Shared Nuclear Deterrence: France's European Vision
Table of Contents
The Rationale Behind France's Proposal for Shared Nuclear Deterrence
France's motivation for promoting shared nuclear deterrence stems from several key factors. The nation seeks to strengthen European strategic autonomy, reducing reliance on external security guarantees and fostering a more unified and independent approach to defense. The growing threat from Russia, its assertive military actions, and its nuclear arsenal, necessitates a robust European response. Shared nuclear deterrence aims to address this threat collectively, distributing the burden and responsibility more equitably among willing partners. Furthermore, a shared framework could help deter nuclear proliferation within Europe, preventing the potential emergence of other nuclear powers in a volatile region.
- Strengthening European Strategic Autonomy: Reducing reliance on the United States for nuclear security guarantees is paramount for France.
- Addressing the Threat from Russia and Others: The need for a credible deterrent against potential aggression is undeniable, given the evolving geopolitical situation.
- Sharing the Burden and Responsibility: Pooling resources and expertise reduces the financial and strategic strain on any single nation.
- Deterring Nuclear Proliferation: A unified front against nuclear proliferation sends a strong signal to potential proliferators.
France's independent nuclear doctrine, established in the post-war era, has evolved significantly. Initially focused on national security, its current trajectory emphasizes a more integrated European approach, aligning with broader European defense cooperation initiatives. This shift reflects a recognition of the shared security challenges facing the continent and the potential synergies achievable through collaboration. The French nuclear arsenal, a core element of its national security strategy, is now being positioned as a cornerstone for a broader European security framework.
Key Aspects of France's Vision: Beyond Simple Nuclear Sharing
France's vision transcends the mere sharing of its nuclear weapons. It envisions a broader strategic partnership built on enhanced cooperation and mutual responsibility. This partnership would encompass:
- Enhanced Intelligence Sharing: Pooling intelligence resources significantly improves the ability to assess threats and respond effectively.
- Joint Military Exercises: Regular joint military exercises foster interoperability and enhance coordination between participating nations.
- Coordinated Defense Strategies: Harmonized defense strategies ensure a unified and coherent response to potential threats.
This enhanced cooperation goes beyond France's nuclear capabilities. Other EU members with advanced military capabilities, such as Germany, could play significant roles, contributing expertise and resources. The concept of "burden-sharing" is central to this vision, encompassing financial contributions, military deployments, and shared responsibility for maintaining a credible deterrent. This equitable distribution of resources and responsibilities aims to secure wider support for the initiative.
Challenges and Obstacles to Implementing Shared Nuclear Deterrence
Despite the potential benefits, implementing shared nuclear deterrence faces significant challenges.
- NATO's Role: Reconciling the proposal with NATO's existing nuclear sharing arrangements and overall security framework presents a major hurdle.
- Nuclear Proliferation Concerns: Strict control mechanisms are necessary to prevent the risk of nuclear proliferation and accidental use.
- Differing National Interests: Harmonizing the security priorities and national interests of diverse European states is a complex undertaking.
- Coordinating Nuclear Strategies: Developing a unified nuclear strategy involving multiple nations requires substantial diplomatic effort and compromises.
Legal and political hurdles abound, ranging from concerns about national sovereignty and control over nuclear weapons to the intricacies of international law governing nuclear weapons. Overcoming these challenges requires careful consideration and a robust diplomatic process. The European Union security policy must be central in addressing these concerns and fostering a cooperative framework.
Potential Benefits of a Shared European Nuclear Deterrence
The potential benefits of a shared European nuclear deterrent are significant:
- Increased Deterrence: A unified nuclear deterrent is more credible and effective than individual national efforts.
- Strengthened European Strategic Independence: This reduces reliance on external powers, particularly the US.
- More Equitable Cost Distribution: Sharing the costs of maintaining a nuclear deterrent is more efficient and fairer.
- Enhanced Credibility of European Defense: A credible European nuclear deterrent strengthens the continent's overall defense capabilities.
For individual member states, benefits include enhanced security guarantees, increased political influence within a strengthened European security architecture, and potentially reduced national defense expenditures.
Conclusion: The Future of Shared Nuclear Deterrence in Europe
France's vision for shared nuclear deterrence presents both significant opportunities and formidable challenges. While enhancing European strategic autonomy and providing a stronger deterrent against potential adversaries are key benefits, overcoming concerns about nuclear proliferation, national sovereignty, and the complexities of coordinating a multi-national nuclear strategy are crucial. The likelihood of success hinges on the willingness of European nations to collaborate, compromise, and address the inherent risks and complexities. The impact on European security could be profound, shifting the balance of power and fostering a more unified and independent approach to defense. Further discussion and research on shared nuclear deterrence, its variations and its implications for the future of European security are vital. Readers are encouraged to explore related topics such as the evolving role of NATO, various European defense initiatives, and the ongoing debate on nuclear arms control. The future of European security may well depend on a thoughtful and comprehensive approach to this critical issue.

