilities.
- Emergency Procedures: Regular training on emergency procedures helps controllers react effectively in critical situations, minimizing the impact of unforeseen events.
- System Familiarization: Keeping controllers updated with the latest technology and system upgrades is crucial to maintain proficiency and adaptability.
- Stress Management Techniques: Providing training in stress management and coping mechanisms helps controllers handle pressure and avoid errors due to fatigue or stress.
Effective training minimizes human error, a major factor in incidents and accidents.
Ergonomic Workspaces and Reduced Controller Workload
Creating a comfortable and efficient workspace is essential for minimizing controller fatigue and maximizing performance.
- Adjustable Seating: Providing controllers with adjustable seating ensures comfort and proper posture, reducing physical strain and fatigue.
- Improved Displays: Modern, high-resolution displays improve readability and reduce eye strain, leading to better situational awareness.
- Workload Management Tools: Implementing tools to optimize workload distribution and prioritize tasks helps controllers handle the demands of their jobs more effectively.
Reducing controller workload minimizes errors caused by stress and fatigue, contributing to overall Air Traffic Control reliability.
Conclusion
Improving Air Traffic Control reliability requires a holistic approach encompassing hardware upgrades, robust software development and cybersecurity, and comprehensive training for air traffic controllers. By prioritizing investments in modern hardware, secure software, and comprehensive training, we can significantly improve Air Traffic Control reliability and prevent future black screens and silent radios, ensuring the safety of air travel for years to come. Enhancing air traffic control safety through these measures is not merely desirable; it is essential for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the global aviation network. Investing in reliable air traffic management systems is an investment in the safety and future of air travel.

