Strengthening Vaccine Oversight: The US Response To The Measles Surge
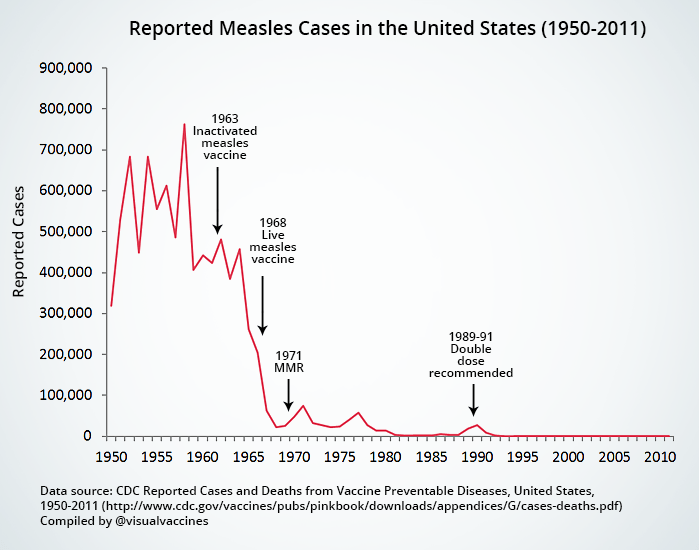
Table of Contents
H2: The Measles Surge: A Case Study in Vaccine Oversight Failures
H3: Analyzing the contributing factors to the outbreak.
The 2019 measles outbreak, the worst in decades, wasn't a random event; it was a consequence of several interconnected factors weakening our collective immunity.
- Decreased Vaccination Rates: Declining vaccination rates, particularly driven by vaccine hesitancy, significantly eroded herd immunity. Data from the CDC shows a clear correlation between lower vaccination coverage and increased measles transmission. [Link to relevant CDC report]
- Misinformation Campaigns: The spread of misinformation, often amplified through social media platforms, played a crucial role in fueling vaccine hesitancy. False claims linking vaccines to autism and other health problems continue to undermine public trust. [Link to research on misinformation and vaccines]
- Weakened Herd Immunity: Declining vaccination rates directly impact herd immunity, the indirect protection conferred to unvaccinated individuals when a significant portion of the population is vaccinated. This weakened immunity creates vulnerabilities for outbreaks to occur and spread rapidly. [Link to research on herd immunity]
- Gaps in Public Health Infrastructure: Insufficient funding and resources for public health programs, including disease surveillance and outbreak response, hindered early detection and containment of the measles outbreak. [Link to report on public health funding]
H3: Examining the impact of vaccine hesitancy on outbreak severity.
Vaccine hesitancy, a complex phenomenon driven by a mix of factors, significantly exacerbated the measles outbreak.
- The Role of Social Media: Social media platforms have become breeding grounds for misinformation, allowing anti-vaccine messages to reach a vast audience and spread rapidly. [Link to research on social media and vaccine hesitancy]
- Anti-vaccine Activism: Organized anti-vaccine movements have actively promoted misinformation and discouraged vaccination, significantly impacting public health. [Link to information on anti-vaccine groups]
- Psychological and Sociological Factors: Trust in healthcare providers, perceived risks of vaccines versus the disease, and cultural influences all contribute to vaccine hesitancy. [Link to relevant sociological research]
H2: The US Government's Response: A Review of Current Strategies
H3: Federal and state-level initiatives to improve vaccination rates.
In response to the measles surge, federal and state governments implemented various initiatives to improve vaccination rates:
- Public Awareness Campaigns: The CDC and state health departments launched campaigns to educate the public about the importance of vaccines and address common misconceptions. [Link to examples of public health campaigns]
- Vaccination Mandates: Several states strengthened vaccination mandates for schools and childcare facilities. [Link to examples of state vaccination mandates]
- Funding for Public Health Programs: Increased funding was allocated to strengthen public health infrastructure and support vaccination efforts. [Link to relevant government funding announcements]
- Collaboration with Healthcare Providers: Efforts were made to enhance communication and collaboration between healthcare providers and the public to improve vaccination uptake. [Link to information on provider-patient communication]
H3: Strengthening disease surveillance and outbreak response mechanisms.
Improvements in disease surveillance and outbreak response were also implemented:
- Improved Data Collection and Analysis: Enhanced data collection and analysis capabilities allowed for better tracking of measles cases and identification of outbreaks. [Link to examples of improved disease surveillance systems]
- Rapid Response Teams: Rapid response teams were deployed to affected areas to contain outbreaks and prevent further spread. [Link to information on rapid response teams]
- Better Communication Strategies: Improved communication strategies ensured timely and accurate information dissemination to the public and healthcare providers. [Link to examples of improved communication strategies]
H2: Recommendations for Enhanced Vaccine Oversight
H3: Improving public health communication and addressing vaccine hesitancy.
To prevent future outbreaks, addressing vaccine hesitancy through effective communication is crucial:
- Targeted Campaigns: Develop targeted campaigns addressing specific concerns and tailoring messages to different demographics.
- Improved Access to Accurate Information: Increase access to reliable and trustworthy information about vaccines through various channels.
- Collaboration with Community Leaders: Engage community leaders and trusted voices to promote vaccination within communities.
H3: Strengthening regulatory frameworks and enforcement.
Strengthening regulatory frameworks and enforcement is also necessary:
- Improved Vaccine Safety Monitoring: Enhance vaccine safety monitoring systems to quickly identify and address any potential adverse events.
- Stricter Enforcement of Vaccination Mandates: Ensure stricter enforcement of existing vaccination mandates and consider expanding them where appropriate.
- Increased Funding for Vaccine Research and Development: Invest in research and development to improve vaccine efficacy and safety.
3. Conclusion:
The measles surge served as a stark reminder of the critical importance of robust vaccine oversight. Addressing vaccine hesitancy through improved public health communication and strengthening regulatory frameworks are essential steps in preventing future outbreaks. Strengthening vaccine oversight is not just a matter of public health; it's a matter of national security. Learn more about how you can contribute to improving vaccine oversight and protecting your community from preventable diseases. Support public health initiatives, advocate for evidence-based policies, and encourage vaccination within your community. Let's work together to build a healthier future through stronger vaccine oversight and greater public health awareness.

Featured Posts
-
 Watanabe Holds Mercedes Mones Tbs Championship A Plea For Return
May 02, 2025
Watanabe Holds Mercedes Mones Tbs Championship A Plea For Return
May 02, 2025 -
 Sheens Generosity 1 Million Debt Relief For 900
May 02, 2025
Sheens Generosity 1 Million Debt Relief For 900
May 02, 2025 -
 Tv Icon Dies Dallas Star Joins Fellow 80s Legends
May 02, 2025
Tv Icon Dies Dallas Star Joins Fellow 80s Legends
May 02, 2025 -
 England Triumphs Over France In Six Nations Clash Thanks To Dalys Late Score
May 02, 2025
England Triumphs Over France In Six Nations Clash Thanks To Dalys Late Score
May 02, 2025 -
 More Classic Games Coming To Play Station Portal Via Cloud Streaming
May 02, 2025
More Classic Games Coming To Play Station Portal Via Cloud Streaming
May 02, 2025
