School Suspensions: A Counterproductive Discipline Strategy
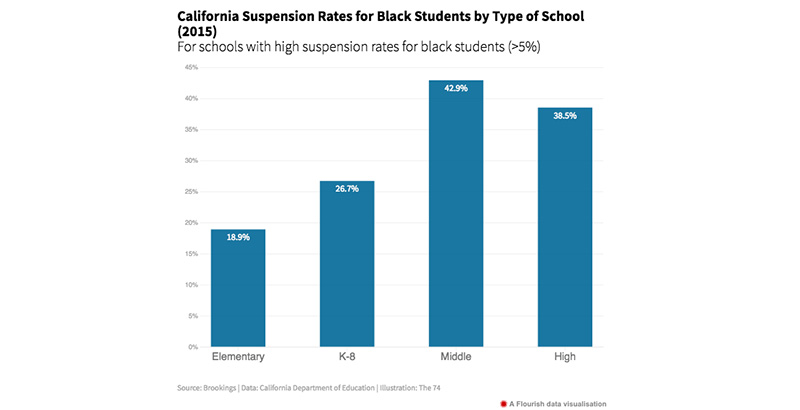
Table of Contents
The Negative Impact of School Suspensions on Academic Achievement
School suspensions significantly hinder a student's academic progress, leading to a cascade of negative consequences. The immediate and long-term effects of this disciplinary strategy must be carefully considered.
Increased Absenteeism and Grade Decline
Suspensions directly contribute to increased absenteeism. Missing even a few days of school can cause students to fall behind their peers, struggle to catch up on missed assignments, and ultimately experience a decline in their grades.
- Increased likelihood of dropping out: Studies show a strong correlation between suspensions and increased dropout rates. Students who are frequently suspended are more likely to disengage from school and eventually leave before graduation.
- Difficulty catching up on missed work: The academic workload missed during a suspension can be overwhelming, leading to further frustration and discouragement. Many students lack the support systems necessary to effectively make up for lost learning.
- Negative impact on GPA: Consistent suspensions directly translate into lower GPAs, impacting college applications and future opportunities.
Research from the National Center for Education Statistics consistently demonstrates a strong link between suspension rates and lower academic performance. This detrimental impact extends far beyond the immediate consequences of missed classes.
Long-Term Educational Disadvantage
The effects of school suspensions extend far beyond the immediate academic setbacks. The long-term consequences can significantly impact future educational success and career prospects.
- Reduced college acceptance rates: A history of suspensions can negatively affect college applications, reducing the likelihood of acceptance into higher education institutions. Admissions officers often view suspensions as indicators of behavioral problems and academic instability.
- Lower earning potential: Studies have shown a correlation between school suspensions and lower future earning potential. This is linked to lower educational attainment and reduced opportunities for career advancement.
- Increased likelihood of incarceration: A significant body of research indicates a strong link between school suspensions and increased rates of juvenile delinquency and incarceration. This highlights the broader societal implications of this disciplinary strategy.
The Social and Emotional Consequences of School Suspensions
Beyond the academic repercussions, school suspensions inflict significant damage on a student's social and emotional well-being. These consequences often exacerbate existing problems rather than providing solutions.
Increased Behavioral Problems
Instead of resolving behavioral issues, suspensions often worsen them. The isolation and alienation experienced during a suspension can reinforce negative behaviors and reduce a student's connection to the school community.
- Increased feelings of alienation: Being removed from the classroom environment can lead to feelings of isolation, exclusion, and resentment towards the school system.
- Reduced connection to school community: Suspension weakens the bond between students and teachers, making it harder for educators to provide support and guidance.
- Potential for involvement in negative peer groups: During suspension, students may associate with peers who engage in negative behaviors, further reinforcing problematic patterns.
Evidence-based research repeatedly demonstrates that punitive disciplinary approaches like suspension often backfire, leading to an escalation of behavioral problems.
Mental Health Implications
School suspensions can have serious negative implications for students' mental health, potentially contributing to depression, anxiety, and other challenges.