Featured Posts
-
 Massive Zebra Mussel Infestation Found On Private Casper Boat Lift
May 22, 2025
Massive Zebra Mussel Infestation Found On Private Casper Boat Lift
May 22, 2025 -
 The Increasing Importance Of Succession Planning For Ultra High Net Worth Families
May 22, 2025
The Increasing Importance Of Succession Planning For Ultra High Net Worth Families
May 22, 2025 -
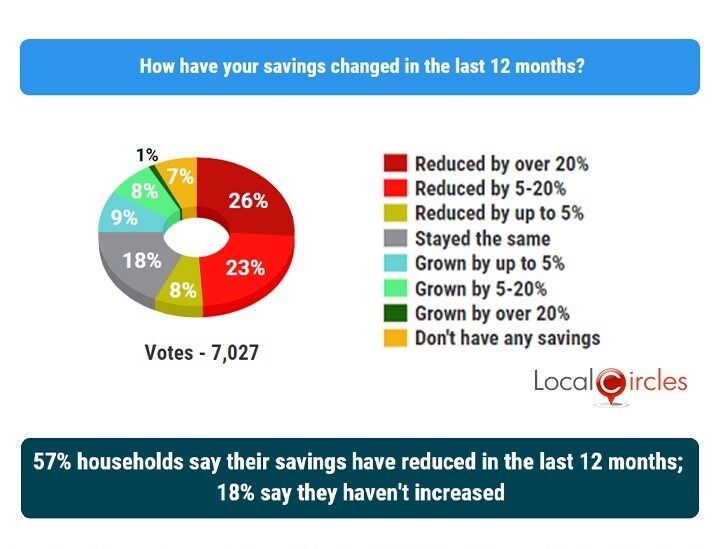 3 Billion Slash To Sse Spending Plan Impact Of Economic Slowdown
May 22, 2025
3 Billion Slash To Sse Spending Plan Impact Of Economic Slowdown
May 22, 2025 -
 Sheriffs Reelection Campaign Suspended Following Five Inmate Escapes In New Orleans
May 22, 2025
Sheriffs Reelection Campaign Suspended Following Five Inmate Escapes In New Orleans
May 22, 2025 -
 Googles Prototype Ai Smart Glasses A Hands On Review
May 22, 2025
Googles Prototype Ai Smart Glasses A Hands On Review
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
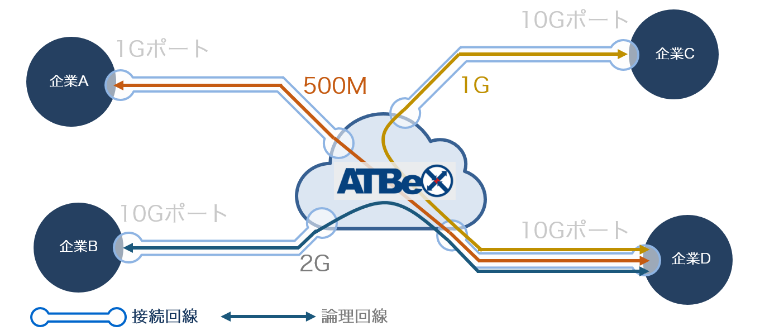 At Be X Ntt Multi Interconnect Ascii Jp
May 22, 2025
At Be X Ntt Multi Interconnect Ascii Jp
May 22, 2025 -
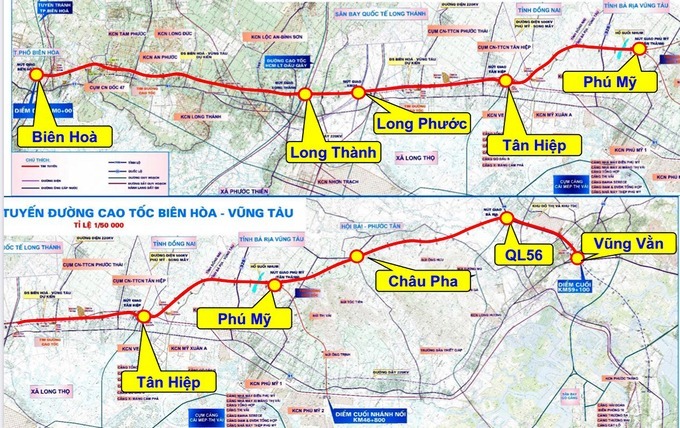 Thong Tin Moi Nhat Cao Toc Noi Dong Nai Va Vung Tau Sap Thong Xe
May 22, 2025
Thong Tin Moi Nhat Cao Toc Noi Dong Nai Va Vung Tau Sap Thong Xe
May 22, 2025 -
 Ascii Jp Ntt Multi Interconnect At Be X
May 22, 2025
Ascii Jp Ntt Multi Interconnect At Be X
May 22, 2025 -
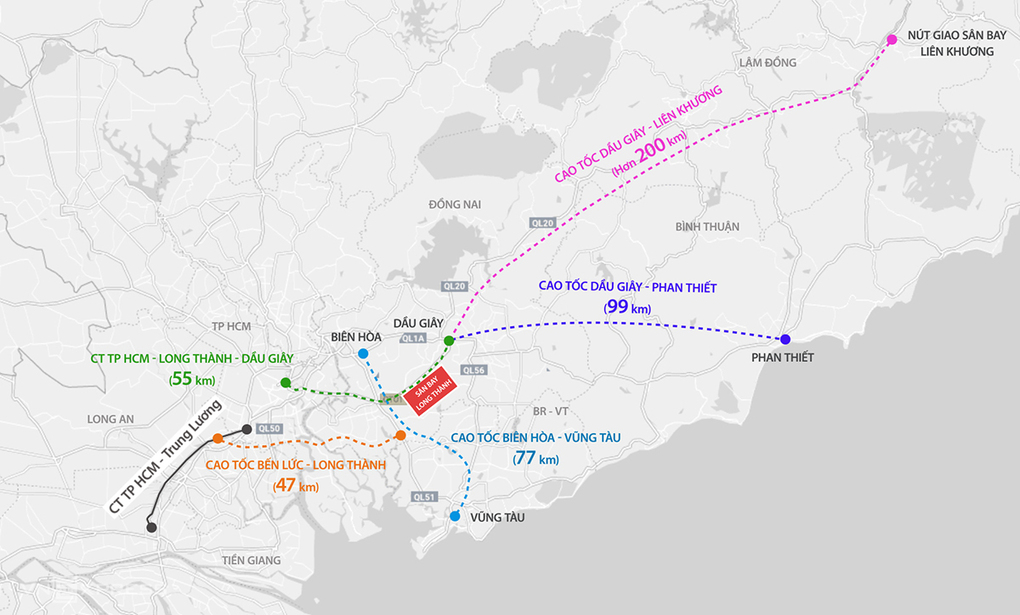 Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Du Kien Thong Xe Thang 9
May 22, 2025
Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Du Kien Thong Xe Thang 9
May 22, 2025 -
 Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Thong Xe Du Kien 2 9
May 22, 2025
Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Thong Xe Du Kien 2 9
May 22, 2025
