Singapore's Political Landscape: The 2024 Election And Beyond

Table of Contents
The Ruling Party: PAP's Continued Dominance and Challenges
The People's Action Party (PAP) has held an unbroken grip on power since Singapore's independence. Maintaining this dominance, however, presents increasing challenges.
PAP's Electoral Strategy and Popularity
The PAP's enduring success stems from a multifaceted electoral strategy. This includes:
- Targeted Policy Initiatives: The party consistently adapts its policies to address evolving citizen concerns, such as housing affordability and healthcare accessibility. Recent initiatives focus on strengthening social safety nets and addressing cost-of-living pressures.
- Effective Communication and Public Relations: The PAP leverages sophisticated communication strategies, including targeted social media campaigns and community engagement programs, to connect with voters.
- Emphasis on Economic Growth and Stability: The party's long-standing focus on economic prosperity remains a cornerstone of its appeal, associating it with national success and stability. However, rising income inequality poses a growing concern.
- Youth Outreach Programs: Recognizing the importance of engaging younger demographics, the PAP actively participates in youth-focused initiatives and fosters dialogue to address their concerns.
However, recent shifts in public opinion indicate a subtle erosion of the PAP's unassailable popularity. While still dominant, the party faces increased scrutiny and demands for greater accountability and transparency. Keywords: PAP, People's Action Party, Singaporean elections, electoral strategy, political dominance.
Internal Dynamics and Leadership Succession
The PAP's internal dynamics are critical to its continued success. Leadership succession planning is a constant and delicate process.
- Identifying Future Leaders: The party is actively grooming a new generation of leaders, although internal factionalism (if any) remains largely unspoken and under the surface. This process is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition of power and maintaining the party's coherence.
- Generational Change: The successful integration of younger leaders into key positions is pivotal. This requires careful balancing of experience and fresh perspectives.
- Maintaining Party Unity: Despite the outward show of unity, navigating internal disagreements and ensuring a cohesive approach remains a key challenge for the PAP.
Keywords: PAP leadership, succession planning, Singaporean politics, generational change.
The Opposition: Growing Strength and Challenges
While the PAP maintains its dominant position, the opposition parties are gradually gaining strength and visibility.
Key Opposition Parties and Their Platforms
Several key opposition parties contribute to a more diverse political landscape. These include:
- Workers' Party (WP): The WP, currently holding a significant number of seats in Parliament, focuses on social justice, workers' rights, and greater transparency in governance. They are gaining traction through their more community-oriented approach.
- Singapore Democratic Party (SDP): The SDP emphasizes fiscal responsibility, economic equity, and a more robust social safety net. Their consistent policy advocacy maintains a consistent presence.
- Other Opposition Groups: Several smaller parties also contest elections, presenting a range of viewpoints and agendas, contributing to a more diversified political discussion.
These parties offer alternative policy platforms, appealing to different segments of the population and challenging the PAP's narrative. Keywords: Workers' Party, SDP, Singaporean opposition, opposition parties, political platforms.
Overcoming Electoral Hurdles and Building Public Trust
Opposition parties in Singapore face significant hurdles in gaining wider public support.
- Electoral System: The Group Representation Constituency (GRC) system, designed to ensure minority representation, often presents challenges for smaller parties.
- Campaign Finance: Securing sufficient funding for campaigns is a persistent challenge, often creating an imbalance with the well-funded PAP.
- Media Coverage: Opposition parties often contend with limited media access and what some perceive as biased reporting, creating an uneven playing field.
- Public Perception: Overcoming deeply ingrained perceptions of the PAP as the guarantor of stability and economic success is a major obstacle for opposition parties.
Overcoming these systemic and perception-based challenges is essential for opposition parties to build broader public trust and secure greater representation. Keywords: Electoral system, campaign finance, media bias, public trust, opposition politics.
Emerging Issues Shaping the Political Landscape
Several key issues are shaping the political landscape and influencing the upcoming election.
Economic Inequality and Social Mobility
Growing concerns about income inequality and limited social mobility are becoming increasingly prominent in Singapore's political discourse.
- Housing Affordability: The rising cost of housing remains a major concern for many Singaporeans, particularly younger generations.
- Education Costs: The cost of education, including tertiary education, presents a significant financial burden for many families.
- Healthcare Access: Ensuring accessible and affordable healthcare is a critical challenge, with concerns about rising medical costs impacting various socio-economic groups.
These issues highlight the need for policies addressing economic inequality and enhancing social mobility. Keywords: Income inequality, social mobility, housing affordability, education costs, healthcare access, Singaporean society.
Geopolitical Factors and Regional Influence
Singapore's political landscape is also impacted by regional and global geopolitical events.
- US-China Relations: The evolving relationship between the US and China significantly influences Singapore's foreign policy and domestic political discussions.
- Regional Security Concerns: Regional security issues, including territorial disputes and transnational crime, impact Singapore's strategic priorities and national security policies.
- ASEAN Role: Singapore's active role in ASEAN and its regional diplomatic efforts shape its domestic political agenda and foreign policy choices.
Navigating these complex geopolitical dynamics is vital for Singapore's continued stability and prosperity. Keywords: Geopolitics, ASEAN, US-China relations, regional security, foreign policy.
Conclusion
The 2024 Singaporean general election and the subsequent political landscape will be profoundly shaped by the PAP's continued dominance, the evolving strategies of the opposition, and the pressing social and geopolitical challenges. Understanding these interacting forces is crucial for comprehending Singapore's future trajectory. Stay informed about the latest developments in Singapore's political landscape to gain a deeper understanding of this dynamic and influential nation. Further research into Singapore's political landscape will reveal a more comprehensive picture of this evolving political environment.

