Soaring Fuel Costs: The Airline Industry's Response To Oil Supply Shocks
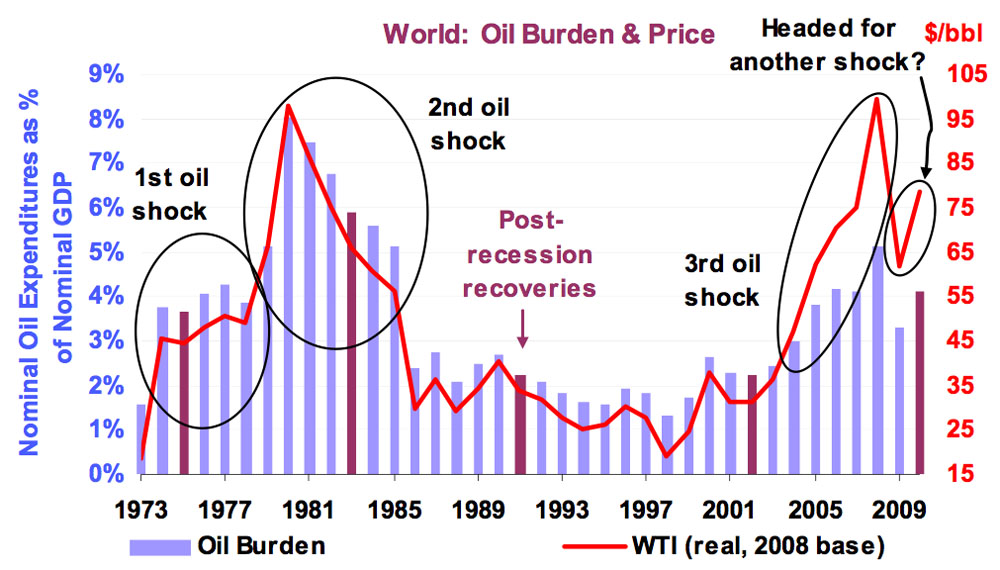
Table of Contents
Fuel Hedging Strategies: A Double-Edged Sword
Fuel hedging is a crucial risk management tool employed by airlines to mitigate the impact of fluctuating oil prices. This involves using financial instruments like forward contracts, options, and swaps to lock in future fuel prices at a predetermined rate. Airlines purchase these contracts to protect themselves against unexpected price increases.
The effectiveness of hedging during periods of high volatility is a complex issue. While it can significantly reduce the risk of massive price fluctuations, it's not a foolproof solution.
-
Pros:
- Reduces risk of price fluctuations, providing price certainty for budget planning.
- Allows airlines to better predict and manage their operating costs.
-
Cons:
- Can lock in losses if oil prices fall unexpectedly, resulting in missed opportunities for savings.
- Requires significant capital investment and sophisticated financial expertise.
- Complex strategies can be difficult to manage effectively.
Different airlines employ varying hedging strategies based on their risk tolerance and market outlook. Some airlines may choose a more conservative approach with a higher percentage of hedged fuel, while others might opt for a more aggressive strategy. For example, some airlines might utilize a combination of forward contracts and options to create a more flexible hedging strategy.
Operational Efficiency and Route Optimization
Airlines are actively pursuing operational efficiency improvements to counter the impact of high fuel costs. This includes investing in new technologies and optimizing their operations to minimize fuel consumption.
-
Investing in new fuel-efficient aircraft: The adoption of fuel-efficient aircraft like the Boeing 787 Dreamliner and Airbus A350 is a key strategy. These modern planes boast significantly improved fuel economy compared to older models.
-
Implementing advanced flight planning software: Sophisticated software helps optimize flight paths, reducing flight distances and minimizing fuel consumption. This includes analyzing weather patterns to avoid headwinds and utilizing more efficient flight profiles.
-
Reducing aircraft weight: Lighter materials are being incorporated into aircraft construction, and cargo loading is optimized to reduce unnecessary weight, leading to further fuel savings.
-
Optimizing routes: Airlines are constantly evaluating and adjusting routes to minimize flight distances and times. This includes avoiding unnecessary detours and optimizing schedules to avoid unfavorable weather conditions. This is a significant component of airline route optimization.
These strategies collectively contribute to significant fuel savings, allowing airlines to partially offset the impact of increased fuel prices on their profitability.
Passing on Costs to Consumers: The Price of Flight
The most direct response to soaring fuel costs has been passing on a portion of the increased expenditure to consumers through higher airfares. Airlines frequently utilize fuel surcharges as a transparent way to communicate these cost increases to passengers.
The elasticity of demand for air travel plays a crucial role in determining the extent to which airlines can pass on these increased costs. While air travel is essential for many, it’s also a discretionary expense for many others. Therefore, there’s a limit to how much consumers will tolerate price increases before seeking alternative travel options or reducing their travel frequency.
