Rare Earth Minerals: Fueling A New Cold War?
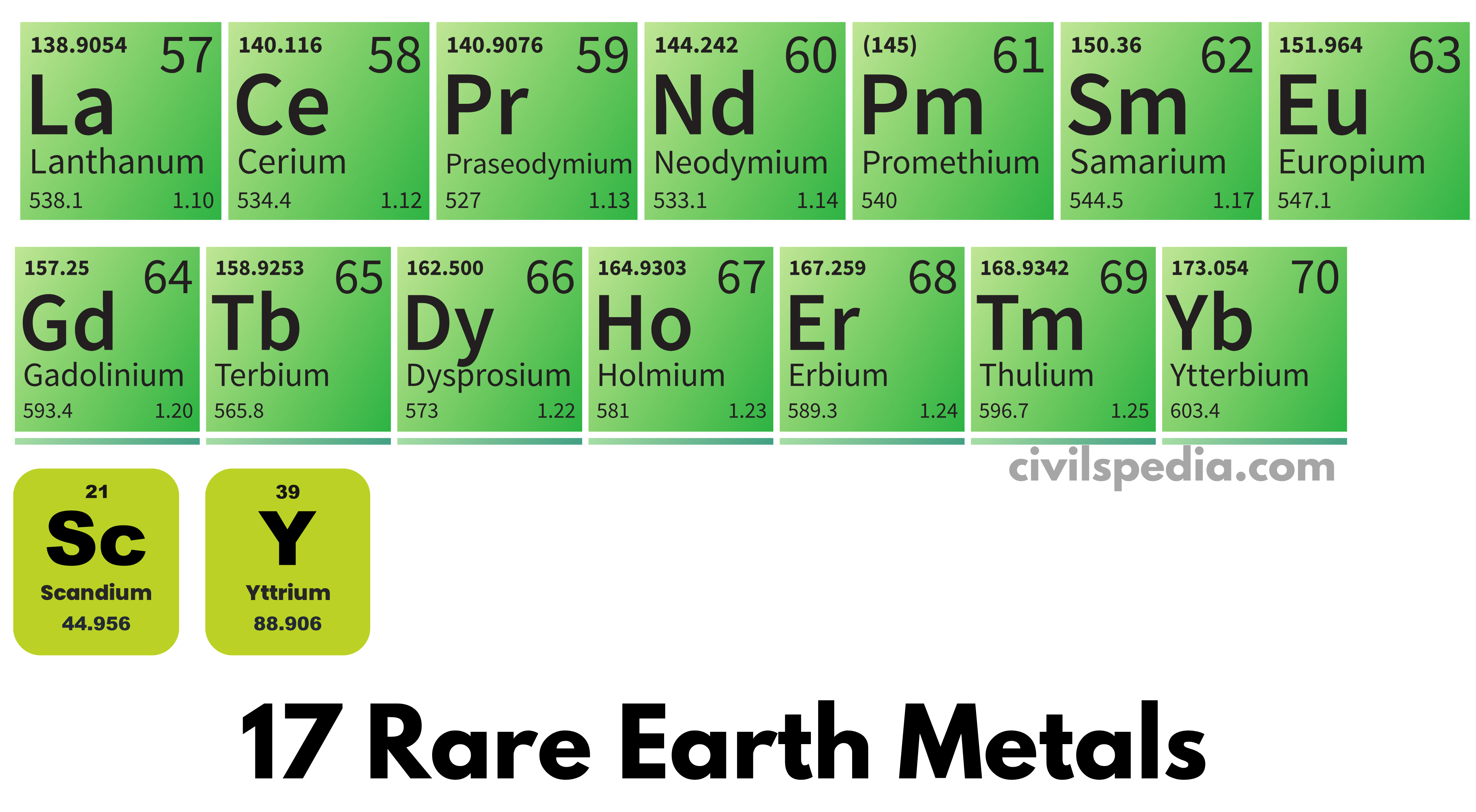
Table of Contents
What are Rare Earth Minerals and Why Are They So Important?
Defining Rare Earth Minerals: The term "rare earth minerals" is somewhat misleading. While the 17 elements classified as rare earth elements (REEs) – scandium, yttrium, and the lanthanides (lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, and lutetium) – aren't necessarily rare in terms of overall abundance in the Earth's crust, they are often dispersed and challenging to extract economically. Their unique properties, however, make them indispensable.
- Unique Properties: REEs possess exceptional magnetic, luminescent, and catalytic properties, allowing for a wide range of applications.
Essential Applications of Rare Earth Minerals: REEs are crucial to numerous high-tech sectors:
Green Technologies: The burgeoning renewable energy sector is heavily reliant on REEs.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Neodymium magnets in EV motors are critical for their performance.
- Wind Turbines: REEs are essential for the powerful generators that convert wind energy into electricity.
- Solar Panels: REEs enhance the efficiency of solar cells, boosting renewable energy production.
- Energy Storage: REEs play a vital role in advanced battery technologies, improving energy density and lifespan. This contributes significantly to the development of sustainable technology.
Military and Defense: National security depends on access to REEs.
