PwC's Withdrawal From Nine Sub-Saharan African Countries: Implications And Analysis

Table of Contents
The recent announcement of PwC's withdrawal from nine Sub-Saharan African countries has sent shockwaves through the business and development communities. This strategic decision, impacting the availability of auditing and consulting services, raises critical questions about the future of these sectors in the region and its overall investment climate. This analysis delves into the implications of PwC's departure and explores its potential long-term consequences, examining the reasons behind the withdrawal and its impact on affected nations. Understanding the nuances of the PwC Sub-Saharan Africa withdrawal is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers alike.
Reasons Behind PwC's Withdrawal
Operational Challenges and Costs
PwC's decision likely stems from a confluence of operational hurdles and escalating costs inherent in operating within certain Sub-Saharan African markets. These challenges significantly impact profitability and operational efficiency.
- Logistical complexities: Navigating complex infrastructure, unreliable transportation networks, and limited communication systems adds significant overhead.
- Security concerns: Operating in regions with political instability or high crime rates increases security risks and necessitates substantial investments in protective measures.
- Talent acquisition and retention: Attracting and retaining skilled professionals in competitive markets often requires offering higher salaries and benefits, impacting profitability.
- Fluctuating exchange rates: Volatile currency markets create uncertainty and can significantly impact project costs and financial planning.
- Compliance burdens: Meeting diverse and evolving regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions increases administrative costs and compliance risks.
Risk Assessment and Reputation Management
PwC's risk assessment likely played a crucial role in its decision. Operating in certain Sub-Saharan African countries presents heightened reputational risks.
- Concerns about corruption: The prevalence of corruption in some regions poses significant reputational risks, potentially damaging PwC's global brand.
- Weak regulatory frameworks: Insufficient regulatory oversight and enforcement can increase the risk of financial irregularities and legal disputes.
- Potential for legal disputes: Operating in environments with unpredictable legal systems increases the likelihood of protracted and costly legal battles.
- Brand protection in volatile environments: Maintaining brand integrity and reputation in politically unstable regions requires considerable investment and vigilance.
Strategic Realignment and Prioritization
PwC's withdrawal aligns with a broader strategic realignment focused on prioritizing key markets and optimizing its global footprint for enhanced profitability.
- Concentration of resources on higher-growth markets: The firm likely prioritizes investing in markets offering greater growth potential and higher returns.
- Streamlining operations: Focusing resources on more stable and predictable markets allows for streamlined operations and cost efficiencies.
- Optimizing global footprint: The withdrawal reflects a strategic decision to optimize PwC's global presence, concentrating its resources on markets offering greater long-term value.
Impact on Affected Countries
Loss of Expertise and Capacity
PwC's departure significantly impacts the availability of auditing and consulting services in the affected countries, leaving a void in expertise and capacity.
- Reduced access to high-quality audit services: Smaller local firms may lack the resources and expertise to adequately fill the gap, potentially impacting the quality of financial reporting.
- Potential increase in financial irregularities: The reduced availability of high-quality audit services could lead to an increase in financial irregularities and a decline in corporate governance standards.
- Challenges for attracting foreign investment: The absence of a prominent global firm like PwC might negatively impact investor confidence and deter foreign direct investment.
Implications for Economic Development
The withdrawal's consequences extend beyond the immediate loss of services, impacting economic development and growth prospects.
- Impact on investor confidence: PwC's departure could signal a lack of confidence in the business environment, potentially discouraging investment.
- Potential slowdown in business expansion: The reduced availability of specialized services could hinder business expansion and growth.
- Risks to financial stability: A decline in auditing standards and corporate governance could pose risks to financial stability and economic growth.
Alternative Service Providers and Market Dynamics
The departure creates opportunities for competing firms, but also presents challenges for those seeking to fill the void left by PwC.
- Market share shifts: Existing players will likely compete to acquire PwC's former clients, leading to potential market share shifts.
- Increased competition among remaining firms: The increased demand for services might intensify competition among remaining firms.
