Rosenberg On Canadian Jobs: Implications For Bank Of Canada Interest Rates
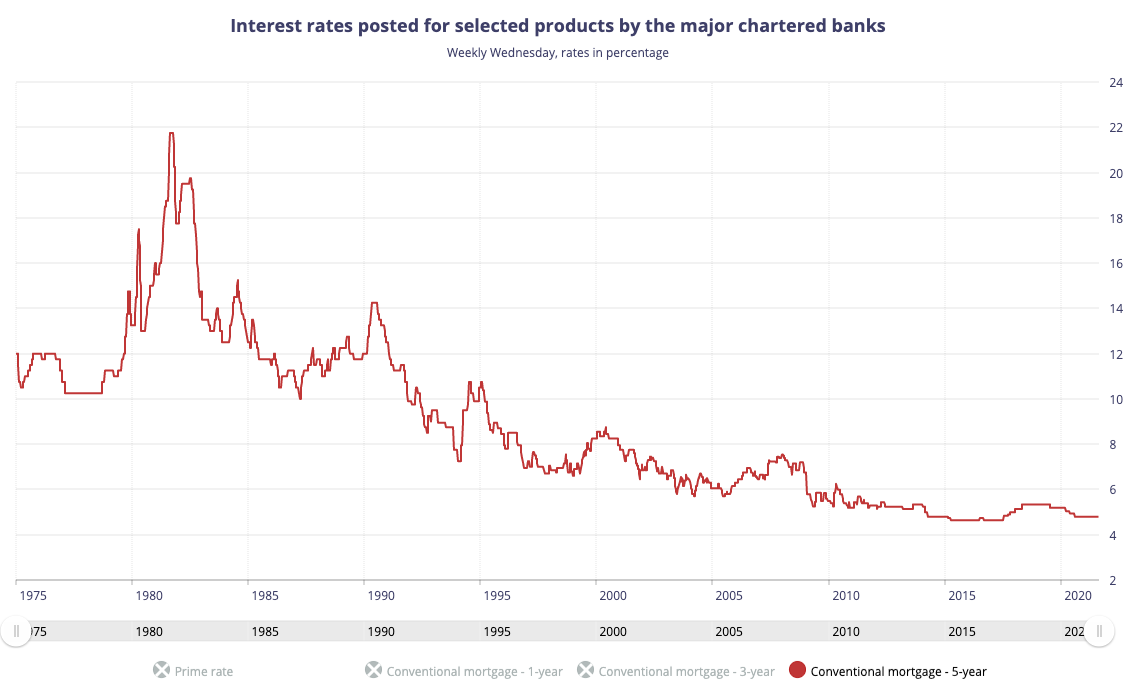
Table of Contents
Rosenberg's Key Findings on the Canadian Job Market
Unemployment Rate and its Interpretation
Rosenberg's perspective on the current Canadian unemployment rate often differs from the official figures. While Statistics Canada might report a low unemployment rate, Rosenberg frequently analyzes the participation rate, arguing that a seemingly low unemployment rate might mask underlying weaknesses in the labor market. He scrutinizes the number of people who have given up looking for work, a factor not always reflected in headline unemployment numbers.
- Specific data point example: While Statistics Canada might report an unemployment rate of 5.0%, Rosenberg might point out that the participation rate has fallen, suggesting a higher level of underemployment.
- Discrepancies: Rosenberg's analysis often highlights discrepancies between official unemployment figures and alternative measures like the U-6 unemployment rate (which includes discouraged workers), painting a more nuanced picture of the labor market.
- Reasons for divergence: Differences in methodology, data collection, and interpretation contribute to the divergence between official statistics and Rosenberg's analysis. He often emphasizes qualitative factors impacting the job market, not fully captured by quantitative data.
Wage Growth and Inflationary Pressures
Rosenberg closely examines wage growth as a key indicator of inflationary pressures. He assesses whether wage increases are outpacing productivity growth, leading to a wage-price spiral. His analysis focuses on the impact of wage growth on the Bank of Canada's inflation targets and monetary policy decisions.
- Specific data on wage growth: Rosenberg might highlight sectors experiencing rapid wage growth, potentially fueling inflation. He may also contrast this with sectors experiencing stagnant wages.
- Connection to inflation figures (CPI): He directly links wage growth data to Consumer Price Index (CPI) figures, assessing the correlation between the two. A strong correlation suggests wage growth is a significant contributor to inflation.
- Rosenberg’s predicted trajectory for wage growth: His forecasts for wage growth are critical in predicting his outlook on interest rate adjustments. He may predict a slowdown, acceleration, or stabilization in wage growth, influencing his interest rate predictions.