Featured Posts
-
 Opec Decision Imminent As Big Oil Resists Production Increase
May 05, 2025
Opec Decision Imminent As Big Oil Resists Production Increase
May 05, 2025 -
 Current Weather Conditions West Bengal Temperature Decrease
May 05, 2025
Current Weather Conditions West Bengal Temperature Decrease
May 05, 2025 -
 How Much Do Lizzo Concert Tickets Cost A Guide To Her In Real Life Tour Prices
May 05, 2025
How Much Do Lizzo Concert Tickets Cost A Guide To Her In Real Life Tour Prices
May 05, 2025 -
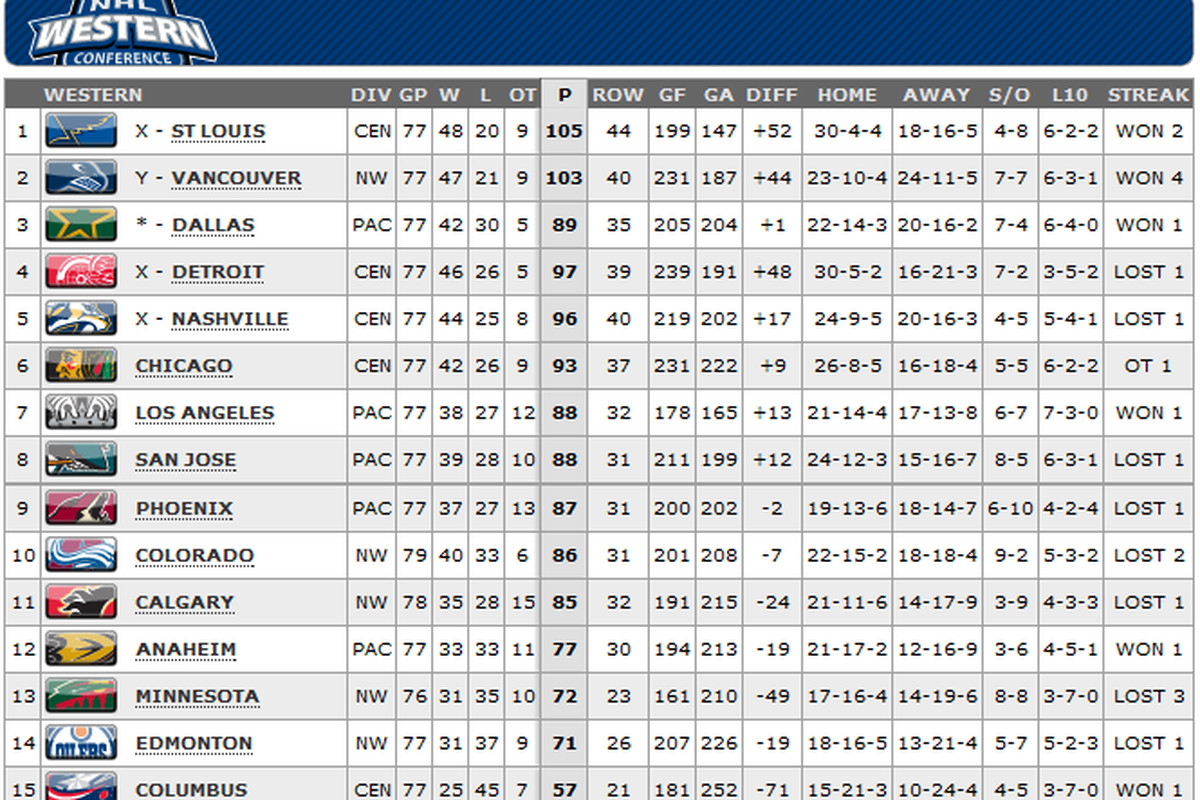 Nhl Standings The Western Conference Wild Card Contenders
May 05, 2025
Nhl Standings The Western Conference Wild Card Contenders
May 05, 2025 -
 Nolan Speaks Out Addressing Allegations Made By Charlie Dixon
May 05, 2025
Nolan Speaks Out Addressing Allegations Made By Charlie Dixon
May 05, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Student Government Election Controversy Popular Vote Winners Disqualified
May 05, 2025
Student Government Election Controversy Popular Vote Winners Disqualified
May 05, 2025 -
 Tynna Voice Concerns For Germany In Eurovision Song Contest
May 05, 2025
Tynna Voice Concerns For Germany In Eurovision Song Contest
May 05, 2025 -
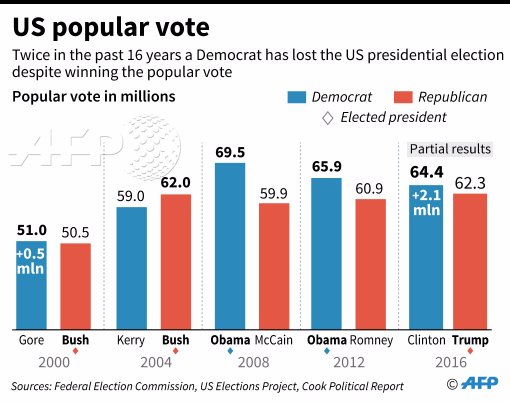 Popular Vote Winners Disqualified Gonzalez And Salzers Unexpected Sg Victory
May 05, 2025
Popular Vote Winners Disqualified Gonzalez And Salzers Unexpected Sg Victory
May 05, 2025 -
 Chefsache Esc 2025 Deutschland Kuert Seine Sieben Halbfinalisten
May 05, 2025
Chefsache Esc 2025 Deutschland Kuert Seine Sieben Halbfinalisten
May 05, 2025 -
 Esc 2025 Wer Vertritt Deutschland Die Sieben Halbfinalisten
May 05, 2025
Esc 2025 Wer Vertritt Deutschland Die Sieben Halbfinalisten
May 05, 2025
