The Crucial Role Of Middle Managers: Supporting Both Companies And Employees
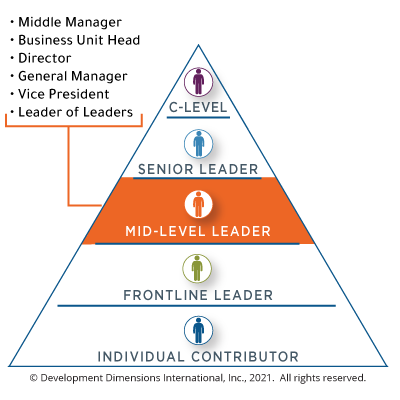
Table of Contents
Bridging the Gap Between Leadership and Employees
Middle managers serve as the critical link between upper management and frontline employees. Their effectiveness directly impacts communication flow, employee development, and overall organizational health.
Effective Communication and Information Flow
Middle managers translate high-level strategies into actionable tasks for their teams. Equally important, they provide crucial feedback from employees to upper management, ensuring that leadership understands the realities on the ground. Effective communication strategies are essential:
- Regular team meetings: Provide a forum for updates, discussions, and problem-solving.
- One-on-one check-ins: Allow for personalized feedback, addressing individual concerns and progress.
- Transparent communication channels: Ensure information flows freely in both directions, fostering trust and understanding. This might include regular newsletters, open-door policies, and readily accessible information hubs.
These strategies promote transparency, build trust, and ensure everyone is working towards common goals. Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful leadership and strong employee relations.
Mentorship and Development
Beyond communication, middle managers play a pivotal role in employee development and mentorship. They guide junior employees, fostering their professional growth and identifying high-potential individuals for future leadership roles. Key aspects include:
- Mentoring programs: Formal or informal programs pairing experienced managers with newer employees.
- Training opportunities: Identifying and providing access to relevant training to enhance skills and knowledge.
- Performance reviews: Providing constructive feedback, setting clear expectations, and identifying areas for improvement.
- Succession planning: Identifying and developing high-potential employees to fill future leadership positions.
Investing in employee development not only benefits individual employees but also strengthens the entire organization by building a robust talent pipeline.
Driving Operational Efficiency and Productivity
Middle managers are the engine room of operational efficiency, translating company objectives into tangible results. Their ability to set goals, manage performance, and optimize resource allocation is crucial for productivity.
Goal Setting and Performance Management
Effective middle managers translate company-wide strategic objectives into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for their teams. They then monitor progress, provide support, and address any performance issues proactively. This includes:
- SMART goal setting: Ensuring goals are clear, measurable, and aligned with overall company objectives.
- Performance tracking: Regularly monitoring progress towards goals and identifying potential roadblocks.
- Regular progress reports: Providing updates to both upper management and team members on progress and challenges.
- Addressing performance issues: Proactively identifying and addressing performance issues through coaching, mentoring, or disciplinary action where necessary.
This systematic approach ensures accountability and drives consistent performance improvement.
Resource Allocation and Optimization
Middle managers are responsible for effectively allocating resources – time, budget, and personnel – to maximize team output. This requires strong problem-solving and conflict resolution skills. Examples include:
- Budget management: Effectively managing team budgets, ensuring resources are used efficiently and effectively.
- Resource prioritization: Determining which tasks and projects should receive the most attention and resources.
- Delegation: Effectively delegating tasks to team members, empowering them and ensuring workload balance.
- Problem-solving: Identifying and resolving problems proactively, minimizing disruptions to workflow.
- Conflict resolution: Addressing conflicts within the team fairly and constructively.
Resource optimization directly impacts productivity and minimizes wasted effort, leading to improved overall efficiency.
Fostering Employee Engagement and Retention
Middle managers are directly responsible for creating a positive work environment that fosters employee engagement and retention. Their actions significantly impact employee morale and loyalty.
Creating a Positive Work Environment
A positive work environment is characterized by open communication, mutual respect, and opportunities for growth. Middle managers contribute to this by:
- Team-building activities: Organizing activities to foster camaraderie and collaboration.
- Recognition and rewards: Acknowledging and rewarding employee contributions and achievements.
- Open communication: Creating a culture where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and concerns.
- Addressing employee concerns: Promptly addressing employee concerns and taking appropriate action.
- Work-life balance initiatives: Supporting employees in maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
A positive and supportive atmosphere boosts morale, enhances productivity, and reduces employee turnover.
Addressing Employee Needs and Concerns
Middle managers act as advocates for their employees, identifying and addressing their needs and concerns promptly. This includes:
- Conflict resolution: Mediating conflicts fairly and effectively.
- Providing support: Offering support and guidance to employees facing challenges.
- Addressing concerns promptly: Responding to employee concerns in a timely and appropriate manner.
- Advocating for employees' needs: Representing employee needs and concerns to upper management.
This proactive approach builds trust and loyalty, resulting in higher employee retention and engagement.
Conclusion
The crucial role of middle managers extends far beyond simply overseeing day-to-day operations. They are essential for bridging the communication gap, driving operational efficiency, and fostering a positive work environment that leads to increased employee engagement and retention. Recognizing and nurturing the crucial role of middle managers is paramount for any organization aiming for sustained success. Invest in your middle management team today, and reap the rewards of increased employee engagement, productivity, and overall company performance. Strengthen your middle management structure for a more thriving and productive workforce.

Featured Posts
-
 Londons Live Music At Risk Examining New Festival Governance
May 19, 2025
Londons Live Music At Risk Examining New Festival Governance
May 19, 2025 -
 Oernskoeldsviks Intresse Foer Eurovision 2026
May 19, 2025
Oernskoeldsviks Intresse Foer Eurovision 2026
May 19, 2025 -
 Austrias Jj Eurovision 2025 Winner With Wasted Love
May 19, 2025
Austrias Jj Eurovision 2025 Winner With Wasted Love
May 19, 2025 -
 Tampoy Nea Dedomena Stoys Fonoys Poy Sokaran
May 19, 2025
Tampoy Nea Dedomena Stoys Fonoys Poy Sokaran
May 19, 2025 -
 Svt Eurovision Vaerd I Sverige Om Kaj Vinner
May 19, 2025
Svt Eurovision Vaerd I Sverige Om Kaj Vinner
May 19, 2025