Quality of Jobs and Labor Market Participation
Rosenberg's analysis extends beyond simple unemployment numbers to consider the quality of jobs created and the overall participation rate in the Canadian workforce. He focuses on whether new jobs are high-paying, full-time positions or low-paying, part-time roles, impacting overall economic health. He also analyzes demographic shifts within the labor force.
- Statistics on job creation by sector: He might analyze job creation data by sector, highlighting strong growth in specific areas and potential weaknesses in others. This granular approach reveals the health of different parts of the economy.
- Analysis of average wages across sectors: He scrutinizes average wages across different sectors, pointing out disparities and their implications for income inequality and overall economic prosperity.
- Trends in labor force participation rates for different demographic groups: Rosenberg might analyze participation rates for various demographic groups (age, gender, education level), identifying potential areas of concern within the Canadian labor market.
Implications for Bank of Canada Monetary Policy
Rosenberg's Predicted Interest Rate Trajectory
Based on his analysis of the Canadian job market, Rosenberg offers a forecast for the Bank of Canada's interest rate trajectory. This prediction considers factors like inflation, wage growth, and overall economic growth.
- Specific predictions on interest rate changes (percentage points and timing): He might predict rate hikes, cuts, or a pause, with specific percentage points and a timeframe for these changes.
- Rationale behind the predictions (e.g., inflation concerns, economic growth outlook): He justifies his predictions based on his assessment of inflation risks, economic growth prospects, and the potential for wage-price spirals. This provides context and transparency to his predictions.
Potential Risks and Uncertainties
Rosenberg acknowledges various uncertainties that could influence the Bank of Canada's decisions. Global economic conditions, geopolitical events, and unexpected shifts in the job market all present significant risks.
- Identification of key risks (e.g., global recession, supply chain disruptions, unexpected inflation surges): He identifies potential pitfalls that could alter the Bank of Canada's plans.
- Analysis of how these risks could impact the Bank of Canada’s response: He assesses how these risks could force the Bank of Canada to adjust its monetary policy, potentially deviating from his initial predictions.
Comparison to Other Economic Forecasts
Comparing Rosenberg's predictions to those of other prominent economists and financial institutions offers valuable context. Areas of agreement and disagreement highlight the range of potential outcomes.
- Summary of other prominent economic forecasts: A summary of competing forecasts from other economists and institutions provides a balanced view.
- Points of convergence and divergence with Rosenberg’s analysis: This comparison helps investors and businesses understand the range of possibilities and the level of uncertainty surrounding future interest rate decisions.
Conclusion
David Rosenberg's analysis of the Canadian job market provides valuable insights into potential future Bank of Canada interest rate decisions. His focus on unemployment, wage growth, job quality, and participation rates offers a nuanced perspective that often differs from mainstream interpretations. While his predictions are insightful, significant uncertainties remain, including global economic conditions and unforeseen shocks to the Canadian economy. Understanding Rosenberg's perspective, alongside other economic forecasts, is crucial for navigating the complexities of the Canadian financial landscape. Stay informed about the evolving Canadian economic landscape and the impact of expert opinions like Rosenberg's on the Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions. Regularly monitor economic indicators and analyses to make informed decisions regarding investments and financial planning in the context of Rosenberg's insights on Canadian jobs and their impact on interest rates. Further research into the work of David Rosenberg and other economists is recommended for a comprehensive understanding of this crucial economic relationship.

Featured Posts
-
 Sanofi Acquiert L Anticorps Bispecifique De Dren Bio Un Portefeuille Immunologie Renforce
May 31, 2025
Sanofi Acquiert L Anticorps Bispecifique De Dren Bio Un Portefeuille Immunologie Renforce
May 31, 2025 -
 Tsitsipas Addresses Ivanisevic Coaching Speculation The Full Story
May 31, 2025
Tsitsipas Addresses Ivanisevic Coaching Speculation The Full Story
May 31, 2025 -
 Idojaras Jelentes Belfoeld Csapadek Toebb Hullamban
May 31, 2025
Idojaras Jelentes Belfoeld Csapadek Toebb Hullamban
May 31, 2025 -
 40 Profit Boost For Dragons Den Business Owner
May 31, 2025
40 Profit Boost For Dragons Den Business Owner
May 31, 2025 -
 Rare Sight Elephant Seal In Cape Town Suburb Halts Traffic
May 31, 2025
Rare Sight Elephant Seal In Cape Town Suburb Halts Traffic
May 31, 2025