-
Historical analysis: Historical data shows a strong correlation between fuel price increases and subsequent airfare adjustments. However, the extent of this price increase varies depending on factors such as competition and consumer demand.
-
Consumer sensitivity: The sensitivity of air travel demand to price changes is a key consideration. Airlines constantly monitor consumer behaviour to assess the optimal price point that balances profitability with maintaining passenger numbers.
-
Competition: The degree of competition within specific markets significantly influences the ability of airlines to pass on fuel surcharges fully. Highly competitive markets may limit the extent to which airlines can increase prices without losing market share.
Government Intervention and Support
Governments play a role in supporting the airline industry during fuel crises. Several forms of intervention are often considered:
-
Tax breaks: Governments may offer tax incentives to airlines to alleviate the financial burden of high fuel costs.
-
Subsidies: Direct financial assistance through subsidies can provide vital support to struggling airlines. This can be particularly relevant for smaller airlines facing financial difficulties.
-
Other forms of assistance: Other forms of support may include loan guarantees or relaxed regulations. These can vary based on specific government policies.
However, government intervention carries potential drawbacks. Excessive support may distort market mechanisms and lead to inefficiencies. Careful consideration is necessary to ensure interventions are targeted and avoid negative long-term consequences. The effectiveness of government interventions varies greatly depending on the scale and specifics of the intervention itself.
The Future of Airline Fuel Costs and Sustainability
The long-term outlook for oil prices remains uncertain, but a transition towards more sustainable practices is crucial for the future of the airline industry. The adoption of sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) is paramount.
-
Projected oil prices: Forecasting future oil prices is challenging, but various scenarios must be considered, impacting airline financial planning and investment decisions.
-
Sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs): SAFs, produced from renewable sources, offer a pathway to reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing carbon emissions. Investments in SAF production and infrastructure are crucial for industry-wide adoption.
-
Technological advancements: Continuous technological improvements in aircraft design and engine efficiency will further reduce fuel consumption. This coupled with increased usage of SAFs will be key to long term profitability.
-
Carbon offsetting: Carbon offsetting programs allow airlines to compensate for their emissions by investing in projects that reduce greenhouse gases elsewhere. Although this is not a solution in itself, it plays a crucial role in the transition to a greener aviation sector.
The future of airline fuel costs and the overall sustainability of the industry hinge on successfully navigating these challenges. A focus on innovation, regulatory support, and the adoption of sustainable practices will be critical for the long-term health of the airline industry.
Conclusion:
Soaring fuel costs present a significant and ongoing challenge to the airline industry. Airlines are responding through a combination of fuel hedging, operational efficiencies, price adjustments, and seeking government support. However, the long-term solution involves a transition towards sustainable aviation fuels and a focus on reducing the industry's carbon footprint. Staying informed about the latest developments in fuel prices and airline strategies related to soaring fuel costs is crucial for both passengers and industry stakeholders. Understanding the multifaceted responses to this crisis allows for better preparedness and a more sustainable future for air travel.

Featured Posts
-
 Fabio Christen Victoria En La Vuelta Ciclista A Murcia
May 04, 2025
Fabio Christen Victoria En La Vuelta Ciclista A Murcia
May 04, 2025 -
 Pay Your Way Spotify Expands I Phone Payment Options
May 04, 2025
Pay Your Way Spotify Expands I Phone Payment Options
May 04, 2025 -
 Actors And Writers Strike The Complete Impact On Hollywood
May 04, 2025
Actors And Writers Strike The Complete Impact On Hollywood
May 04, 2025 -
 Federal Judge Blocks Trumps Action Targeting Perkins Coie
May 04, 2025
Federal Judge Blocks Trumps Action Targeting Perkins Coie
May 04, 2025 -
 Ray Epps Defamation Lawsuit Against Fox News January 6th Allegations
May 04, 2025
Ray Epps Defamation Lawsuit Against Fox News January 6th Allegations
May 04, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 New Lizzo Single Ignites The Charts
May 04, 2025
New Lizzo Single Ignites The Charts
May 04, 2025 -
 Lizzos Relationship With Myke Wright A Comprehensive Overview
May 04, 2025
Lizzos Relationship With Myke Wright A Comprehensive Overview
May 04, 2025 -
 Lizzos Fiery New Single Proof Shes Still Got It
May 04, 2025
Lizzos Fiery New Single Proof Shes Still Got It
May 04, 2025 -
 Lizzos La Performance Celebrating Her Figure
May 04, 2025
Lizzos La Performance Celebrating Her Figure
May 04, 2025 -
 How Lizzos Weight Loss Is Inspiring Fans Worldwide
May 04, 2025
How Lizzos Weight Loss Is Inspiring Fans Worldwide
May 04, 2025