- Opportunities for local firms: Local firms may see increased opportunities to expand their client base and develop their capabilities.
Future Implications and Outlook
Long-Term Effects on the African Auditing Landscape
PwC's withdrawal will have long-term implications for auditing standards and regulatory frameworks within the affected Sub-Saharan African countries.
- Potential need for strengthened regulatory oversight: The departure might necessitate enhanced regulatory oversight and enforcement to maintain auditing standards.
- Development of local expertise: The void left by PwC might accelerate the development of local expertise and capacity within the auditing and consulting sectors.
- Increased scrutiny of financial reporting: Regulatory bodies may implement stricter controls and increase scrutiny of financial reporting practices.
Potential for Restructuring or Re-entry
PwC's decision isn't necessarily irreversible. Future changes could lead to a reconsideration of their withdrawal.
- Changes in regulatory environments: Improvements in regulatory frameworks and governance could make the region more attractive.
- Improved security: Enhanced security conditions might reduce operational risks and make the region more appealing for investment.
- Economic growth: Significant economic growth and development could attract PwC back into the market.
Lessons Learned for Other Multinational Firms
PwC's experience offers valuable lessons for other multinational firms operating in challenging environments.
- Importance of robust risk assessment: Thorough risk assessments are crucial for making informed decisions about market entry and sustained operations.
- Careful consideration of operational challenges: A realistic evaluation of operational challenges is necessary for successful operations in developing markets.
- Sustainable business models in developing markets: Developing sustainable business models tailored to the specific challenges of each market is vital for long-term success.
Conclusion:
PwC's withdrawal from nine Sub-Saharan African countries represents a significant event with far-reaching consequences. The decision underscores the complexities of operating in challenging environments and highlights the importance of robust risk assessment. The PwC Sub-Saharan Africa withdrawal will reshape the auditing and consulting landscape, potentially affecting economic growth, investor confidence, and the availability of crucial expertise. Careful monitoring and further analysis are necessary to fully grasp the long-term ramifications of this strategic shift. Understanding the implications of this withdrawal is crucial for all stakeholders invested in the future of Sub-Saharan Africa.

Featured Posts
-
 Parita Sul Lavoro I Progressi Ci Sono Ma La Strada E Ancora Lunga
Apr 29, 2025
Parita Sul Lavoro I Progressi Ci Sono Ma La Strada E Ancora Lunga
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Arizona Boating Competition Speedboat Flips During Record Attempt
Apr 29, 2025
Arizona Boating Competition Speedboat Flips During Record Attempt
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Akeso Plunges Cancer Drug Trial Disappoints
Apr 29, 2025
Akeso Plunges Cancer Drug Trial Disappoints
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Porsche Cayenne Gts Coupe Moje Wrazenia Po Jezdzie Testowym
Apr 29, 2025
Porsche Cayenne Gts Coupe Moje Wrazenia Po Jezdzie Testowym
Apr 29, 2025 -
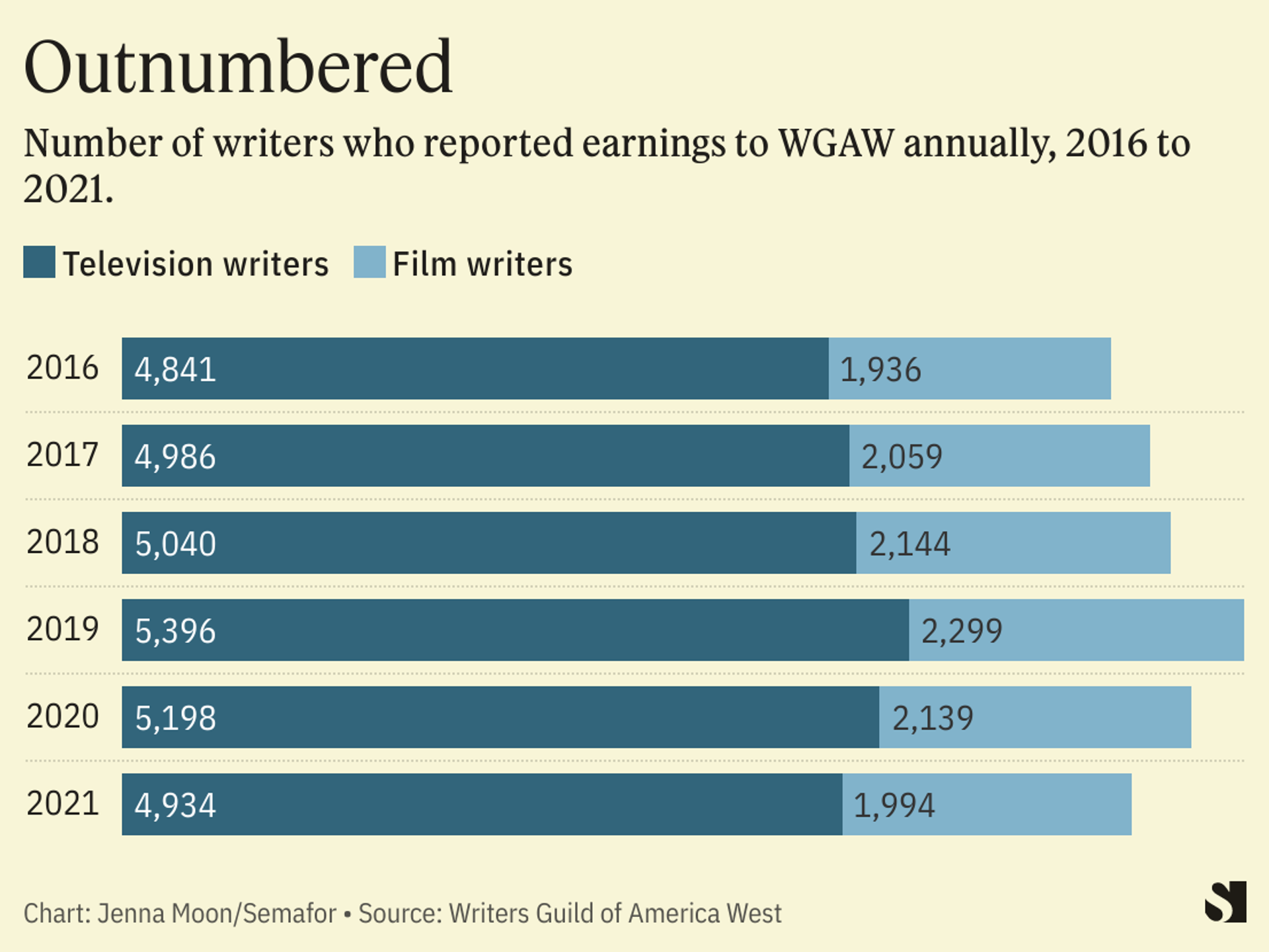 Double Strike Cripples Hollywood Actors And Writers Demand Fair Treatment
Apr 29, 2025
Double Strike Cripples Hollywood Actors And Writers Demand Fair Treatment
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Gripna Vlna Ofitsialno Sobschenie Ot Prof Iva Khristova
Apr 29, 2025
Gripna Vlna Ofitsialno Sobschenie Ot Prof Iva Khristova
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Ekspertno Mnenie Prof Iva Khristova Za Gripnata Vlna
Apr 29, 2025
Ekspertno Mnenie Prof Iva Khristova Za Gripnata Vlna
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Skolmassakern Historien Om Helena Och Iva
Apr 29, 2025
Skolmassakern Historien Om Helena Och Iva
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Prof Iva Khristova Nyama Danni Za Vtora Gripna Vlna
Apr 29, 2025
Prof Iva Khristova Nyama Danni Za Vtora Gripna Vlna
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Helena Och Iva Oegonvittnen Till Skolmassakern
Apr 29, 2025
Helena Och Iva Oegonvittnen Till Skolmassakern
Apr 29, 2025