- Increased stress levels: The experience of suspension, the fear of future suspensions, and the stigma associated with it can cause significant stress and anxiety.
- Feelings of shame and failure: Being suspended can lead to feelings of inadequacy, shame, and a sense of failure, negatively impacting self-esteem.
- Potential for self-harm: In extreme cases, the emotional distress caused by suspension can contribute to self-harm or suicidal ideation. Schools must provide access to mental health resources for affected students.
Organizations such as the American Psychological Association have published research supporting the link between harsh disciplinary practices and negative mental health outcomes in children and adolescents.
More Effective Alternatives to School Suspensions
Fortunately, numerous effective alternatives to school suspensions exist. These strategies focus on addressing the root causes of misbehavior and fostering positive school climates.
Restorative Justice Practices
Restorative justice approaches prioritize repairing harm and promoting reconciliation between individuals involved in conflicts.
- Mediation between students: Mediation provides a structured process for students to address the harm caused and develop solutions together.
- Conflict resolution: These practices equip students with conflict-resolution skills, enabling them to manage disagreements peacefully and respectfully.
- Community involvement: Restorative justice often includes the involvement of the broader school community to help address the underlying issues contributing to conflict.
Numerous studies demonstrate the effectiveness of restorative justice programs in reducing suspension rates and improving school climate.
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS)
PBIS is a proactive approach that emphasizes preventing behavioral problems before they arise.
- Teaching positive behavior: PBIS focuses on teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors through clear expectations, consistent application of rules, and positive reinforcement.
- Establishing clear expectations: Clear expectations and consistent application of rules reduce ambiguity and prevent misunderstandings.
- Rewarding good behavior: Recognizing and rewarding positive behaviors strengthens desired conduct and creates a more positive school environment.
Schools implementing PBIS frameworks have reported significant reductions in disciplinary incidents and improvements in student behavior.
Addressing Underlying Issues
Addressing the root causes of student misbehavior is crucial for effective discipline. Many behaviors stem from underlying issues that require targeted support.
- Providing counseling services: Access to counseling services helps students address emotional and mental health challenges contributing to disruptive behavior.
- Offering academic support: Academic support programs can help students struggling academically, reducing frustration and improving engagement.
- Addressing social-emotional needs: Meeting students' social-emotional needs through programs focused on emotional regulation, empathy, and conflict resolution can significantly reduce behavioral issues.
Schools must actively work to identify and support students facing challenges such as poverty, trauma, or learning disabilities.
Conclusion
School suspensions are demonstrably ineffective and harmful, causing significant academic, social, and emotional damage to students. This counterproductive disciplinary strategy perpetuates a cycle of negativity, hindering academic achievement and negatively impacting long-term well-being. We must replace these outdated practices with evidence-based strategies that prioritize student support and positive behavior. Let's replace counterproductive school suspensions with restorative justice, PBIS, and a focus on addressing underlying issues. Join the movement to end the harmful practice of school suspensions and promote positive disciplinary approaches that support the holistic development of all students. Let's create schools where every student thrives.

Featured Posts
-
 Check The Winning Lotto Numbers Saturday April 12th Draw
May 02, 2025
Check The Winning Lotto Numbers Saturday April 12th Draw
May 02, 2025 -
 Neispricana Prica O Prvoj Ljubavi Zdravka Colica
May 02, 2025
Neispricana Prica O Prvoj Ljubavi Zdravka Colica
May 02, 2025 -
 Loyle Carner To Play 3 Arena In Dublin
May 02, 2025
Loyle Carner To Play 3 Arena In Dublin
May 02, 2025 -
 Optimaal Profiteren Van Enexis Auto Opladen Buiten Piektijden In Noord Nederland
May 02, 2025
Optimaal Profiteren Van Enexis Auto Opladen Buiten Piektijden In Noord Nederland
May 02, 2025 -
 Fortnite Refund Indicates Potential Overhaul Of Cosmetic System
May 02, 2025
Fortnite Refund Indicates Potential Overhaul Of Cosmetic System
May 02, 2025