Featured Posts
-
 Nottingham Families Protest Farcical Misconduct Proceedings Seek Delay
May 10, 2025
Nottingham Families Protest Farcical Misconduct Proceedings Seek Delay
May 10, 2025 -
 The Luis Enrique Effect Paris Saint Germains Road To Ligue 1 Success
May 10, 2025
The Luis Enrique Effect Paris Saint Germains Road To Ligue 1 Success
May 10, 2025 -
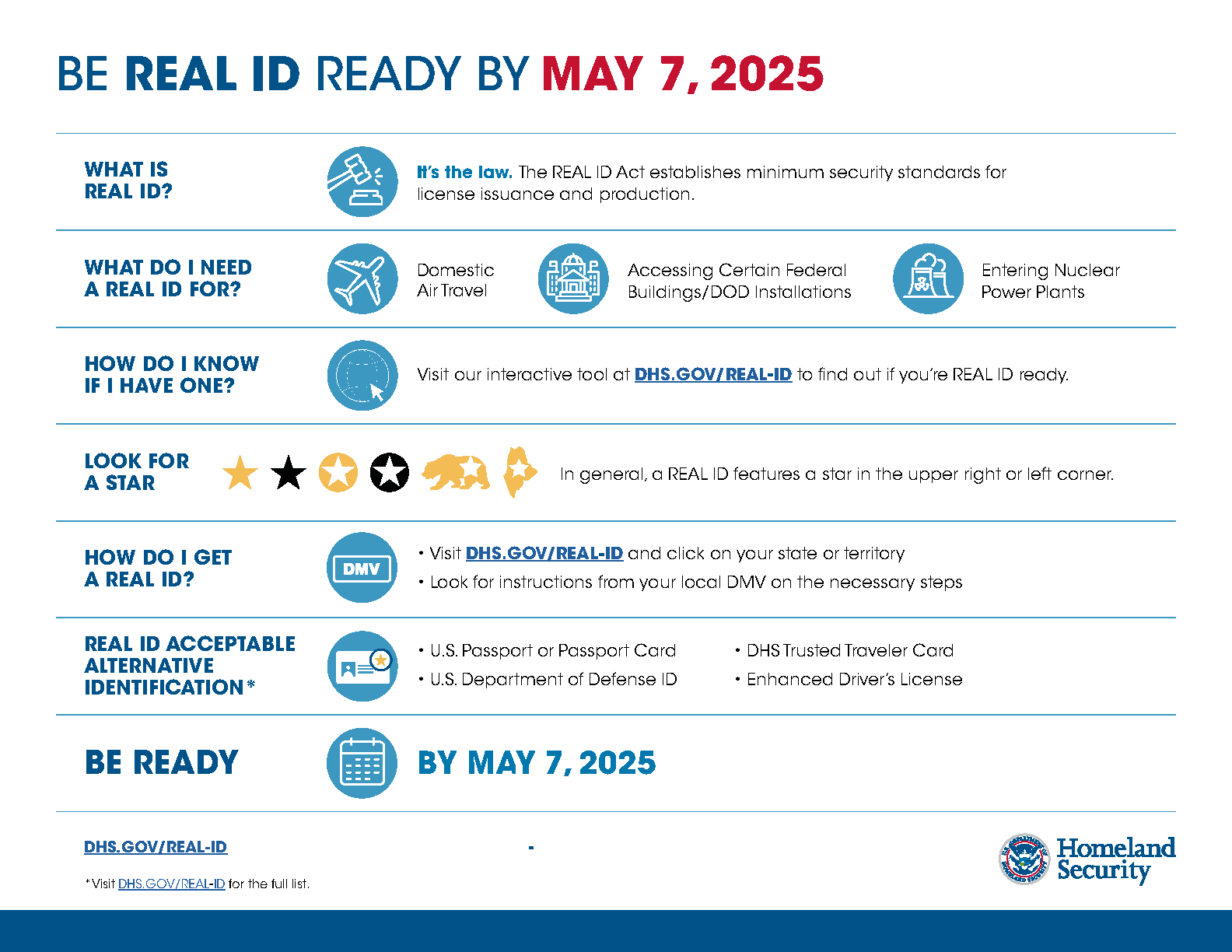 Summer Travel Essential Guide To Real Id Requirements
May 10, 2025
Summer Travel Essential Guide To Real Id Requirements
May 10, 2025 -
 Real Id Enforcement Summer Travel Planning Guide
May 10, 2025
Real Id Enforcement Summer Travel Planning Guide
May 10, 2025 -
 Ihsaa Bans Transgender Athletes Following Trump Administration Order
May 10, 2025
Ihsaa Bans Transgender Athletes Following Trump Administration Order
May 10, 2025
