Reducing Long COVID Risk: The Effectiveness Of COVID-19 Vaccines
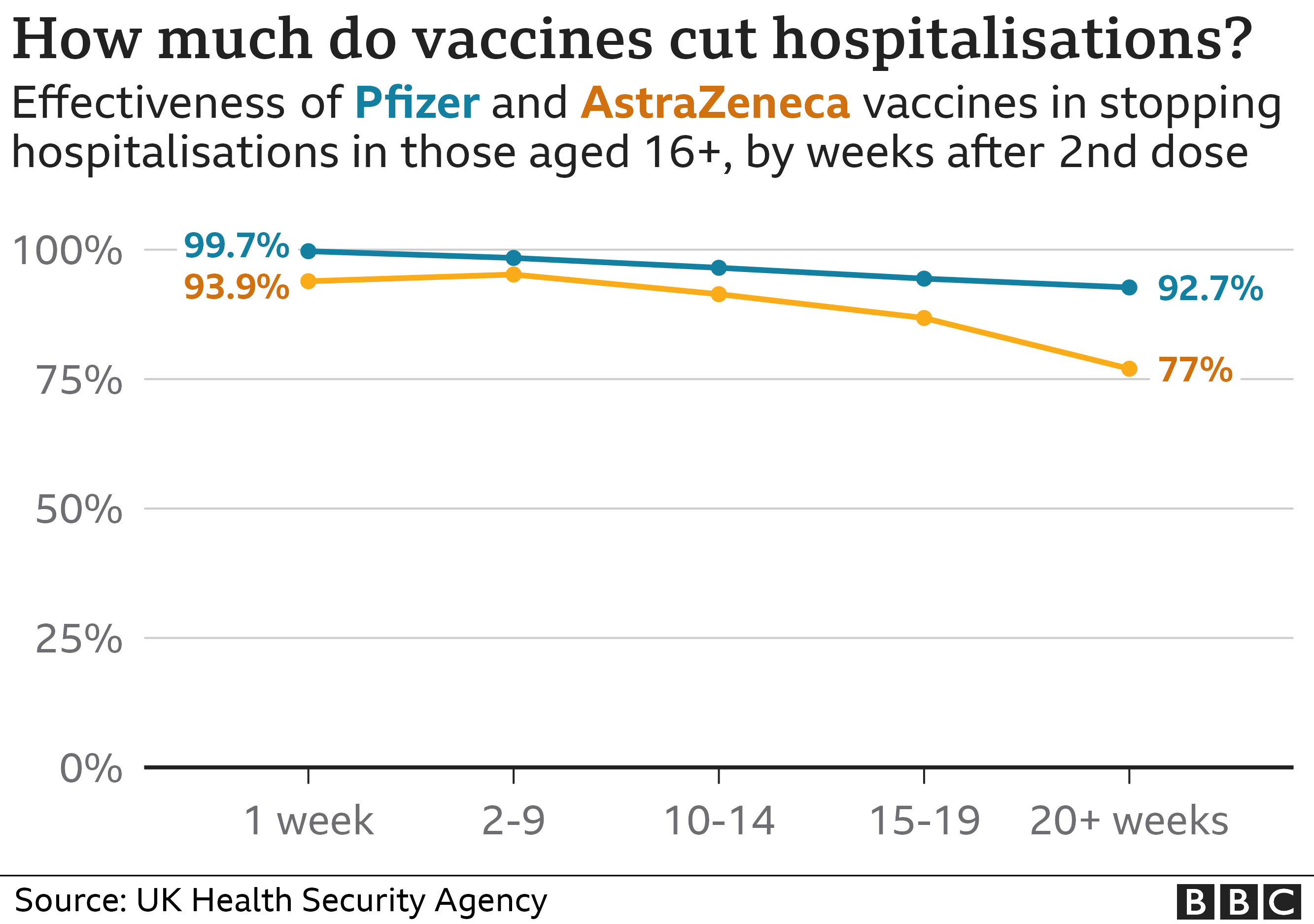
Table of Contents
How COVID-19 Vaccines Protect Against Severe Illness and Long COVID
COVID-19 vaccines work by triggering your body's immune system to produce antibodies and T cells that recognize and fight the virus. This vaccine-induced immunity plays a crucial role in mitigating the risk of Long COVID. By stimulating a robust immune response, vaccines reduce the viral load—the amount of virus in your body—during infection. This is critical because a lower viral load translates to:
- Reduced inflammation and tissue damage: High viral loads can lead to significant inflammation throughout the body, potentially causing lasting damage to organs and tissues, contributing to Long COVID symptoms. Vaccines help minimize this inflammation.
- Minimized duration of infection: A strong immune response clears the virus more quickly, shortening the overall duration of infection. This reduction in infection time directly lessens the opportunity for long-term effects to develop.