- Guided Missiles: REEs are used in precision-guided munitions and targeting systems.
- Radar Systems: Their magnetic properties are essential for advanced radar and sonar technologies.
- Communication Technologies: REEs are integral to many communication and navigation systems. These are essential components of modern defense technology.
Consumer Electronics: Our daily lives are intertwined with REE-dependent technologies.
- Smartphones: REEs are found in screens, speakers, and vibration motors.
- Computers: REEs contribute to the performance of hard drives and other components.
Geopolitical Landscape of Rare Earth Mineral Production and Trade
China's Dominance in Rare Earth Mining and Processing: China currently dominates the global rare earth market, controlling a vast majority of the mining and processing capacity. This creates significant vulnerabilities in global supply chains. China's rare earth monopoly gives it considerable economic and political leverage, enabling the implementation of trade restrictions and export controls. This resource nationalism raises concerns about potential disruptions to global REE supply.
Diversification Efforts and the Search for Alternative Sources: Recognizing the risks associated with over-reliance on China, many countries are investing heavily in diversifying their REE sources.
- New Mining Projects: Australia, the United States, and Canada, among others, are actively exploring and developing new rare earth mines. This rare earth mining push aims to bolster domestic REE production.
- Processing Challenges: Establishing REE processing facilities is complex and expensive, presenting a significant hurdle to diversification efforts. The development of robust REE exploration techniques is also vital for success.
The Potential for Conflict and Cooperation
The Risk of Resource Conflicts: The scarcity of rare earth minerals creates a fertile ground for geopolitical tensions.
- Territorial Disputes: Competition for access to REE deposits could exacerbate existing territorial disputes.
- Trade Wars: Restrictions on REE exports could escalate into broader trade conflicts between nations.
- International Organizations: Organizations like the UN play a crucial role in managing these risks through international agreements and conflict resolution mechanisms.
Opportunities for International Cooperation: While the potential for conflict is real, there is also a pressing need for international cooperation.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Collaborative efforts are crucial to ensuring the responsible mining and processing of REEs, minimizing environmental damage.
- Transparent Trade Agreements: Fair and transparent trade agreements can promote equitable access to rare earth minerals and prevent exploitation. Global cooperation is essential to achieving this goal.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Rare Earth Minerals
The scarcity of rare earth minerals presents significant geopolitical challenges. Their crucial role in both technological advancement and national security cannot be overstated. Diversifying REE sources and fostering international cooperation are not merely desirable goals; they are essential for mitigating the risks of resource conflicts and ensuring a stable supply of rare earth elements for the future. We must proactively engage in discussions about responsible resource management and global cooperation to prevent a "rare earth war." The future security of rare earth mineral supply and its implications for rare earth resources requires immediate attention and strategic planning. Learn more about the issues surrounding rare earth minerals and advocate for policies promoting responsible resource management and global cooperation.

Featured Posts
-
 Covid 19 Vaccine Policy Change Proposed Rfk Jr S Hhs To Reconsider Routine Vaccinations
May 17, 2025
Covid 19 Vaccine Policy Change Proposed Rfk Jr S Hhs To Reconsider Routine Vaccinations
May 17, 2025 -
 Rossiyskie Investitsii V Uzbekistane Voshli V Troyku Liderov
May 17, 2025
Rossiyskie Investitsii V Uzbekistane Voshli V Troyku Liderov
May 17, 2025 -
 Free Live Stream Seattle Mariners Vs Chicago Cubs Spring Training
May 17, 2025
Free Live Stream Seattle Mariners Vs Chicago Cubs Spring Training
May 17, 2025 -
 Officials Admit Missed Call In Knicks Pistons Game
May 17, 2025
Officials Admit Missed Call In Knicks Pistons Game
May 17, 2025 -
 Recent Developments In The Oil Market May 16 2024
May 17, 2025
Recent Developments In The Oil Market May 16 2024
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 2025s Top Rated Crypto Casinos Bitcoin Casinos With Fast Withdrawals And Exclusive Bonuses
May 17, 2025
2025s Top Rated Crypto Casinos Bitcoin Casinos With Fast Withdrawals And Exclusive Bonuses
May 17, 2025 -
 Top Bitcoin Casinos 2025 Easy Withdrawals Exclusive Bonuses And Best Crypto Gambling Sites
May 17, 2025
Top Bitcoin Casinos 2025 Easy Withdrawals Exclusive Bonuses And Best Crypto Gambling Sites
May 17, 2025 -
 Best Crypto Casinos 2025 Top Bitcoin Casinos With Easy Withdrawals And Exclusive Bonuses
May 17, 2025
Best Crypto Casinos 2025 Top Bitcoin Casinos With Easy Withdrawals And Exclusive Bonuses
May 17, 2025 -
 Jackbit Your Best Crypto Casino Choice In 2025
May 17, 2025
Jackbit Your Best Crypto Casino Choice In 2025
May 17, 2025 -
 Review Of Jackbit A Top Bitcoin Casino With Fast Withdrawals
May 17, 2025
Review Of Jackbit A Top Bitcoin Casino With Fast Withdrawals
May 17, 2025