- Lower chances of persistent symptoms: By preventing severe illness and controlling viral replication, vaccines significantly reduce the likelihood of persistent symptoms associated with post-COVID syndrome (Long COVID). The stronger your immune response, the less likely you are to experience prolonged symptoms.
Evidence Supporting the Link Between Vaccination and Reduced Long COVID Risk
Numerous studies and clinical trials strongly support the link between COVID-19 vaccination and a reduced risk of Long COVID. These findings consistently demonstrate that vaccination significantly lowers the incidence and severity of Long COVID.
- Large-scale epidemiological studies conducted by organizations like the CDC and WHO have shown a substantial reduction in Long COVID cases among vaccinated individuals compared to unvaccinated individuals. [Insert links to relevant CDC and WHO reports here].
- Clinical trials have analyzed the effectiveness of different vaccine types, including mRNA vaccines and viral vector vaccines, in preventing Long COVID. Results consistently indicate a strong correlation between vaccination and reduced risk. [Insert links to relevant peer-reviewed journal articles here].
- Statistical data reveals a markedly lower prevalence of Long COVID among fully vaccinated individuals, emphasizing the protective effect of vaccination against this debilitating condition. The specific reduction percentages vary depending on the study and vaccine type but consistently show a significant benefit.
Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions About Vaccination and Long COVID
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting vaccination, some concerns and misconceptions persist. Let's address these directly:
- Vaccine side effects and Long COVID: While some individuals experience mild side effects after vaccination (e.g., soreness, fatigue), these are generally temporary and unrelated to Long COVID. In fact, the risk of developing Long COVID is far greater if you contract COVID-19 than if you experience minor vaccine side effects.
- Importance of complete vaccination: Achieving complete vaccination, including booster shots, is crucial for maximizing protection against severe illness and Long COVID. Booster shots enhance your immune response and provide sustained protection against emerging variants.
- Concerns about specific vaccine types: While different vaccines have varying efficacies, all authorized COVID-19 vaccines significantly reduce the risk of severe illness and Long COVID. Consult your healthcare provider to discuss which vaccine is most appropriate for you.
Beyond Vaccination: Other Strategies to Minimize Long COVID Risk
While vaccination is a cornerstone of Long COVID prevention, other strategies can further reduce your risk:
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, strengthens your overall immune system and resilience to infection.
- Early treatment of COVID-19 infection: If you contract COVID-19, seeking early medical attention and treatment can help reduce the severity and duration of illness, potentially minimizing the risk of Long COVID.
- Prompt medical attention for persistent symptoms: If you experience persistent symptoms after a COVID-19 infection, consult your doctor immediately. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can improve outcomes and reduce the long-term impact of Long COVID. Post-COVID rehabilitation programs can also be beneficial.
Protecting Yourself From Long COVID Through Vaccination
The evidence is clear: COVID-19 vaccination is a highly effective strategy for reducing the risk of Long COVID. Vaccination significantly lowers the likelihood of developing this debilitating condition and minimizes its potential severity. Don't let Long COVID impact your life. Schedule your COVID-19 vaccination and booster shots today to significantly reduce your risk. Protect yourself and your community by getting vaccinated against COVID-19 and reducing your risk of Long COVID.

Featured Posts
-
 Fullstendig Program For 17 Mai Feiringen I Moss
May 29, 2025
Fullstendig Program For 17 Mai Feiringen I Moss
May 29, 2025 -
 Zoellner Family Presents Paraeducator Of The Year Award
May 29, 2025
Zoellner Family Presents Paraeducator Of The Year Award
May 29, 2025 -
 Bayrn Mywnkh Wbrshlwnt Srae Mhtdm Ela Sfqt Jdydt
May 29, 2025
Bayrn Mywnkh Wbrshlwnt Srae Mhtdm Ela Sfqt Jdydt
May 29, 2025 -
 Pokemon Tcg Pocket Event Details On The Five New Promo Cards
May 29, 2025
Pokemon Tcg Pocket Event Details On The Five New Promo Cards
May 29, 2025 -
 Bring Her Back New Horror Movie Image Promises A Terrifying Experience
May 29, 2025
Bring Her Back New Horror Movie Image Promises A Terrifying Experience
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nyt Mini Crossword Solutions For Tuesday April 8th
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Solutions For Tuesday April 8th
May 31, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Answers For Thursday April 10th
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Answers For Thursday April 10th
May 31, 2025 -
 Complete Guide Nyt Mini Crossword Answers For March 16 2025
May 31, 2025
Complete Guide Nyt Mini Crossword Answers For March 16 2025
May 31, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers Thursday April 10th
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Clues And Answers Thursday April 10th
May 31, 2025 -
 Complete Guide Nyt Mini Crossword Answers March 24 2025
May 31, 2025
Complete Guide Nyt Mini Crossword Answers March 24 2025
May 31, 2025
